Interactive Marketing 2.0
- 1. Interactive Marketing 2.0 Lecturer: Jürgen Rösger (Interactive Marketing Group) Thorsten Dirks (E-Plus) University of Mannheim Term spring/summer 2010 page 1
- 2. Agenda 1. Introduction 2. Branding and Consideration 3. Transaction and Customer Relationship Management 4. Trends and Perspectives page 2
- 3. Introduction page 3
- 4. Outline 1. Advertising 2. Economy of attention 3. Advertising market 4. Web 1.0 – 3.0 5. Social media 6. Practical examples page 4
- 5. Definition of advertising Advertising … … is the placement of announcements and persuasive messages... … in any of the mass media by business firms, nonprofit organizations, government agencies, and individuals... … who seek to inform and / or persuade members of a particular target market or audience about their products, services, organizations, or ideas. American Marketing Association, 2009 page 5
- 6. "You listen to radio, you watch TV, but you use the internet. You go there for particular content and you are actively in control. The best way for advertisers to play a part in that world is to develop such a relevant and engaging experience that consumers choose to spend time with that campaign." Adam Good, Marketing Director at Tribal DDB Sydney page 6
- 7. Outline 1. Advertising 2. Economy of attention 3. Advertising market 4. Web 1.0 – 3.0 5. Social media 6. Practical examples page 7
- 8. The attention-deficit disorder in advertising Consumersareoverextended! • Human attentionis a scarcecommodity • Information overloadoccursdue to: • 3,2 milliontvspots per year • 776,628 registeredbrands in Germany in 2009 (50,000 registrations per year) • Activevocabulary of oneperson: 12,000 words Consequences of attention-deficitdisorder: • Despitemarketcrisisgrowingadvertisingbudgets • Butdecrease of advertisingimpact Source: gwa.de page 8
- 9. Significant shift in utilisation of media Media utilisation (minutes per day) Internet utilisation Internet TV Total % 14-29 years old total population 100 86 623 76 594 80 600 574 59 60 60 49 40 500 19 35 20 5 4 11 0 400 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 300 220 209 189 200 140 96 100 44 0 2005 2010 2015 Source:Allensbacher Markt- und Werbeträgeranalysen, AWA 2008. page 9
- 10. Media utilisation affects search behaviour Information channels during the vehicle buying process 27% 18% 16% 15% 12% 12% 12% 11% 11% 11% 9% 9% 8% 6% 6% 6% 5% -9% -9% -3% -3% 3% 3% +1% +1% +3% +5% +12% 0% News- Television Brochures Magazines Radio Friends/ Other/ Manuf. Buying Internet paper Assoc. Misc. Info Guides 1992 2003 Source:CNW Research, TNS/CMR, Booz Allen Analysis page 10
- 11. Media utilisation affects search behaviour The Internet‘s rise as a research tool in the vehicle buying process (% of consumer saying they use the Internet as an information source) Source: Capgemini 2008 page 11
- 12. Challenging conditions for efficient communication Competitive environment Customer perspective • Homogeneity of service • Individualization of values offerings Interactive and • Information overload • Decreasing efficiency of individual customer • Instability of consumption communication targeting and patterns • Dilemma of differentiation treatment is needed • Hybrid consumer behavior • Focus: costs Source: Meffert, Marketing Centrum Münster (MCM), 2002 page 12
- 13. There is only one way to survive Classic Communication Interactive Communication Operates from every direction Is bundling all marketing activities and chases the customer and adjusting them towards the uncoordinated. consumer throughout all different communication channels. Cross-linking of all activities to center the consumer and reach him …where he will be positioned in future! page 13
- 14. The Interactive-Tableau helps to structure communication activities Communication cycle Branding Consideration Transaction CRM PR Possible crossmedia integration PP + Progr. Print TV Online DM + Mobile Outlet page 14
- 15. Outline 1. Advertising 2. Economy of attention 3. Advertising market 4. Web 1.0 – 3.0 5. Social Media 6. Practical examples page 15
- 16. Structure of the advertising market Manufacturer Provider of products Advertising spot Money of contents Advertising Contents, revenue information Medium Products Money Information Money Information Range of media Consumer page 16
