IBM Think Session 8598 Domino and JavaScript Development MasterClass
- 1. 8598 TIPS AND TRICKS: DOMINO AND JAVASCRIPT DEVELOPMENT MASTERCLASS Paul Withers, Intec Systems Ltd John Jardin, Agilit-e Think 2018 #IBMThink
- 2. PAUL WITHERS ICS Developer, Intec Systems OpenNTF Board Member Lifetime IBM Champion @paulswithers Notes Developer XPages Developer Java Developer Microservices Developer
- 3. JOHN JARDIN CTO, Agilit-e and Ukuvuma IBM Champion (Cloud and ICS) Guy who head bangs to Chainsmokers @JohnJardinCodes Integration & Cloud Architect XPages Developer DevOps Engineer AI Programming
- 4. AGENDA - Introduction - Domino as a datastore and API Gateway - What about scheduled tasks? - Microservices For Domino - Container Clustering - ReactJS
- 5. INTRODUCTION
- 6. THIS SESSION? IS NOT: - How to write your app using XYZ JavaScript framework and package it in the NSF - A first step in ultimately migrating away from a Notes and Domino ecosystem IS: - About using Domino as the datastore and master API Gateway for a microservice architecture - About embracing new tools and technologies - About a shift in mind-set
- 7. DOMINO THE MONOLITH? Domino for Directory Management Domino TLS Domino HTTP Server / Port 1352 NoSQL Data Store (NSF) UI, MVC and Data (NSF) Domino languages for workflow (LS / SSJS / Java) nupdate for indexing Domino replication / clustering Standard templates for auditing (log.nsf etc.) Domino SMTP for mail routing
- 8. THE REALITY LDAP as an alternative for Directory Management nginx / IBM HTTP Server on top of Domino ODBC / JDBC / LEI / agents processing flat files Web Services / agents to connect externally UI and MVC in an XPages NSF, data in another NSF Lotus Workflow for BPM Third-party tools for better auditing (incl. OpenLog) Export to data warehouse / NotesSQL for reporting Mail routing via non-Domino SMTP server
- 9. MUTATO NOMINE DE TE FABULA NARRATUR There are similarities to a microservice architecture, just differences of scale - Custom workflow around ERP processes - Custom integration for multiple non-Domino systems - Configuration pulled from external systems
- 10. CHANGE YOUR THINKING Pros - Greater flexibility - Best of breed - Increased standardisation Cons - Code for failure - Step outside comfort zone - More integration points
- 11. DEMO
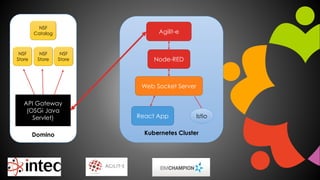
- 12. Kubernetes ClusterDomino NSF Store NSF Store NSF Store NSF Catalog API Gateway (OSGi Java Servlet) Node-RED Web Socket Server Agilit-e React App Istio
- 13. DOMINO AS A DATASTORE AND API GATEWAY
- 14. DOMINO REST OPTIONS DAS (Domino Access Services) validation / visibility concerns XAgents viewState=“nostate” allows caching in applicationScope SmartNSF written using Domain Specific Language ODA Starter Servlet develop in Eclipse, local Domino server development and deployment without Domino Designer allows powerful caching for better performance Darwino Microservices Newsflash: Domino10 brings NodeJS, dominoDB, LoopBack, (Node-RED)
- 15. REST VS API API-first approach means - More planning up-front - Longer initial development lifecycle - Increased portability - Better separation between database and interface - Easier extensibility into other systems Code for failure and “bad data” – ON BOTH SIDES - Missing parameters - Invalid enums
- 16. REST VS API CONT. Security considerations - How to restrict access to apps: API key, OAuth? - Use header / query params correctly - Secure e.g. scheduled endpoints differently - Additional logging of transactions? Be careful what you expose - Should your “status” field be editable - Or just set via workflow methods
- 17. REST PERFORMANCE REST = stateless, servlet = stateful Cache with… - ConcurrentHashMap (think applicationScope) - Google Guava Caches (better management) - Cache Server (e.g. memcache, Ehcache)
- 18. DOCUMENTATION Swagger / Open API Specification is standard Swagger Editor online, local node.js app or Docker OpenAPI 3.0 released July 2017 Samples not yet updated Swagger 2.0 has many examples Swagger Hub or tools like Mermade will convert (between the 2) Swagger UI allows testing against actual server Swagger mock server can be created for UI dev
- 19. CREATING A SWAGGER DEFINITION Write as YAML or JSON YAML – no quotes around strings, no commas, no curly braces operationIds can be added If used, required on all for that path Use enums for options OpenAPI 3.0 allows examples, but clarify and add value “Framework for good documentation”, does not guarantee good documentation
- 20. TESTING Various REST service tools are available - Postman (Electron desktop app) - RestClient plugin for Firefox JUST USE NODE-RED!
