ICANS 2011
- 1. PERFORMANCE LEADERSHIP I.C.A.N.S. Leading People for Greater Performance 2011
- 2. The top challenges for leaders in 2011… 1. Excellence in execution 2. Improvements to profitability 3. Engaging workforce
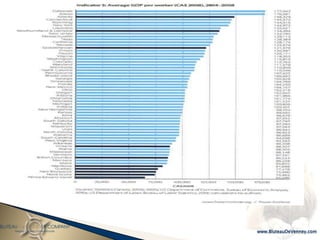
- 3. Canada shows a lack of urgency and leadership in resolving their productivity and competitiveness issues.
- 4. The Result:
- 5. Our Objective Today Translating Potential to Performance
- 6. The Role of Leaders
- 7. Execution remains the top challenge for all organizational leaders. “Key elements of Canada’s history and industrial structure may have nurtured a complacent business culture.” Don Drummond, TD Bank
- 8. Productivity is often understood to be working harder or working longer. “Nothing can be farther from the truth, it’s deriving more output from the same amount of time and effort.” Don Drummond, TD Bank
- 9. Where is performance going now?
- 10. Approximately 78% of execution losses are due to issues of people performance. How can organizations support people to perform at higher levels to execute against the strategy?
- 11. Organizations achieve 63% of their potential performance! HBR Study 2009
- 12. Execution is more important than strategy – 85% of bottom line results are due to people performance via execution than the strategy itself.
- 13. The leader who understands how to maximize return on execution depends on an awareness of the strengths of the team’s talent in order to execute the game plan.
- 14. The levers to increase the return on execution are business alignment and people performance.
- 15. Define the strategic drivers What are the performance elements that if done better would most impact the execution of the strategy (positions or actions).
- 16. Know Your People The greater the leader’s insight into the performance capability of the team (and individual members) the more likely an increase in execution will occur.
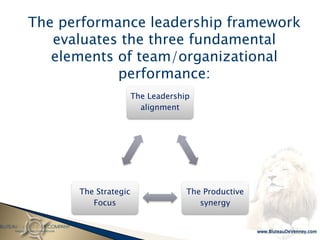
- 18. The performance leadership framework evaluates the three fundamental elements of team/organizational performance: The Leadership alignment The Strategic The Productive Focus synergy
- 19. The Execution Advantage The productivity economy will reward “do it smarter” organizations that build a better business model. Smart organizations will increase their return on execution by focusing on drivers to achieve alignment and productive synergy.
- 20. The Performance Leader
- 21. Where do you focus to be an effective performance leader?
- 22. “Only when you know yourself and operate from your strengths can you achieve true excellence as a manager.” Peter Drucker
- 23. What do people need to be successful in their new role as performance-based leaders? “Help me understand what success is going to look like in my new role, show me with examples, help me think differently so I can apply these things to the development of my people and the appropriate influencing of the organization.”
- 25. Skills most needed for performance leaders: • Self-awareness and Emotional Intelligence • Vision and Strategy • Communication • Tactical Management • Leading Others 3.0 – coaching, delegating, and feedback
- 26. The three steps to developing individual operational leadership: Focus • Tactical • Individual - Know • Strategic – Know What, Whe – Know Yourself n and How Where & Who Clarity Follow Through
- 28. Organizational strategy is a learning process that includes five elements: 1. Assessing where we are 2. Understanding who we are and where we want to go 3. Learning how to get there 4. Making the journey 5. Checking progress
- 29. Leaders display performance leadership when they think, act, and influence in ways that promote the sustainable competitive advantage of the organization.
- 30. Only 27% of organizations integrate strategy and tactics. Benchmarking Solutions Study
- 31. Leaders need to focus on the strategic drivers of the organization … • The relatively few determinants of sustainable competitive advantage for a particular organization in a particular industry or environment.
- 32. Most organizations have 3 to 5 strategic drivers at any point in time. Drivers can change – or the relative emphasis – over time.
- 33. Business strategy is the pattern of choices an organization makes to sustainable competitive advantage. Leadership strategy describes the organizational and human capabilities needed to fulfill the business strategy effectively.
- 35. Strategic thinking revolves around the ability of a leader to help people make sense of the world around them – the challenges they collectively face and how they will face them together.
- 36. Strategic Acting
- 37. Strategic acting is committing resources to build sustainable competitive advantage. Not every action is strategic – it is critical to apply actions that will impact the strategic drivers of the organization.
- 38. Strategic decisions always involve uncertainty … The key is not to make quick decisions but to make timely decisions.
- 39. Without strategic clarity and focus it is nearly impossible to make sound tactical decisions.
- 41. Forging relationships inside and outside the organization, inviting others to the process, building and sustaining momentum, and purposefully using organizational systems and culture.
- 42. Influence must be used in all directions … up to senior executives, laterally to peers, down to reports, and outside to stakeholders and customers.