- 17. The value-added chain involves many players (Volume: 30 bill. Euro) (10 bill. Euro) Creative Advertiser Clear message agency Marketing Sales Creation (possible joint development) Budget (20 bill. Euro) Media agency Margin Intermediate Creating schematic diagram: • Where? • Which media? Mall • Which formats? Offline Online Request / Booking “Brings advertising Recipient material closer Marketer towards recipient” Recall / Recognition AIDA Attitude towards brand TV Print Online SOR Intention to Purchase Checking inventory Delivering 1 (20 bill. Euro) Source: Statistisches Bundesamt (BIP 2003) page 17
- 18. Advertising market in Germany Total expenditure 2008: 80.9 bill. Euro (3.25% of GDP) Media with direct components % (exhibitions, couponing, % mobile marketing, etc.) Classical media (TV, radio, ads, etc.) Direct marketing media % (mail/email marketing, phone marketing, etc.) Almost 2/3 spent for direct marketing or media with direct elements Source: MRSC/TNS Infratest, Deutsche Post 2009 page 18
- 19. Net-advertising revenues of advertising media Media 2005 % 2006 % 2007 % 2008 % Daily newspaper 4.476 -0.6 4.532 1.3 4.567 0.8 4.373 -4.2 TV 3.939 1.8 4.114 4.7 4.155 1.0 4.035 -2.9 Advertising via mail 3.398 0 3.318 -2.3 3.347 0.9 3.291 -1.7 Advertising paper 1.898 3.4 1.943 2.4 1.971 1.4 2.008 1.9 Consumer magazine 1.791 -2.6 1.855 3.6 1.822 -1.8 1.693 -7.1 Register / directory 1.197 0.1 1.198 0.1 1.214 1.3 1.224 0.9 Professional journal 902 4.3 956 6.0 1.016 6.3 1.031 1.5 Outdoor advertising 769 6.8 787 2.4 820 4.2 805 -1.8 Online 332 22.5 495 49.1 689 39.2 754 9.4 Radio 663 7.4 680 2.5 743 9.2 711 -4.3 Weekly / sunday newspaper 252 5.6 260 2.9 269 3.7 265 -1.5 Newspaper supplements 91 1.1 89 -1.2 89 -0.4 86 -3.0 Movie 132 -9.8 117 -11.3 106 -9.6 76 -27.8 Total 19.833 1.3 20.350 2.6 20812 2.3 20.357 -2.2 Source: ZAW, 2009 page 19
- 20. Classical media and online marketer TV marketer RTL, VOX, n-tv, Super RTL Sat.1, ProSieben, Kabel 1, N24 ARD Print marketer Focus, Bunte, Chip, Playboy Stern, Gala, Capital, GEO, Brigitte Woman Fernsehwoche, TV-Movie Bild, Hörzu, Die Welt, Computerbild TV-Spielfilm, Max, Cinema Online marketer page 20
- 21. Outline 1. Advertising 2. Economy of attention 3. Advertising market 4. Web 1.0 – 3.0 5. Social media 6. Practical examples page 21
- 22. Web 1.0 Web 1.0 Strategic positioning • The Web as further distribution channel of innovative firms Software Databases solutions PUSH principle • Impression • Consumption • Value expert judgement • Personal judgement • Pre-structured B2x Core competences • Software based solutions • User is just a consumer • Few pages in the centre of attention • Solely company related motivation concerning the further development of Accounting Sales applications and contents systems platforms Source: Zentrum für angewandte Informatik, Universität Köln(2006) page 22
- 23. Then: New applications Personal Blogs Video sharing Social networks homepages … • 22% of the online- • ~35 mill. blogs are • Over 100 mill. videos • MySpace possesses teens have an own existing and the regarded – per day more than 100 mill. homepage (US) amount is doubling • Growth in the first half users, 15 mill. logins every six months of 2006 already about daily and is growing • 32% of the online- about 240„000 users a teens are providing • Posting-volume 300% day. input for foreign accounts for 1.6 mill. homepages or blogs blogs a day • As measured by visits, MySpace is • 19% of the online- ranked shortly behind teens have a blog and Yahoo, but 38% are reading blogs significantly in front of (US) MSN Microsoft, Time Warner (incl. • 7% of the adult AOL), eBay or Google Internet users have a blog, 27% are reading those (US) Source: Pew Internet & American Life Project, Booz Allen Analysis page 23
- 24. Web 2.0 Web 2.0 Strategic positioning • The Web as platform for an interactive (social) dialogue Ad-games and commerce PULL principle Blogs Podcasts • Relevance • Participation • Value end-user judgement & opinion • Reputation / referral Online- IP TV • Adaptive / usage-based structures advertising Core competences • Services, not software applications • Principle of participation& interaction Online auctions Peer-to-peer • Faith in user as co-developer • Utilisation of collective intelligence • Creation of communities etc. Avatars Source: Zentrum für angewandte Informatik, Universität Köln (2006) page 24
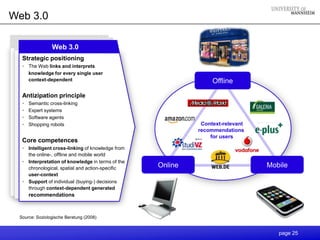
- 25. Web 3.0 Web 3.0 Strategic positioning • The Web links and interprets knowledge for every single user context-dependent Offline Antizipation principle • Semantic cross-linking • Expert systems • Software agents • Shopping robots Context-relevant recommendations for users Core competences • Intelligent cross-linking of knowledge from the online-, offline and mobile world • Interpretation of knowledge in terms of the chronological, spatial and action-specific Online Mobile user-context • Support of individual (buying-) decisions through context-dependent generated recommendations Source: Soziologische Beratung (2008) page 25
