Hr slide 6
- 1. Group HR Training & Development Welcome Good Evening
- 2. Group HR Would you prefer to work for an organization that has no training possibilities?
- 3. Group HR • Training Vs Development – Both refer to the learning of job-related behaviour • Training – Focuses on job performance – Emphasis is on acquisition of specific KSAs needed for present job • Development – Focuses on personal growth, longer-term development – Emphasis is on acquiring KSAs needed for future job or organizational need
- 4. Group HR Trends Affecting Training • Training and development activities have been increasing – Tight labour market • Organizations compete to attract & retain employees, by offering better T&D opportunities – New and changing technology – new KSAs – Globalization – training for employees with international assignments – Mergers, acquisitions, restructuring • Jobs change, employees need new KSAs
- 5. Group HR What is Training?
- 6. Group HR Training Process Model 1. Needs assessment 2. Design training objectives 3. Develop program content 4. Implement training program 5. Evaluate effectiveness of training program
- 7. Group HR Result Based Training Design Model Results • Learning • Performance • Financials • Strategic Design • Objectives • Deliverables • Budgets/Schedules • Project Management • Blueprints/ Prototypes Develop • Materials • Tests/Assessments • Quality Control • Production Implement • Train the trainer • Classroom Delivery • Non-classroom Delivery Evaluate • Evaluation’s Role • Reactions • Learning • Transfer of Training • Business Results Analyze • Needs Analysis • Needs Assessment • Performance Analysis • Job/Task Analysis • Learner Analysis • Context Analysis • Skill-Gap Analysis
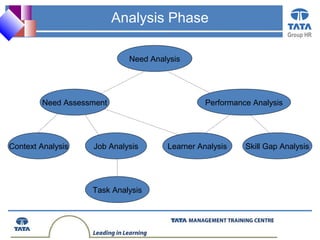
- 8. Group HR Need Assessment Performance Analysis Context Analysis Job Analysis Learner Analysis Skill Gap Analysis Task Analysis Need Analysis Analysis Phase
- 9. Group HR Need Analysis: investigation into whether training or some other organizational intervention can solve a problem or enable desired new performance in the work place. Need Assessment: is the process of determining what knowledge, skills and attitudes (KSAs) employee need to perform their job. If lack of knowledge is not an underlying cause of performance problems, then trainers should look at other issues, including management systems, tools and technologies, work processes, job design and performer’s motivation, to find the cause for the performance problem and recommend solutions. Performance Assessment: is the broader look at the possible underlying causes of performance problems.
- 10. Group HR Learner analysis: learning styles, culture, values, knowledge & skills levels, attitude, motivation to learn and perform etc. Job / task analysis: KSA requirements Skill-Gap analysis: Gaps between employee KSAs and KSAs required by jobs. E.g., performance evaluations, self- or supervisor identification Context analysis: Size of the group to be trained, facilities available for training, audio visual aids and equipment available, frequency of course delivery, cost of training delivery and who will bear it, the match between training environment and work environment.
- 11. Group HR Skill-Gap Analysis Model Measure Existing Skills Develop Skill Profile Estimate Future Skills Develop Vision Develop Plan to Close Gap G A P
- 12. Group HR Design Stage Must include: • The desired behavior • The conditions under which it is to occur • Performance criteria Develop Training Objectives
- 13. Group HR Content and Learning Principles • Issues to consider • Audience • Class size • Time availability • Cost • Training format • Learning principles
- 14. Group HR Organizational Influences on Transfer of Training • Relates to trainee’s outcome expectancies – Will the behaviour lead to desired outcomes? • Rewards, pay, & promotion – Are there rewards for demonstrating the new behaviour? • Environmental constraints / obstacles – Lack of equipment, information, time, etc. • Supervisory and peer support – Reinforce training: provide opportunities, reward – Train coworkers together – reinforce each other • Organization’s learning climate – Learning is encouraged, supported, rewarded, etc.
- 15. Group HR Strengths and Weaknesses of Few Methods Method Knowledge Skills Attitudes Transfer Lecture Yes No No Low Video Yes No Yes Med Role play No Yes Yes High Simulation Yes Yes No High Case study Yes Med Yes Med
- 16. Group HR Active Learning Passive Learning Trial & Error Simulations Games Role Plays Drill Practice Q & A Self Study Lecture Approaches to the Learning Process
- 17. Group HR Evaluating Training Effectiveness • 5 Criteria - Kirkpatrick’s 4 levels plus 1 1. Reaction • Are participants satisfied with training? 1. Learning • How much has been learned? 1. Attitude Change (no. 1 of Kirkpatrick’s 4 criteria) • Did training result in attitude change? 1. Behaviour change • Did the learning transfer to the job? 1. Results criteria • Was the training worth the cost to the company?
- 18. Group HR Key metrics for evaluating training programs under the Modified Kirkpatrick Models: •Amount of knowledge acquired •Change in employee on-the- job behaviors •Change in profitability as expressed through productivity •Quality of work, and sales •Trainee satisfaction Training Metrics
- 19. Group HR • ROI - measure of the monetary benefits obtained by an organization over a specified amount of time for a given investment in a training program. • ROI can be used both to justify a planned investment and to evaluate the extent to which the desired return was achieved. • ROI is calculated by making estimates or obtaining measurements of the costs and benefits associated with a training initiative. Business units can utilize this information and effectively allocate resources to improve performance and ensure organizational success. Calculating Training Return On Investment (Roi)
- 20. Group HR Alternate metrics for evaluating training programs are the following: • Customer service gains and operational efficiency • Internal promotions • Return on expectations Training Metrics
- 21. Group HR • Does training work fast enough to make a difference? • Does having a well-trained employee really make a difference in our industry? • Does having a well-funded training function help the organization attract and retain the best people? • If the training budget was doubled, would productivity double? Planning training metrics - keep the following CEO-type questions in mind: