Hazardous Waste Management & Its Legal Requirement in India
- 1. PRESENTATION ON HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT AND ITS LEGAL REQUIREMENTS BY MR. NIKESH BANWADE ASSISTANT MANAGER - ENVIRONMENT
- 2. Waste is any material which is no longer useful as it has served its purpose or at the end of the process has no further use and it is generally discarded. It is unwanted material and object that people have thrown away. It is often also called trash, garbage, rubbish, or junk. It can be solid, liquid or gas or it can be waste heat. There are many different kinds of waste WHAT IS WASTE? Types of Wastes: Municipal Solid Waste Hazardous wastes E-Waste Plastic waste Waste Water Bio Medical waste Solid Waste (Other waste in solid state) Radioactive Waste
- 3. HAZARDOUS WASTE What is Hazardous Wastes? Any waste which by reason of characteristics such as: • Physical • Chemical • Biological • Reactive • Toxic • Flammable • Explosive or corrosive which causes danger or likely to cause danger to health or environment, whether alone or in contact with other wastes or substances, is called Hazardous Wastes.
- 4. Hazardous wastes, which may be in solid, liquid or gaseous form, may cause danger to health or environment, either alone or when in contact with other wastes Generation Over 6.2 million tonnes annually It is presumed that about 10 to 15 percent of wastes produced by industries are hazardous Generation of hazardous wastes is increasing at the rate of 2 to 5 percent per year Total 141 dumpsites identified and 88 critically polluted areas. FACTS ABOUT THE HAZARDOUS WASTE
- 5. Source – - National Inventory of Hazardous Wastes Generating Industries & Hazardous Waste Management in India Feb 2009 - http://ebtc.eu/pdf/111031_SNA_Snapshot_Waste-management-in-India.pdf HAZARDOUS WASTE GENERATION: INDIA • Hazardous Waste Generating Industries in India - 36,165 Nos. • Hazardous Waste Generation - 62,32,507 MTA • The category-wise classification of this quantity is Land Fillable HW – 27,28,326 MTA Incinerable HW - 4,15,794 MTA Recyclable HW - 30,88,387 MTA
- 6. Name of State Quantity of Hazardous Waste generation (MTA) Total Landfillable Incinerable Recyclable Andhra Pradesh 211442 31660 313217 556319 Chhattisgarh 5277 6897 283213 295387 Gujarat 1107128 108622 577037 1792787 Jharkhand 23135 9813 204236 237184 Maharashtra 568135 152791 847442 1568368 Punjab 13601 14831 89481 117913 Rajasthan 165107 23025 84739 272871 Tamil Nadu 157909 11145 89593 258647 MAJOR HAZARDOUS WASTE GENERATING STATES IN INDIA
- 7. EFFECTS OF HW ON ENVIRONMENT • Improper storage allow HHW chemicals to leak into the environment, causing dangerous chemical reactions, poisoning or pollution. • Improper disposal allow HHW chemicals to contaminate soil and/or water. • Groundwater contamination if dumped on the ground • Pollutes rivers, streams and lakes when poured through storm drains. • Toxic materials in wastewater can kill the helpful bacteria and the Wastewater treatment system will not operate properly. • Contribute to air pollution or an explosion when burnt.