- 26. Smart Personal Assistant SPA is a web 3.0 portal solution that integrates web 2.0 and semantic web technologies: You can simultaneously check: • restaurants, movies • clubs, weather forecast • and availability of your friends to plan your saturday evening. page 26
- 27. Outline 1. Advertising 2. Economy of attention 3. Advertising market 4. Web 1.0 – 3.0 5. Social media 6. Practical examples page 27
- 28. What is social media? Source: www.newmediachatter.com page 28
- 29. Benefits of social media Company Customer Right in the middle instead of just near by Company as creator, moderator and Product comparison, rating and participant of the social exchange benchmarking Quick and direct opportunities of action for companies Identification of trends and perspectives Acquisition of unbiased customer Exchange of experiences with other information users Customer statements are not biased due Active generation of information via to questioning of the company discussions and systematic questioning Social Media as a highly credible way of communication Other customers are more credible than employees of the enterprise Positive effects of a successful social media strategy: Customer retention, satisfaction, identification, enhancement of attention and increase in sales page 29
- 30. Concrete opportunities of action for companies 1. Reactive customer communication Responses to questions and concerns Increase of customer satisfaction, creation of a positive image 2. Initiation of discussions Systematic placement of topics allows conclusions about customer behavior and attitude Increase of attention, support of strategic aims like increase in sales 3. Call for interactivity Advertising for contests or lotteries via social communities or profiles Increase of attention and identification with product 4. Active integration of customers E.g. participation of customers as moderators within official forums Increase of brand acceptance and trust in the brand 5. Consistent social media monitoring E.g. as early-warning system. What distracts customers from (re-)purchasing? Fast possibilities to respond / improvement of customer orientation page 30
- 31. Example (Service-Development) page 31
- 32. Example (Product-Development) page 32
- 33. Example (CSR) page 33
- 34. Fan communities within social media How many internet users can be addressed by DAX enterprises via Facebook, Twitter and Youtube? Adidas 4,271,763 Deutsche Telekom 2,301,850 BMW 1,340,234 Volksw agen 581,494 Daimler 396,567 Siemens 326,125 Infineon 634 Eon 138,176 Beiersdorf 495 SAP 90,927 Linde 224 Lufthansa 46,190 Salzgitter 160 Deutsche Bank 21,978 Fresenius Med. 110 Deutsche Post 14,462 Bayer 8,808 Commerzbank 23 RWE 8,170 Fresenius Med. 13 Henkel 7,324 K+S 0 BASF 6,948 Merck 0 Deutsche Börse 3,674 Metro 0 Allianz 1,392 Munich Re 0 ThyssenKrupp 777 MAN 760 Source: Vierpartner, 2009. page 34
- 35. Outline 1. Advertising 2. Economy of attention 3. Advertising market 4. Web 1.0 – 3.0 5. Social media 6. Practical examples page 35
- 36. Example - Revlon (US-Case) Challenge: Create a holistic IM idea that will… 1. Leverage limited investment 2. Build a product “story” 3. Make the magic of Hollywood accessible to consumers 4. Let intrinsic “interact” with the brand Solution: Leverage Time Warner‟s most relevant entertainment assets to create “Revlon on the Red Carpet” - a high profile and engaging 360 degree experience page 36
- 37. Example - Revlon (US-Case) All media involved and integrated page 37
- 38. Example - Revlon (US-Case) Return on objective Excellent Consumers engaged with Revlon on the results Red Carpet… in the end! • Users spend over 4 minutes on average with online custom content • Surpassed entry goals by 300% • Achieved 33% opt-in rate for remarketing page 38
- 39. Example – MINI MINI@IAA MINI@the streets Take a picture of you in the Write a personal message on a MINI and choose a celebrity special microsite, get a RFID as your co-driver. chip and then cross along the billboard – here is your message! page 39
- 40. Example – MINI MINI online Car configuration Merchandise shop Games … page 40
- 41. Example – MINI Meet MINI MINI Challenge MINI to read page 41
- 42. Example – Red Bull Sport - events and sponsoring page 42
- 43. Example – Red Bull Fun and lifestyle page 43