- 43. Key strategic influencing tactics… -Influence others by involving them in the process - Create common understanding, create champions, demonstrate others are valued
- 44. Key strategic influencing tactics… -Influence others by connecting on an emotional level - Learn what is important to others - Use the power of language - Connect to aspirations
- 45. Developing Performance Leadership: • Assessing where you are, to • Understand who you are and where you want to go, to • Learn how to get there, to • Make the journey, and • Check your progress
- 46. The Evolution of Strategic Management
- 47. Strategy arose as a managerial discipline in the 1960s.
- 48. Models were developed to define strategy. Boston Consulting Group and McKinsey & Company were key in developing frameworks to explain strategy.
- 49. The Definition of Strategy: An integrated set of actions designed to create a sustainable advantage over competitors.
- 50. The Evolution of Strategic Management – four phases …
- 51. Planning routinely progresses through four discrete phases of development. At each phase, a company adopts attitudes and gains capabilities needed in the phases to come.
- 52. Phase One Financial Planning Annual budgeting process to forecast revenue, costs, and capital needs over the next year.
- 53. Phase Two Forecast-based Planning Extend the financial budgeting beyond the one-year time horizon Start using trend analysis, regression models, and simulation models
- 54. Phase Three Externally Oriented Planning Issues orientation – responsibility to lay out the key issues facing the organization
- 55. Attention is shifted externally to customers, suppliers, and competitors. Resource allocation becomes dynamic and plans are adaptive Portfolio analysis is used to focus on competitive attractiveness and strengths
- 56. Phase Four Strategic Management Planning techniques are cascaded throughout the organization and strategic thinking is linked to operational decision making
- 57. Discussions are defined by tomorrow’s strategic issues rather than today’s organizational structure Systems are in place to negotiate trade- offs, review progress, and motivate and reward performance
- 58. The Performance Edge Strategy for a Bigger Future
- 59. For achievers and teams, the struggle is focus.
- 60. The Dip Between Potential and Performance
- 61. How do we bridge the gap between potential and performance?
- 63. Strategy is the North Star that drives action and performance.
- 64. Strategy … • Builds prepared minds • Provides a framework for effective decision-making • Acts as a catalyst for team engagement
- 65. STRATEGY is the real competitive advantage.
- 66. Most individuals and teams don’t do strategy well: • Only 8% of strategies achieve results as planned • 37% of strategies fail outright • Teams assess leaders as 69% effective at performing against plans
- 67. Why is strategy so difficult?
- 68. It is human nature to talk about the future and then move directly to short-term tactics. We skip strategy!
- 69. Without strategy, we become distracted by… • Shiny Object Syndrome • Commitment Creep
- 70. The results: • The short term takes over • The pace is accelerated • Work is reactive rather than proactive • We are tactical not strategic
- 71. Defining Strategy: The plan that a team takes to differentiate itself positively from the competition using its strengths to provide value to satisfy customer needs now and in the future.
- 72. Strategy involves: • Clear, concise and measurable statement of 3- 5 objectives • Realistic assessment of key factors guiding team actions • Description of key approaches used to realize results
- 73. We need to resist the urge to hit the ground running.
- 74. The Strategy Perspective: Bridging the Performance Gap Diagnose before the cure
- 75. The Strategy Triangle: Working the Sweet Spot Understand the interaction of the three key influencers on your performance … your team, your clients, and your competitors.
- 76. The Strategic Sweet Spot The strategic sweet spot of a company is where it meets customers’ needs in a way that rivals can’t, given the context in which it competes. CONTEXT (Technology, Industry demographics, regulation, and so on) COMPETITORS’ CUSTOMERS’ offerings needs Sweet Spot COMPANY’S capabilities
- 77. The Strategic Drivers: The Art of Focus Mindpower over manpower.
- 78. Start with the end in mind and clarify your results – then work back.
- 79. Focus on five key strategies – gives a great feeling of motivation for everyone.
- 80. The Performance Scorecard: Measuring for Success “What gets measured gets better”
- 81. The Performance Scorecard is an instrument to navigate your future success, and a means of effective communication and motivation. You link cause and effect.
- 82. The Strategic Roadmap A two-page summary of your strategy.
- 83. The solution to connect potential to performance is to proactively set up the environment for success.
- 84. The Strategic Roadmap The Performance Scorecard Critical to your success.
- 85. The benefits: • Create a winning team • Sharpen your client focus • Add value • Consistent and coordinated action
- 87. The Performance Edge: Mindset for progress not perfection. Focus strategically to achieve best results.
- 95. A strong vision is correlated with:
- 97. • • • • •
- 99. • • •
- 102. • •
- 103. • •
- 105. •
- 110. • •
- 115. • •
- 127. Organizations face a daunting and seemingly contradictory set of goals: • Provide a differentiated client experience at lower costs • Generate significant growth while managing the bottom line
- 128. Organizations face a daunting and seemingly contradictory set of goals: • Use technology for greater efficiency without losing personal client connection • Standardize and … customize
- 129. The Common Element: People – people are more than ever a source of critical skill and knowledge as well as the foundation for sustainable competitive advantage.