- 21. HTTP REQUEST TYPES GET – Read data (No body data allowed) POST – Submit data (Read/Write) PUT – Replacing entire document data PATCH – Minor update to existing data PATCH not enabled by default on Domino DELETE – Deleting Records (No body data allowed)
- 22. HTTP STATUS CODES 1xx – Received and understood, stand by… 2xx – Received, understood and accepted 3xx – Redirecting 4xx – You did something wrong! 5xx – We did something wrong! See Wikipedia
- 23. HTTP STATUS CODES CONT. 200 – OK 202 – Accepted for processing 302 – URL found but server is redirecting 400 – Bad request 401 – Unauthorised 403 – Forbidden 404 – Not found 405 – Method not allowed 500 – Internal server error
- 25. SCHEDULED TASKS Scheduled Agents NSF only, language constraints (LS or Painful Java) DOTS Server only, deployment constraints How about a different approach?
- 26. API + NODE-RED = FLEXIBILITY API XAgent / SmartNSF / or REST endpoint Use Xots for background processing Utility methods added to ODA to boilerplate code Node-RED – Installable alongside Domino with NodeJS Scheduling of flows that includes Web APIs Other schedulers would work, as long as they can call a Web API
- 27. NODE-RED An integration tool for wiring together APIs and online services Available on IBM Cloud, local node.js app or Docker Note: Docker containers not aware of host’s “localhost” or other containers Schedule tasks via Inject node (or Big Timer) Additional nodes for e.g. Watson Services Basic authentication can be set Flows can be imported / exported as JSON DASHBOARDS
- 28. INTEGRATING PRIVATE / PUBLIC “Private” needs to be made “public” ngrok provides secure tunnels cmder is a good console emulator for Windows
- 30. MICROSERVICE PATTERNS • Micro-Functions • Breakdown functions into re-usable/modular code blocks • Each function should do one thing and do it well • Simplify and optimize the code within each function • A function shouldn’t contain more than 80- 100 lines of code • Develop ”Pure Functions” whenever possible
- 31. MICROSERVICE PATTERNS CONT. • Micro-Services • Define which micro-functions can become services to 3rd party platforms and applications • Create API Endpoints that trigger your micro- functions • Ensure a strong security layer for 3rd parties to interface with before triggering your services
- 32. A DIFFERENT APPROACH • Don’t build 3rd party technologies into Domino • Have these technologies exist as a sidecar to a Domino environment • Each technology or service existing independently as a container • All communication occurs using APIs
- 33. A DIFFERENT APPROACH CONT. • Example 1: ReactJS User Interface • Develop React UI using NodeJS and Webpack • In Domino, create API Endpoints for all relevant calls or use DAS • Deploy React App as a standalone container • Example 2: Web Socket Server • Create Web Socket Server using socket.io and NodeJS • In Domino, include socket.io for client-side communication • Create Web Socket events for all relevant communication • Deploy Web Socket Server as standalone container
- 35. CONTAINER CLUSTERING • Cluster all relevant containers using Kubernetes • Run Kubernetes as a sidecar to your Domino environment • IBM Cloud Private provides enterprise-level container management using Kubernetes • Minikube can be used for development and testing environments (low availability) • Inject new services and containers into cluster as and when needed • Manage integration, security, testing and more with Istio
- 36. BENEFITS OF CONTAINER CLUSTERING • High availability • Seamless disaster recovery • Horizontal and vertical scaling • Continuous delivery • No downtime during updates and upgrades • CPU and Memory can be assigned and managed per container/container group
- 37. REACTJS
- 38. WHAT IS REACTJS • A JavaScript library for building user interfaces • React is NOT a framework • React is the “V” of MVC (Model/View/Controller) • HTML is placed in JavaScript classes to create Web Components • This is similar to Custom Controls in XPages • React makes use of a Virtual DOM and Diffing
- 39. PLATFORM AGNOSTIC • React exists as a platform-agnostic solution • Webpack and Babel compile React to a single JS file • The ”create-react-app” module provides all required build tools • A typical React dev environment: • Atom/VS Code (Editor) • NodeJS • ExpressJS • Webpack
- 40. FUTURE IDEAS - Add JUnit tests - Add Node-RED test flows - Extend Watson Workspace with Raspberry Pi to create ToDo via speech - Split app to show one ToDo store at a time - Create scheduler to post offline-created ToDos - Post ToDo from IoT flow if above a threshold - Create Node-RED dashboards for ToDos - Update React app layout to fit nicely on mobile
- 41. THANK YOU AND QUESTIONS? Paul Withers Intec Systems Ltd http://www.intec.co.uk/blog @paulswithers http://watsonwork.me/pwit hers@intec.co.uk John Jardin Agilit-e Website: https://www.agilite.io Blog: http://bleedingcode.com Twitter: @JohnJardinCodes