- 8. EFFECTS OF HHW ON HUMAN BEINGS • Nausea and vomiting • Headache • Skin rashes, such as dermatitis • Chemical burns • Birth defects • Disorders of the lungs, kidney or liver • Nervous system disorders. • Death – In case of lethal dose
- 9. THE HAZARDOUS AND OTHER WASTES (MANAGEMENT AND TRANSBOUNDARY MOVEMENT) RULES • THE HAZARDOUS AND OTHER WASTES (MANAGEMENT AND TRANSBOUNDARY MOVEMENT) RULES 2018 2018
- 10. A. List of processes generating hazardous wastes: Schedule I B. List of Waste Constituents with Concentration Limits: Schedule-II C. Based on Hazardous Characteristics: HAZARDOUS WASTES CATEGORIZATION C1: Flammable C2: Corrosive C3: Reactive or Explosive C4: Toxic C5: Wastes liable to Spontaneous Combustion C6: Substances or Wastes which in contact with water emit flammable Gases C7: Oxidizing C8: Organic Peroxide C9: Poisons (Acute) C10: Infectious C11: Liberation of Toxic Gases in contact with Air or Water C12: Eco-Toxic C13: Capable
- 11. Sample of the waste has any of the following properties, namely:- • Flammable liquids, or mixture of liquids, or liquids containing solids in solution or suspension which give off a flammable vapour at temperature less than 60°C. • It is not a liquid and is capable, under standard temperature and pressure, of causing fire through friction, absorption of moisture or spontaneous chemical changes and, when ignited, burns vigorously and persistently creating a hazard; • It is an ignitable compressed gas; • It is an oxidizer and for the purposes of characterization CLASS C1 - FLAMMABLE
- 12. Sample of the waste has any of the following properties, Namely:- • It is aqueous and has a pH less than or equal to 2 or greater than or equal to 12.5; • It is a liquid and corrodes steel (SAE 1020) at a rate greater than 6.35 mm per year at a test temperature of 55 °C; • It is not aqueous and, when mixed with an equivalent weight of water, produces a solution having a pH less than or equal to 2 or greater than or equal to 12.5; CLASS C2 - CORROSIVE • It is not a liquid and, when mixed with an equivalent weight of water, produces a liquid that corrodes steel (SAE1020) at a rate greater than 6.35 mm per year at a test temperature of 55 °C.
- 13. Sample of the waste has any of the following properties, Namely:- • It is normally unstable and readily undergoes violent change without detonating; • It reacts violently with water or forms potentially explosive mixtures with water; • when mixed with water, it generates toxic gases, vapours or fumes in a quantity, sufficient to present a danger to human health or the environment; • It is a cyanide or sulphide bearing waste which, when exposed to pH conditions between 2 and 12.5, can generate toxic gases, vapours or fumes in a quantity sufficient to present a danger to human health or the environmental; • It is capable of detonation or explosive reaction if it is subjected to a strong initiating source or if heated under confinement; • It is readily capable of detonation or explosive decomposition or reaction • It is a forbidden explosive. CLASS C3 - REACTIVE OR EXPLOSIVE
- 14. Sample of the waste has any of the following properties, Namely:- • It has an acute oral LD50 less than 2,500 milligrams per kilogram; • It has an acute dermal LD50 less than 4,300 milligrams per kilogram; • It has an acute inhalation LC50 less than 10,000 parts per million as a gas or vapour; • It has acute aquatic toxicity with 50% mortality within 96 hours for zebra fish (Brachidanio rerio) at a concentration of 500 milligrams per liter in dilution water and test conditions as specified in BIS test method 6582 – 2001. CLASS C4 - TOXIC LD50 : It is the amount of the substance required (usually per body weight) to kill 50% of the test population
- 15. CLASS C5: Substances or Wastes liable to spontaneous combustion - Substances or Wastes which are liable to spontaneous heating under normal conditions encountered in transport, or to heating up on contact with air, and being then liable to catch fire. CLASS C6: Substances or Wastes which, in contact with water emit flammable gases, Substances or Wastes which, by interaction with water, are liable to become spontaneously flammable or to give off flammable gases in dangerous quantities. CLASS C5: Oxidizing - Substances or Wastes which, while in themselves not necessarily combustible, may, generally by yielding oxygen cause, or contribute to, the combustion of other materials. CLASS C5, C6, C7
- 16. CLASS C8: Organic Peroxides - Organic substances or Wastes which contain the bivalent O−O structure, which may undergo exothermic self-accelerating decomposition. CLASS C9: Poisons (acute) - Substances or Wastes liable either to cause death or serious injury or to harm human health if swallowed or inhaled or by skin contact. CLASS C10: Infectious substances - Substances or Wastes containing viable micro-organisms or their toxins which are known or suspected to cause disease in animals or humans. CLASS C85, C9, C10
- 17. CLASS C11: Liberation of toxic gases in contact with air or water - Substances or Wastes which, by interaction with air or water, are liable to give off toxic gases in dangerous quantities. CLASS C12: Eco-toxic- Substances or Wastes which if released, present or may present immediate or delayed adverse impacts to the environment by means of bioaccumulation or toxic effects upon biotic systems or both. CLASS C13: Capable, by any means, after disposal, of yielding another material, e.g., leachate, which possesses any of the characteristics listed above. CLASS C11, C12, C13
- 18. For the management of hazardous and other wastes, an occupier shall follow the following steps, namely:- (a) Prevention; (b) Minimization; (c) Reuse, (d) Recycling; (e) Recovery, Utilization including co-processing; (f) Safe disposal. RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE OCCUPIER FOR HW MANAGEMENT
- 19. RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE OCCUPIER FOR HW MANAGEMENT • The occupier shall be responsible for safe and environmentally sound management of hazardous and other wastes. • The hazardous and other wastes generated in the establishment of an occupier shall be sent or sold to an authorized actual user or shall be disposed of in an authorized disposal facility. • The hazardous and other wastes shall be transported from an occupier’s establishment to an authorized actual user or to an authorized disposal facility in accordance with the provisions of these rules.
