Hurricane Katrina
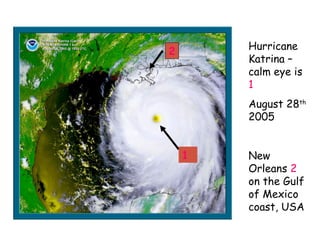
- 1. Hurricane Katrina – calm eye is 1 August 28th 2005 New Orleans 2 on the Gulf of Mexico coast, USA 2 1
- 2. After crossing southern Florida - where it left some 100,000 homes without power - it strengthened further before veering inland towards Louisiana, eventually making landfall 90km south of New Orleans, at 10am local time on 29 August. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/shared Animation features in hyperlink
- 3. It was the sixth-strongest Atlantic hurricane ever recorded and the third-strongest landfalling U.S. hurricane on record. The track of the hurricane 23rd to 29th August 2005.
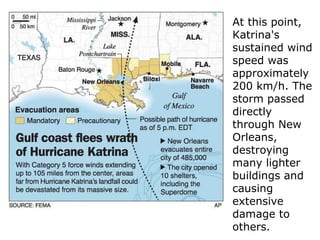
- 4. At this point, Katrina's sustained wind speed was approximately 200 km/h. The storm passed directly through New Orleans, destroying many lighter buildings and causing extensive damage to others.
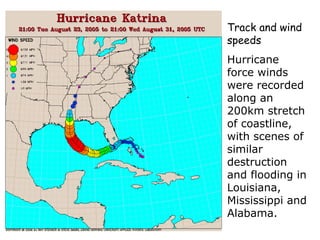
- 5. Track and wind speeds Hurricane force winds were recorded along an 200km stretch of coastline, with scenes of similar destruction and flooding in Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama.
- 6. Storm Surge The intense LOW PRESSURE and strong winds … allows sea level to rise … Flooding coastal areas -several kilometres inland in some places
- 7. Storm Surge: Sea level about 9metres above normal Katrina was a Category 5 storm with sustained winds of about 160 mph as it approached the Gulf Coast.
- 8. Initially it was hoped that New Orleans had weathered the worst of Katrina, but within hours of the storm passing, it emerged that several key levees had been breached ….. … causing floodwater to pour into the low- lying city.
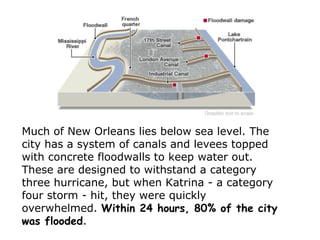
- 9. Much of New Orleans lies below sea level. The city has a system of canals and levees topped with concrete floodwalls to keep water out. These are designed to withstand a category three hurricane, but when Katrina - a category four storm - hit, they were quickly overwhelmed. Within 24 hours, 80% of the city was flooded.
- 10. Mississippi Delta Levees broken and land flooded Especially around New Orleans city. By August 31, 2005, 80% of the city was flooded, with some parts under 6.1 meters of water. Four of the city's protective levees were breached, including the 17th Street Canal levee, the Industrial Canal levee, and the London Avenue Canal floodwall.
- 11. Flooding affected large parts of the poor areas of the City in general The situation quickly deteriorated as it became apparent that thousands of people had been unable to evacuate or chosen to stay put.
- 12. Many took refuge in the city's Superdome, but without sanitation or proper supplies, conditions inside the crowded, overheated stadium became increasingly unbearable. …
- 13. … Law and order across the city broke down, with reports of widespread looting and violence. 7,000 active-duty troops sent to Louisiana for additional hurricane relief. Despite hopes all would be evacuated Friday, some New Orleans flood victims remain at the Superdome. Security forces are still trying to restore order, and engineers are working to drain the city.
- 14. On 2 September a series of huge blasts, apparently at a chemical plant near the French Quarter, rocked the city. Large fires also broke out in several other districts
- 15. Although more than 80% of residents evacuated, the rest remained There was blistering criticism from the mayor of New Orleans and others who said the federal (US) government (Bush) had bungled the relief effort and let people die in the streets for lack of food, water or medicine.
- 16. Enormous social, environmental and economic effects. Lowest pressure: 902 mbar Damages: $81.2 billion (2005 USD) (costliest Atlantic hurricane in history) Fatalities: ≥1,723 total
- 17. Idea of area affected by impact on Postal Deliveries two weeks later.
- 18. Repairing the levees By August 2005 –one year on, the city's levees and floodwalls have been repaired to a standard equalling their prior condition.Despite this work, critics say not enough has yet been done to improve the city's storm protection system.
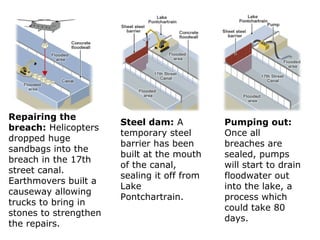
- 19. Repairing the breach: Helicopters dropped huge sandbags into the breach in the 17th street canal. Earthmovers built a causeway allowing trucks to bring in stones to strengthen the repairs. Steel dam: A temporary steel barrier has been built at the mouth of the canal, sealing it off from Lake Pontchartrain. Pumping out: Once all breaches are sealed, pumps will start to drain floodwater out into the lake, a process which could take 80 days.
- 20. About $1bn (£542m) in relief meant for victims of Hurricane Katrina was lost to fraud, with bogus claimants spending the money on Hawaiian holidays, football tickets, diamond jewellery and Girls Gone Wild porn videos (allegedly). A year on and still New Orleans is eerily empty. Of a pre-Katrina population of half-a-million fewer than 200,000 have returned.