- 130. The Global Engagement Gap Where does Canada stand? 7% 23% Engaged 25% Enrolled 45% Disenchated Disengaged Source: Towers Perrin (2009)
- 131. The engagement gap can be defined as: the difference between the discretionary effort that employers need for competitive advantage and employers’ ability to elicit this effort from a significant portion of their workforce.
- 132. Workforce Engagement is a Normal Distribution
- 133. The Economics of Engagement Part 1 Improving the engagement – and in turn the performance – of an employee has the potential to increase overall productivity by up to 23% on average. Source: Cascio (2009)
- 134. The Economics of Engagement Part 2 Approximately 68% of your employees have the potential to increase overall engagement and leverage productivity. Source: Cascio (2009)
- 135. The Economics of Engagement Part 3 The key question is not which talent group has the greatest value but rather in which talent group would a change in performance variation have the greatest impact?
- 136. The Economics of Engagement Part 4 Performance varies across jobs. • The nature and scope of the job • The relative value of variations in performance of the job
- 137. The Economics of Engagement Part 5 Potential engagement / productivity enhancement is position dependent Low complexity position … 15% boost Moderate complexity position … 25% boost High complexity position … 46% boost Source: Cascio (2009)
- 138. The Economics of Engagement What are the high complexity positions in your organization that can be most highly leveraged with an increase in engagement to a boost in productivity?
- 139. The Economics of Engagement Invest in positions where the value of performance variance is the highest and the organization gains the most strategic return. Find the most pivotal position.
- 140. Leaders play a pivotal role in the engagement equation: The need for effective leadership at the top The need for customizing the culture and work environment to support employee engagement Putting employees under the same microscope as customers to take actions
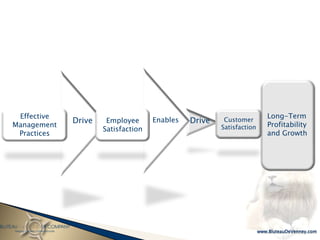
- 141. Effective Long-Term Drive Employee Enables Drive Customer Profitability Management Satisfaction Satisfaction Practices and Growth
- 142. Continued business productivity growth today depends on closing the engagement gap and maximizing employee input.
- 143. How Engagement Affects Financial Performance Source: Towers Perrin (2009)
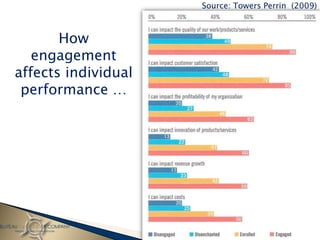
- 144. Source: Towers Perrin (2009) How engagement affects individual performance …
- 145. How Employees Rate Leaders on Key Engagement Supports Source: Towers Perrin (2009)
- 146. The Leadership Divide Many senior leaders began their careers in specific professional / technical positions with key analytical and rational skills. Empathy, communication, and gaining perspective may not be key strengths even now.
- 147. The Five Steps 1. Start with the end in mind 2. Specify the skills needed 3. Develop the right skills the right way 4. Support the transition of pivot positions 5. Engage and inspire people to meet business needs
- 148. The Pivotal Investment Overall workforce engagement can be increased with the greatest leverage through the right investment – leaders are the critical supporters needed for this investment.
- 149. The Pivotal Investment To move the productivity curve outward … “An investment in knowledge pays the best interest.” Benjamin Franklin
- 151. People Performance
- 152. People Performance The leader’s ability to measure and manage the team’s (and individual’s) instinctive approach to the drivers of the strategy will close the gap.
- 153. The Performance Process Productive Action Motivation Reason Instincts Will Affective Conative Cognitive
- 154. The Five-Factor Framework™: Improving Execution through People Performance 1. Define the strategic drivers 2. Measure the instinctive leadership approach 3. Measure & assess the instinctive culture to support the strategy and the organizational culture 4. Assess the organizational instinctive performance map 5. Identify and close gaps
- 155. Define the strategic drivers What are the performance elements that if done better would most impact the execution of the strategy (positions or actions).
- 156. Measure the leader’s instinctive approach
- 157. Measure the instinctive strategy culture
- 158. Measure the instinctive organizational culture
- 159. Measure the instinctive strategy and organizational culture
- 160. Assess the organizational instinctive performance map
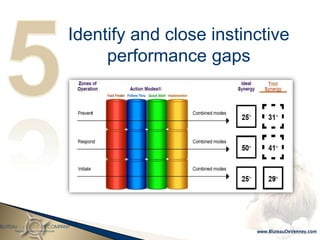
- 161. Identify and close instinctive performance gaps
- 163. Thank You! For More Information, Please contact us at: (902) 425 – 0467 or email GetResults@BluteauDeVenney.com