HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING
- 2. AFTER STUDYING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Understand Human Resource Planning (HRP) and purpose of HRP. Identify the relationship between strategy and HRP. Identify the steps of HR planning process. Describe the approaches to understand the jobs. Discuss the phases of job analysis, including what it is and how it’s used. Design model for forecasting HR requirements and employee requisition form. Develop job descriptions , including summaries and job functions, using the Internet and traditional methods by using Job analysis questionnaire. Develop job specifications using the Internet as well as your judgment. Explain job analysis in a “jobless” world, including what it means and how it’s done in practice.
- 3. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING The process of analyzing and identifying the need for and availability of Human Resources so that the Organization can meet its objectives. The Process of determining an Organization’s human resources needs. Or
- 4. PURPOSE OF HR PLANNING To maximize the use of Human Resources and ensure their ongoing development. To secure the Production Capacity required to support Organizational objectives. 2 To synchronize human resources activities with the organizational objectives. 3 To increase the organization’s productivity.4 1
- 5. HR PLANNING PROCESS HR Strategies & Plans Organizational Objectives & Strategies Scanning the External Environment Analyze Internal inventory of HR Capabilities Forecasting Organizational Need for People Survey of People Available
- 6. a.LINKING ORGANIZATIONAL STRATEGY TO THE EMPLOYMENT PLANNING Determining what business in the organization will be in. Mission Setting goals and Objectives Objective and Goal Determining how goals and objectives will be attained Strategy Determining what jobs need to be done and by whom Structure Matching skills, knowledge, and abilities to required jobs People
- 7. HUMAN RESOUCE PLANNING PROCESS Process of studying the environment of the organization to pinpoint opportunities and threats. b.ENVIRONMENTAL SCANNING:
- 8. HUMAN RESOUCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . c.Internal Assessment of the Organizational Workforce : Analyzing the jobs that will need to be done and the skills of people currently available to do them is the next part of HR planning. C. Internal Assessment of the Organizational Workforce i. Auditing Jobs and Skills ii. Organizational Capabilities Inventory
- 9. HUMAN RESOUCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . i.Auditing Jobs and Skills : Following questions are addressed during internal assessment What jobs exist now? How essential is each job? How many individuals are performing each job? What jobs will be needed in future?
- 10. ii.Organizational Capabilities Inventory: HUMAN RESOUCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . By Utilizing different databases in an HRIS ,it is possible to identify the employees SKA’S. planners can use these inventories to determine long term needs for staffing and HR development. Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS): Database systems containing the records and qualifications of each employee that can be accessed to facilitate employment planning decisions.
- 12. HUMAN RESOUCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . Uses of an HR Information System (HRIS)
- 13. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . d.Forecasting : Forecasting is the use of Information from the Past and Present to identify expected future conditions. i. Forecasting Demand for Human Resources FORECASTING ii. Forecasting Supply for Human Resources
- 14. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . i.Forecasting Demand for Human Resources: 1. Organization-wide estimate for total demand. 2. Unit breakdown for specific skill needs by number and type of employee. Develop decision rules (“fill rates”) for positions to be filled internally and externally. Develop additional decision rules for positions impacted by the chain effects of internal promotions and transfers.
- 15. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . ii.Forecasting Supply for Human Resources: 1. Forecasting External HR Supply 2. Forecasting Internal HR Supply
- 16. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . 1. Forecasting External HR Supply The Following factors affect the External HR Supply. Individuals Demographics Technological Developments and Shifts Actions of Competing Employers Government Regulations and Pressures
- 17. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . 1. Forecasting Internal HR Supply: a. Through Promotions, Lateral Moves, and Terminations. b. Succession Analysis: A method used to forecast the supply of people for certain positions Replacement Charts (Succession Plans) Transition Matrix (Markov Matrix)
- 18. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . .
- 19. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . Job Title Exit Manager Supervisor Line Worker Manager 0.15 0.85 0.00 0.00 Supervisor 0.10 0.15 0.70 0.05 Line Worker 0.20 0.00 0.15 0.65 Transition Matrix (Markov Matrix)
- 20. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . e.Managing Human Resource Surplus or Shortage: i. WORKFORCE REALIGNMENT: “Downsizing”, “Rightsizing”, and “Reduction in Force” (RIF) all mean reducing the number of employees in an organization. Weak Product demand, loss of Market Share to Competitors. Technological Change, Mergers and Acquisitions. Economic Structural
- 21. HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING PROCESS Cont . . . f.HR Strategies and Plan: i. The means used to anticipate and manage the supply of and demand for human resources. Provide overall direction for the way in which HR activities will be developed and managed. Overall Strategic Plan Human Resources Strategic Plan HR Activities
- 22. f.Employee Requisition Form: Marie Stopes Society Wateen Telecom Fauz
- 26. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS 1. Job Analysis 4. JD & JS 2. Job Design 3. Work Analysis Approaches to Understand the Jobs
- 27. 1. Job Analysis: A Systematic way of gathering and analyzing information about the Content, Context, and the Human Requirements of jobs. Phases of Job Analysis Methods & Uses of Job Analysis
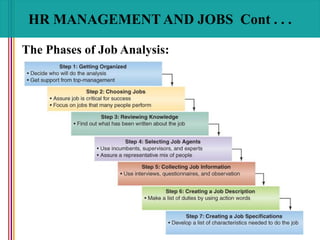
- 28. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . The Phases of Job Analysis:
- 29. Methods & Uses of Job Analysis:
- 30. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . Components of Job Analysis Questionnaire:
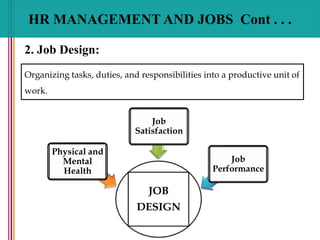
- 31. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . 2. Job Design: Organizing tasks, duties, and responsibilities into a productive unit of work. JOB DESIGN Job Satisfaction Job Performance Physical and Mental Health
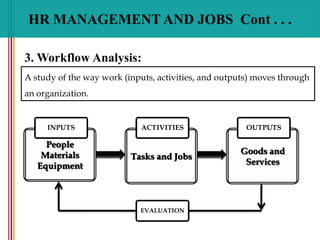
- 32. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . 3. Workflow Analysis: A study of the way work (inputs, activities, and outputs) moves through an organization. People Materials Equipment INPUTS Tasks and Jobs ACTIVITIES Goods and Services OUTPUTS EVALUATION
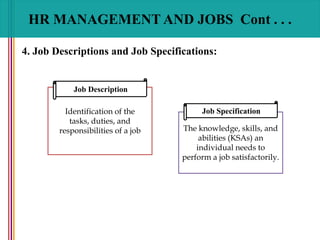
- 33. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . Identification of the tasks, duties, and responsibilities of a job Job Description The knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) an individual needs to perform a job satisfactorily. Job Specification 4. Job Descriptions and Job Specifications:
- 34. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . Job Description Components: Identification Job Title Reporting Relationship Department Location Date of Analysis General Summary Describes the job’s distinguishing responsibilities and components Essential Functions and Duties Task Duties Responsibilities Job Specifications Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities Education and Experience Physical Requirements Disclaimer Of Implied Contract Signature of Approvals -------------------------
- 35. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . Sample of job Description and Specification:
- 36. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . .
- 37. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . .
- 38. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . Job Analysis in a “Jobless” World JOB: Generally defined as “A set of closely related Activities carried out for Pay.”
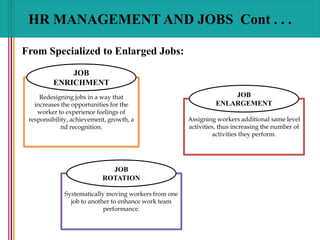
- 39. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . From Specialized to Enlarged Jobs: Assigning workers additional same level activities, thus increasing the number of activities they perform. Redesigning jobs in a way that increases the opportunities for the worker to experience feelings of responsibility, achievement, growth, a nd recognition. JOB ENLARGEMENT JOB ENRICHMENT Systematically moving workers from one job to another to enhance work team performance. JOB ROTATION
- 40. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . Why Managers are De Jobbing their Companies: DE JOBBING: Broadening the responsibilities of the company’s jobs. Encouraging Employee Initiative. DE JOBBING Internal factors leading to De Jobbing External factors leading to De Jobbing
- 41. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . INTERNAL FACTORS LEADING TO DE JOBBING Flatter Organizations Work Teams Boundary Less Organizations Reengineering EXTERNAL FACTORS LEADING TO DE JOBBING Rapid Product and Technological Change Global Competition Deregulation, Political Instability, Demographic Changes Rise of a Service Economy Why Managers are De Jobbing their Companies:
- 42. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . Competency-Based Job Analysis: COMPETENCY • Demonstrable characteristics of a person that enable performance of a job. COMPETENCY- BASED JOB ANALYSIS •Describing a job in terms of the measurable, observable, behavioral competencies (knowledge, skills, and/or behaviors) an employee must exhibit to do a job well.
- 43. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . Why Use Competency Analysis? Traditional job descriptions (with their lists of specific duties) may actually backfire if a high- performance work system is the goal. To Support HPWS Describing the job in terms of the skills, knowledge, and competencies the worker needs is more strategic. Maintain a Strategic Focus Measurable skills, knowledge, and competencies are the heart of any company’s performance management process. Measuring performance
- 44. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . Examples of Competencies: Reading, Writing, and Mathematical reasoning. General competencies Leadership, Strategic Thinking, and Teaching others. Leadership competencies Specific Technical Competencies required for specific types of jobs and/or Occupations. Technical competencies
- 45. HR MANAGEMENT AND JOBS Cont . . . The Skills Matrix for One Job at BP Note: The light blue boxes indicate the minimum level of skill required for the job.
- 46. Human resource planning HR Planning Process Environment Scanning Purpose of HR Planning • To Maximize the use of Human Resources & ensure their ongoing development • To secure the production capacity required to support organizational objectives • To synchronize human resources activities with the organizational objectives. • To increase the organizational productivity. Scanning the External Environment Internal Assessment of Organizational Workforce Organizational Capabilities inventory Auditing Jobs & Skills Human Resource Information System Uses of an HRIS System Forecasting HR Demand & Supply Forecasting Forecasting Demand for HR Forecasting Supply for HR External Supply Internal Supply • Replacement Charts • Transition Matrix Managing Human Resource Surplus or Shortage Workforce Realignment HR Strategies & Plan Overall Strategic Plan HR Strategies Plan HR Activities HR Management & Jobs Workflow AnalysisInputs Activities Outputs Job Design Job Analysis JD & JS • Getting Organized • Choosing Jobs • Reviewing Knowledge • Selecting Job Agents • Collecting Job Information • Creating a JD • Creating a JS CHAPTER : 2 Management Quality Circle Job Analysis in a “Jobless” World From Specialized to Enlarged Jobs Job Enlargement Job Enrichment Job Rotation Job Satisfaction Job Performance Job Rotation Why Managers are De Jobbing their Companies Competency-Based Job Analysis
- 47. THOUGHT FOR THE DAY The Journey to Happiness involves finding the courage to go down into ourselves and take responsibility for what's there: all of it. (Richard Rohr)