- 20. • The occupier who intends to get its hazardous and other wastes treated and disposed of by the operator of a treatment, storage and disposal facility shall give to the operator of that facility, such specific information as may be needed for safe storage and disposal. • The occupier shall take all the steps while managing hazardous and other wastes to i. contain contaminants and prevent accidents and limit their consequences on human beings and the environment; and ii. Provide persons working in the site with appropriate training, equipment and the information necessary to ensure their safety. RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE OCCUPIER FOR HW MANAGEMENT
- 21. Storage of hazardous and other wastes.- The occupiers of facilities may store the hazardous and other wastes for a period not exceeding Ninety Days and shall maintain a record of sale, transfer, storage, recycling, recovery, pre-processing, co-processing and utilization of such wastes and make these records available for inspection: Provided that the State Pollution Control Board may extend the said period of ninety days in following cases, namely:- • Small generators (up to ten tons per annum) up to one hundred and eighty days of their annual capacity; • Actual users and disposal facility operators up to one hundred and eighty days of their annual capacity, • Occupiers who do not have access to any treatment, storage, disposal facility in the concerned State; • The waste which needs to be specificallystored for development of a process for its recycling, recovery, pre-processing, co-processing or utilization; • In any other case, on justifiable grounds up to one hundred and eighty days. STORAGE OF HAZARDOUS AND OTHER WASTES
- 22. STORAGE SITE SELECTION & ITS REQUIREMENT Storage Site: Follow 4L Rule • In waste generator premises • Not subject to flooding • Away from manufacturing/processing areas • Away from employee activities • Good access to public infrastructure eg roads, emergency services • Minimise risk of explosion or unplanned releases • Keep incompatible wastes separate • Not < 15m from site boundary (where possible)
- 23. STORAGE SITE REQUIREMENT • Impermeable base material • Leak and spill containment • Protection from climate • Good ventilation • Limit height of stacked containers • Eye wash station • Provide drainage system or elevate • Adsorbent material for spills or Spill control arrangement • Re-packaging area & material • Comply with regulations
- 24. • An artificial or natural barrier, which completely surrounds the storage area • A means to control entry at all times DANGER Unauthorized Personnel Keep Out Sign with STORAGE SITE REQUIREMENT
- 25. HAZARDOUS WASTE COMPATIBILITY Need compatibility between: • Waste & container • Wastes stored together • Wastes stored close to each other • Wastes & environment Compatibility = the ability of two or more materials to exist in close association with each other without the formation of harmful chemical or physical reactions
- 26. HAZARDOUS WASTE LABELING • The labelling shall be done as per Form 8.
