Hospital Pharmacy
- 1. HOSPITAL PHARMACY SERVICES DR.N C DAS
- 2. HOSPITAL PHARMACY SERVICES Pharmacy are premises licensed for retail sale or supply to the hospital, which have qualified licensed persons and indulged in compounding of drugs. The pharmacy act was passed in 1948 which rationalized the pharmacy services. - The act was amended from time to time in 1959 and 1976. The act regulate the practice of pharmacy as stable responsibility. Regulates minimum educational qualification by Central Government. The pharmacy is responsible for providing safe medication to the patients.
- 3. PHARMACY SERVICES PHARMACY SERVICES TYPES OF PHARMACY INDENTING STORAGE DISTRIBUTION PHYSICAL PLANNING FUNCTIONS STAFFING ORGANIZING
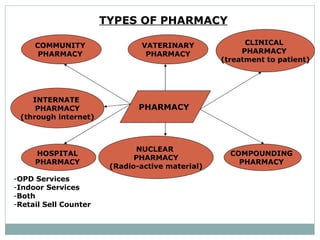
- 4. TYPES OF PHARMACY PHARMACY COMMUNITY PHARMACY INTERNATE PHARMACY (through internet) HOSPITAL PHARMACY VATERINARY PHARMACY NUCLEAR PHARMACY (Radio-active material) CLINICAL PHARMACY (treatment to patient) COMPOUNDING PHARMACY OPD Services Indoor Services Both Retail Sell Counter
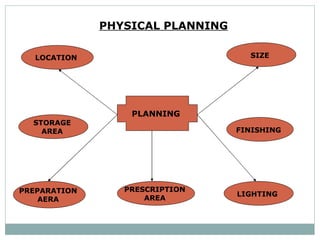
- 5. PHYSICAL PLANNING PLANNING LOCATION STORAGE AREA PREPARATION AERA SIZE FINISHING LIGHTING PRESCRIPTION AREA
- 6. LOCATION: In the ground floor with storage in basement. Readily accessible to elevator. Accessible to all areas of hospital. OPD Unit to serve OPD patients. SIZE: 10 sq ft/ bed - 100 bedded hospital 6 sq ft/ bed - 200 bedded hospital 5 sq ft/ bed - 500 bedded or more
- 7. FINISHING FLOOR: Floor should be smooth, tough and resistant to acid, base. A heavy linoleum flooring is preferred. WALL: Walls to be smooth without crevices, washable, light color. Drug cabinet light coloured wood or steel. Sterile solution room, water proof, smooth, non skid surface with drainage system. Arrangement of fixtures to be made in such a way day light can be used. LIGHT: Plenty of windows for day light. To make dust free Venetian window blinds to be used. Florescent light on prescription and distribution area. Adequate electric sockets and exhaust for gases.
- 8. PRESCRIPTION AREA: Prescription desk with cabinets and drawers. Sectional drawer cabinets with cupboards bases. Desk, office equipment, computer, telephone. Drug available list, information board. PREPARATION AREA: Work table for manufacture of solutions. Empty, adjustable glass storage shelves. Sterilization facilities. The standard counter heights 36’’x30’’x74’’ with acid resistant tops. Acid proof sinks. STORAGE AREA: Storage cabinet with proper leveling Space for loading of wood packs Space for pharmacy lab with testing equipments. Equipments for compounding, dispensing
- 9. STAFFING - There should be Drug & Therapeutic Committee for advise and decision making. A chief pharmacist in hospital more than 200 beds. 2 pharmacist for 100 bedded hospital. 3 pharmacist for 200 bedded hospital. - 7 pharmacist for 500 bedded and more.
- 10. DRUG & THERAPEUTIC COMMITTEE Medical Superintendent - Chairman All HODs - Member Nursing Superintendent - Member Chief Pharmacist - Member Secretary FUNCTIONS Preparation of hospital drug formulary. Selection of manufacturer and supplier, mode of procurement. Addition of new drugs, deletion of old drugs. Drugs to be supplied in OPD. Policy formulation for pharmacy and monitoring Budget demand for pharmacy Developing Drug Information System Checking of pharmacy records and drug quality Maintenance of drug standard and quality control Disposal of Expiry Drugs
- 11. ROLE OF CHIEF PHARMACIST Implementation of decision of Therapeutic Committee Dispensing of drugs, pharmaceuticals and chemicals to different areas Maintenance of approved stock of emergency drugs and antidotes Dispensing of Narcotic drugs and accounting Specification for various fluids Inspection of drugs at various points of use Preparation of indents, issue and receipt voucher Inventory Control Maintenance of stores, ledgers and records Provision of alternate electricity supply Inspection and Quality Control Teaching and training of pharmacist Periodic utilization report of pharmacy Patient Education
- 12. RECORDS AND REGISTERS Stock ledger of different group of drugs Indent and receipt voucher Drug Inspection Report Index Register and bin cards Expiry Date Register Adverse Reaction Record File of correspondence with suppliers and units Ledger account for payment of vouchers Condemnation record of Non-consumables & Consumables Annual Stock Verification Record Hospital Formulary Antibiotic Policy
- 13. INDENTING OF DRUGS The hospital must have a laid down hospital formulary containing 250-300 drugs. Modern management techniques like ABC, VED analysis. Drug to be indented keeping safety stock in mind. Economic order quantity to be followed to prevent over stocking or pilferage Order be issued as soon as critical level is reached. In case of imported drugs, sufficient lead time to be given. RECEIPT OF DRUGS All drugs received must be checked, weighed, batch no., quantity, date of expiry . Random sample of each batch sample to be sent to lab for quality testing. In case of any suspicion of sub standard, drug to be used only after lab test.
- 14. STORAGE OF DRUGS STORAGE GENERAL DRUGS INFLAMMABLE DRUGS NARCOTIC DRUGS COLD STORAGE
- 15. GENERAL DRUGS - Drug to be arranged alphabetically in Cabinet. OR as per use i.e. antibiotics, anti hypertensive etc. Bin card showing stock position. Short expiry to be placed in front and long expiry at the back. FIFO (first in first out) method to be followed. The drugs to be used before date of expiry or transferred to other hospitals . - Expiry drugs to be disposed up as per rule . COLD STORAGE - Drugs such as antibiotics, vitamins, liver extracts should be stored in Cold Room between 15 to 20 0 C. The room to be air conditioned with temperature control facility. Drugs like vaccines, sera, hormones etc to be stored at 2 0 to 8 0 C in deep freezers or walk in cooler. Temperature monitoring through dial thermometer and temperature charting.
- 16. NARCOTIC DRUGS There should be separate, special arrangement for narcotic drugs like morphine, pethidine, barbiturates. Proper recording to be maintained Always to be kept under lock and key INFLAMMABLE ITEMS Separate enclosure to be made for inflammables like spirit, gases & chemicals. Adequate ventilation and fire fighting arrangements. Exhaust fans & sky scrappers for air to pass through.
- 17. DISTRIBUTION OF DRUGS Drugs are distributed to various areas of hospital, OPD & emergency. Three methods of indenting is practiced FLOOR STOCK METHOD INDENT PATIENT SPECIFIC DRUG ORDER UNIT STOCK METHOD Drug used for patient from the nurses stock. 15 days indent is made to store In stock out emergency indent is made. Disadvantage Drug may or may not available in store, delay in treatment. A drug not available in stock. Prescription written is sent for emergency indent in patient name . Drug received given to the specific patient. Disadvantage There may be a delay in medication. Medicines for each patient packed separately as per prescription Dispensed in one packet Chances of pilferage less Suits computerization
- 18. FUNCTIONS OF PHARMACY OBJECTIVE OF FUNCTIONS: - Cost Containment - Effective and Efficient Service - Patient Satisfaction - Effective Staff Utilization PHARMACY SERVICES OPD TRAINING & RESEARCH QUALITY CONTROL INDOOR PROCUREMENT EMERGENCY THERAPEUTIC COMMITTEE INSPECTION & RECEIPT
- 19. ROLE OF PHARMACY a) Demand Estimation: Provisioning, purchasing, receiving, inspection, quality test, storage and distribution. b) Compounding and Manufacturing: Various kinds of fluids, sterile water, mixtures. Ensuring potency & quality: Ensuring potency & quality of drugs procured, compounded and distributed. d) Dispensing Prescription: Dispensing prescription to inpatients and outpatients as per physicians prescription. e) Maintaining Information: Maintaining information on quality, cost, source of supply, drug reaction. f) Investigate: Investigate adverse drug reaction with drawl of supply. g) Ensuring Adherence: Ensuring adherence to laws, acts and rules and regulation of drug controller and applicable to storage and use. h) To promote economy in use of drugs, establishing accounting procedures and utilization. i) Strict implementation of policies and guide lines of Therapeutic committee. j) Assists in training, teaching, research and drug trials. k) Education of patients and relatives about drugs use. l) Maintaining of proper receipt, utilization and storage record. m) Periodic inspection by CMO I/c pharmacy/ drug controller.
- 20. PROBLEMS OF PHARMACY SERVICES PROBLEMS PILFERAGE CARRYING COST DESTRUCTION BY INSECTS & RATS STORAGE COST EXPIRY DRUGS OUT DATED DRUGS
- 21. HOSPITAL ADMINISTRATION MADE EASY http//hospiad.blogspot.com An effort solely to help students and aspirants in their attempt to become a successful Hospital Administrator. hospi ad DR. N. C. DAS