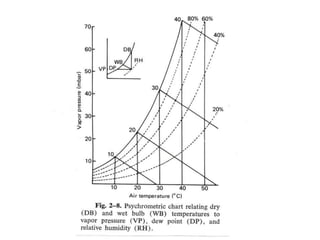
Humidity
- 1. HUMIDITY
- 2. ABSOLUTE HUMIDITY: Absolute humidity (expressed as grams of water vapor per cubic meter volume of air) is a measure of the actual amount of water vapor (moisture) in the air, regardless of the air's temperature. The higher the amount (weight) of water vapor per kilogram, the higher the absolute humidity. RELATIVE HUMIDITY: Relative humidity (RH) (expressed as a percent) also measures water vapor, but RELATIVE to the temperature of the air. In other words, it is a measure of the actual amount of water vapor in the air compared to the total amount of vapor that can exist in the air at its current temperature. WARM AIR CAN HOLD MORE WATER VAPOR THAN COLD AIR, so with the same amount of absolute/specific humidity, cooler air will have a HIGHER relative humidity, and warmer air a LOWER relative humidity.
- 3. Humidity • Capacity of air is primarily a function of temperature • Relative Humidity (RH) = (actual water vapor content) x 100 (max. water vapor capacity of the air) • Heated air becomes lower in RH because denominator gets larger • Cooled air becomes higher in RH
- 4. Saturation vs Air Temperature The actual amount of 47 grams 104 F Water air can hold changes With air temperature Air at 104 F can hold 3 times As much water as 68 F air ! 68 F (47 grams vs only 15 grams) 15 grams 32 F Air at 68 F can hold 4 times 4 grams As much water as air at 0 F (15 grams vs only 4 grams)
- 7. Saturation and Dew Point • Saturated v. unsaturated air • Dew-point temperature – temperature to which air must be cooled to reach saturation (100% RH) • water on outside of drinking glass • ice on your car window • dew and fog
- 8. After Saturation Occurs the Air Must Release Extra Water as Fluid Water forms on the outside of a cold glass as the cold Air surrounding the glass chills the air to the Dew Point Temperature The resulting water is not from the glass, the water is from condensation of moisture in the air around the glass
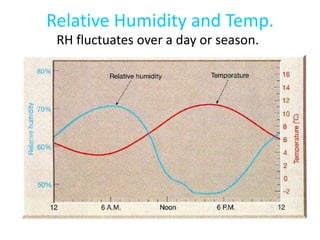
- 9. Relative Humidity and Temp. RH fluctuates over a day or season.
- 10. Measuring Relative Humidity Sling psychrometer Hair hygrometer
- 11. Which environment has higher water vapor content?