- 27. • The State Government, occupier, operator of a facility or any association of occupiers shall individually or jointly or severally be responsible for identification of sites for establishing the facility for treatment, storage and disposal of the hazardous and other waste in the State. • The operator of common facility or occupier of a captive facility, shall design and set up the treatment, storage and disposal facility as per technical guidelines issued by the Central Pollution Control Board in this regard from time to time and shall obtain approval from the State Pollution Control Board for design and layout in this regard. • The State Pollution Control Board shall monitor the setting up and operation of the common or captive treatment, storage and disposal facility, regularly. TREATMENT/ DISPOSAL OF HAZARDOUS AND OTHER WASTES
- 28. • Operator shall have to take the authorization for the hazardous waste storage and treatment, storage and disposal by making an application in FORM 1. • The operator of common facility or occupier of a captive facility shall be responsible for safe and environmentally sound operation of the facility and its closure and post closure phase, as per guidelines or standard operating procedures issued by the Central Pollution Control Board from time to time. • The operator of common facility or occupier of a captive facility shall maintain records of hazardous and other wastes handled by him in FORM 3. • The operator of common facility or occupier of a captive facility shall file an annual return in FORM 4 to the State Pollution Control Board on or before the 30th of June following the financial year to which that return relates. TREATMENT/ DISPOSAL OF HAZARDOUS AND OTHER WASTES
- 29. • No import of the hazardous and other wastes from any country to India for disposal shall be permitted. • The import of hazardous and other wastes from any country shall be permitted only for recycling, recovery, reuse and utilization including co-processing. • Users intending to import or transit for transboundary movement of hazardous and other wastes specified in Part A and Part B of Schedule III shall apply in FORM 5 & informed to Customs authorities as per FORM 6. • Importer who is a trader shall obtain one time authorization in FORM 7 IMPORT AND EXPORT OF HAZARDOUS & OTHER WASTES
- 30. • No import of the hazardous and other wastes from any country to India for disposal shall be permitted. • The import of hazardous and other wastes from any country shall be permitted only for recycling, recovery, reuse and utilization including co-processing. • Users intending to import or transit for transboundary movement of hazardous and other wastes specified in Part A and Part B of Schedule III shall apply in FORM 5 & informed to Customs authorities as per FORM 6. • Importer who is a trader shall obtain one time authorization in FORM 7 IMPORT AND EXPORT OF HAZARDOUS & OTHER WASTES
- 31. • The occupier shall provide the transporter with the relevant information in FORM 9, regarding the hazardous nature of the wastes and measures to be taken in case of an emergency and shall label the hazardous and other wastes containers as per FORM 8. • In case of transportation of hazardous and other waste for final disposal to a facility existing in a State other than the State where the waste is generated, the sender shall obtain ‘No Objection Certificate’ from the State Pollution Control Board of both the States. • In case of transportation of hazardous and other waste for recycling or utilization including co-processing, the sender shall intimate both the State Pollution Control Boards before handing over the waste to the transporter. TRANSPORTATION OF HAZARDOUS & OTHER WASTES
- 32. • In case of transit of hazardous and other waste for recycling, utilization including co-processing or disposal through a State other than the States of origin and destination, the sender shall give prior intimation to the concerned State Pollution Control Board of the States of transit before handing over the wastes to the transporter. • In case of transportation of hazardous and other waste, the responsibility of safe transport shall be either of the sender or the receiver whosoever arranges the transport and has the necessary authorization for transport from the concerned State Pollution Control Board. This responsibility should be clearly indicatedin the manifest. • The authorization for transport shall be obtained either by the sender or the receiver on whose behalf the transport is being arranged. TRANSPORTATION OF HAZARDOUS & OTHER WASTES
- 33. TRANSPORTATION OF HAZARDOUS & OTHER WASTES
- 34. HAZARDOUS WASTES MANIFEST SYSTEM
- 35. • The sender shall forward COPY 1 (white) to the State Pollution Control Board, and in case the hazardous or other wastes is likely to be transported through any transit State, the sender shall intimateState Pollution Control Boards of transit States about the movementof the waste. • No transporter shall accept waste from the sender for transport unless it is accompanied by signed COPIES 3 TO 7 of the manifest. • The transporter shall submit COPIES 3 TO 7 of the manifest duly signed with date to the receiver along with the waste consignment. • The receiver after acceptance of the waste shall hand over COPY 4 (ORANGE) to the transporter and send COPY 5 (GREEN) to his State Pollution Control Board and send COPY 6 (BLUE) to the sender and the COPY 3 (PINK) shall be retained by the receiver. • The COPY 7 (GREY) shall only be sent to State Pollution Control Board of sender, if sender is in another State. HAZARDOUS WASTES MANIFEST SYSTEM
- 36. • Accident reporting. - Where an accident occurs at the facility of the occupier handling hazardous or other wastes and operator of the disposal facility or during transportation, the occupier or the operator or the transporter shall immediately intimate the State Pollution Control Board through telephone, e-mail about the accident and subsequently send a report in FORM 11. HAZARDOUS WASTES ACCIDENT
- 37. HAZARDOUS WASTES MANAGEMENT Hazardous wastes Can be Managed or treated by Following Methods • Reduce : Generation Reduction • Reuse : In house use of Hazardous Waste • Recycle : Treatment of the Hazardous waste to make it suitable for reuse • Incineration : Burn the hazardous waste at 850 °C & above temperature • Landfilling : Dumping of the hazardous waste in or on Land • Co-Processing : Utilization of Hazardous waste in cement manufacturing as AFR- Source of Fuel or raw material
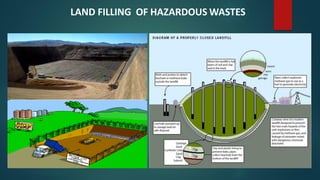
- 38. LAND FILLING OF HAZARDOUS WASTES
- 39. CO-PROCESSING OF HAZARDOUS WASTES Cement industry like Lord Shiva for other Industries, Lord Shiva drunk the Halahal (Poison) generated during Samudra Manthan to save the world, Cement Industry is also disposing the Hazardous Waste generated from other industries during their product manufacturing to save the Earth
- 40. CO-PROCESSING OF HAZARDOUS WASTES
- 41. Hazardous wastes generated or likely to be generated in Cement plant & limes Stone mines are: • Used/Spent Oil (5.1), • Wastes or residues containing oil (5.2), • Cargo residue, washing water & sludge containing oil (Oily Sludge), • Asbestos containing residues (15.1), • Discarded Asbestos (15.2), • Empty barrels/containers/liners contaminated with hazardous chemicals/wastes (33.1), • Contaminated cotton rags or other cleaning materials (33.2), • Sludge from treatment of waste water arising out of cleaning /disposal of barrels/containers (34.2), • Oil and grease skimming THE HAZARDOUS AND OTHER WASTES AT CEMENT INDUSTRY
- 42. THE HAZARDOUS WASTE WHICH CAN BE CO- PROCESSED AT CEMENT KILN Sr No Name of HW Category Qty MT/Year Method of Disposal 1 Chemical Sludge from Waste Water Treatment Plant (Chemical Gypsum) 35.3 24000 Reception,Collection, Storage, transportation and reuse in Cement Manufacturing 2 Chemical Sludge from Waste Water Treatment Plant (ETP Sludge) 35.3 1000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 3 Tarry residue & Still Bottomfrom distillation (TDI Tar) 1.2 6000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 4 Tarry residue & Still Bottomfrom distillation (Coal Tar) 1.2 16000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 5 Mix Waste Liquid of RSPL - 16000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 6 Mix Waste Liquid of RSPL - 6000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 7 Spent Carbon 28.3 1000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 8 Process waste residues & sludge (Paint Sludge) 21.1 1000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln
- 43. Sr No Name of HW Category Qty MT/Year Method of Disposal 9 Spent ion exchange resin containingtoxic metals (Plastic& Resin Waste) 35.2 5500 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 10 waste OR Residue containingoil 5.2 2000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 11 Empty barrels / liners contaminatedwith hazardous chemicals / wastes (only from plant industriessector) (ContaminatedPlastic Waste) 33.1 1000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 12 PhosphateSludge 12.5 1000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 13 Contaminatedcotton rags or other cleaning materials (Oily Rags) 33.2 1000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 14 Off Specification Products 28.4 500 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 15 Process Waste,sludge / residuescontaining acid, toxic metals,organic compounds 28.3 1000 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln 16 Date Expired Products 28.5 500 Co-Processingin Cement Kiln THE HAZARDOUS WASTE WHICH CAN BE CO- PROCESSED AT CEMENT KILN
- 44. Sr No Name of HW Category Qty MT/Year Method of Disposal 17 Organic Residue from process 4.4/I 15000 Co-Processingin kiln 18 Spent Clay ContainingOil 4.5/I 15000 Co-Processingin kiln 19 Plating Metal Sludge 12.8/I 10,000 Co-Processingin kiln 20 Sludge from acid Recovery unit 13.2/I 15,000 Co-Processingin kiln 21 Residue or Sludge containingphenol 19.1/I 10,000 Co-Processingin kiln 22 Spent Solvent 20.2/I 10,000 Co-Processingin kiln 23 Distillationresidue 20.3/I 20,000 Co-Processingin kiln 24 Waste or residue 23.1/I 1000 Co-Processingin kiln 25 Process Waste/ Residue 26.1/I 15000 Co-Processingin kiln 26 Iron Sludge 26.2/I 24,000 Co-Processingin kiln 27 Process residue & waste 28.1/I 24,000 Co-Processingin kiln THE HAZARDOUS WASTE WHICH CAN BE CO- PROCESSED AT CEMENT KILN
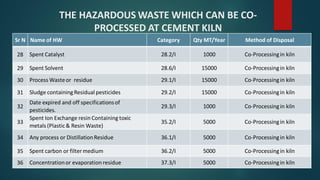
- 45. Sr N Name of HW Category Qty MT/Year Method of Disposal 28 Spent Catalyst 28.2/I 1000 Co-Processingin kiln 29 Spent Solvent 28.6/I 15000 Co-Processingin kiln 30 Process Wasteor residue 29.1/I 15000 Co-Processingin kiln 31 Sludge containingResidual pesticides 29.2/I 15000 Co-Processingin kiln 32 Date expired and off specificationsof pesticides. 29.3/I 1000 Co-Processingin kiln 33 Spent Ion Exchange resin Containing toxic metals (Plastic& Resin Waste) 35.2/I 5000 Co-Processingin kiln 34 Any process or DistillationResidue 36.1/I 5000 Co-Processingin kiln 35 Spent carbon or filter medium 36.2/I 5000 Co-Processingin kiln 36 Concentrationor evaporation residue 37.3/I 5000 Co-Processingin kiln THE HAZARDOUS WASTE WHICH CAN BE CO- PROCESSED AT CEMENT KILN
- 46. SN Name of HW Category Qty MT/Year Method of Disposal 1 Tyre Chips - 2000 Co-Processingin kiln 2 carbon Black - 10000 Co-Processingin kiln 3 Agro Waste - 30000 Co-Processingin kiln 4 Plastic Waste - 2000 Co-Processingin kiln 5 Saw Oust - 5000 Co-Processingin kiln 6 Trade Relect - 1000 Co-Processingin kiln 7 MSW - 20000 Co-Processingin kiln 8 C BAM / Product / By-product - 60,000 Co-Processingin kiln 9 Bio-Sludge - 60,000 Co-Processingin kiln 10 Cotton Husk / peanut shell - 75,600 Co-Processingin kiln THE HAZARDOUS WASTE WHICH CAN BE CO- PROCESSED AT CEMENT KILN
- 47. THE HAZARDOUS WASTE AT YOUR HOME
- 48. THE HAZARDOUS WASTE AT YOUR HOME S. N. Type of Household Hazardous Waste Toxicity 1. Pesticides, Insecticides and Disinfectants Amitrol, Attrazine, Arsenite, Benzophenone, Benzo(a)pyrene, Bisphenole A, Butylated hydroxyanisole(A), Cadmium, DDT, Dithiocarbamate, Dieldrin, Endosulfan, Furans, Heptachlor, Kepone, Lindane, Malathion, Methoxychlor, Mirex, Pentachlorophenol, Phthalates, Thiram, Toxaphene, Trifluralin, Zineb, Ziram, Phenol, Cresol 2. Broken Tube lights Lead, Mercury Vapor 3. Paints, Dyes & Varnishes Aromatic hydrocarbon thinners, Mineral spirits, Benzene, Lead, Esters, Alcohols, Chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons, Ketones 4. Discarded drugs Arsenic, Barium, Chloroform, Cadmium, Chromium, Lindane, m Cresol. Mercury (thim erosol), Selenium, Silver, Antineoplastic agents
- 49. ANY QUESTIONS, QUERY OR SUGGESTIONS ?
- 50. FROM NIKESH BANWADE ASSISTANT MANAGER ENVIRONMENT