Igneous rock ppt
- 1. Dr. V. R GhodakeDr. V. R Ghodake SCOE, PuneSCOE, Pune
- 2. DefinitionDefinition It is a aggregate of mineral. They form major part of the earthIt is a aggregate of mineral. They form major part of the earth crust.crust. Rocks are divided in to three major groupsRocks are divided in to three major groups 1)1)Igneous RocksIgneous Rocks 2)2)Sedimentary RocksSedimentary Rocks 3)3)Metamorphic RocksMetamorphic Rocks Igneous Rocks:Igneous Rocks: Igneous rocks are formed by cooling andIgneous rocks are formed by cooling and solidification of magma. Magma is hot, viscous, siliceoussolidification of magma. Magma is hot, viscous, siliceous melts, containing water vapor and gases. It comes frommelts, containing water vapor and gases. It comes from great depth below the earth surface it is mainly composedgreat depth below the earth surface it is mainly composed of O, Si, Al, Fe, Na, Mg, Ca and K.of O, Si, Al, Fe, Na, Mg, Ca and K. when magma comes upon the surface it iswhen magma comes upon the surface it is called as ‘Lava’called as ‘Lava’ R o c k sR o c k s
- 3. Chemical Composition of Igneous RocksChemical Composition of Igneous Rocks • Acid MagmaAcid Magma :: is rich in Si, Na, & K and Poor in Ca, Mg, Feis rich in Si, Na, & K and Poor in Ca, Mg, Fe • Basic Magma:Basic Magma: is rich in Ca, Fe & Mg and Poor in Si, Na, & Kis rich in Ca, Fe & Mg and Poor in Si, Na, & K Basic Magma is divided in to three groupsBasic Magma is divided in to three groups 1)1)Ultra Basic rock:Ultra Basic rock: these contains less than 45% of Si. Example Perioditethese contains less than 45% of Si. Example Periodite 2)2)Basic Rock :Basic Rock : These contain Si between 45 to 55 %. Example Gabbro &These contain Si between 45 to 55 %. Example Gabbro & BasaltBasalt 3)3)Intermediate Rock :Intermediate Rock : These contains Si between 55 to 65%. ExampleThese contains Si between 55 to 65%. Example DioriteDiorite 4)4)Acid Rock :Acid Rock : In this Si contains more than 65%. Example GraniteIn this Si contains more than 65%. Example Granite Peridotite Gabbro Basalt Diorite
- 4. Igneous rocks can also be classified asIgneous rocks can also be classified as 1)1)Over saturated:Over saturated: contains high amount of Si & abundant Qtz. & alkalicontains high amount of Si & abundant Qtz. & alkali FeldsparsFeldspars 2)2)Saturated:Saturated: contains sufficient amount of Si & do not contains Qtz.contains sufficient amount of Si & do not contains Qtz. 3)3)Under saturated:Under saturated: contains less Si & High in Alkali & aluminum Oxides.contains less Si & High in Alkali & aluminum Oxides. Types of Igneous RocksTypes of Igneous Rocks 1)1)Extrusive RocksExtrusive Rocks 2)2)Intrusive Rocks :Intrusive Rocks : These are divided in to two typesThese are divided in to two types Plutonic RocksPlutonic Rocks Hypabyssal RocksHypabyssal Rocks
- 5. Texture of Igneous RocksTexture of Igneous Rocks Texture means Size, Shape and arrangement of mineral grains in a rockTexture means Size, Shape and arrangement of mineral grains in a rock In general the slower cooling or solidification of magma shows coarser grain rocks.In general the slower cooling or solidification of magma shows coarser grain rocks. To study texture following four parts are important.To study texture following four parts are important. 1)1)Degree of crystallizationDegree of crystallization 2)2)Size of grainsSize of grains 3)3)Shape of crystalShape of crystal 4)4)Mutual relation between mineral grainsMutual relation between mineral grains Lava 1)1) Degree of Crystallization : It divides in two partsDegree of Crystallization : It divides in two parts a)a) Holocrystalline texture:Holocrystalline texture: Rocks shows entirely crystalline textureRocks shows entirely crystalline texture b)b) Holohyalline texture:Holohyalline texture: Rocks shows entirely glassy textureRocks shows entirely glassy texture 2) Size of grains:2) Size of grains: a)a) Phaneric : constituent minerals grains can be see by necked eyes.Phaneric : constituent minerals grains can be see by necked eyes. i)i) Coarse grained ii) Medium grained iii) Fine grainedCoarse grained ii) Medium grained iii) Fine grained ii)ii) Aphanitic : whose mineral grains are too small but can be see by necked eyesAphanitic : whose mineral grains are too small but can be see by necked eyes Phaneric TexturePhaneric Texture Aphanitic TextureAphanitic Texture
- 6. Shape of crystals:Shape of crystals: Well developed crystals faces of grains calledWell developed crystals faces of grains called EuhedralEuhedral Partly developed crystal faces calledPartly developed crystal faces called SubhedralSubhedral The crystal faces are absent such grains of rock calledThe crystal faces are absent such grains of rock called UnhedralUnhedral Mutual relation of grainsMutual relation of grains.. i)i) Equigranular textureEquigranular texture ii)ii) Inequigranular textureInequigranular texture a) Porphyritic texture b) Poikilitic texture c) Ophitic texturea) Porphyritic texture b) Poikilitic texture c) Ophitic texture Porphyritic texturePorphyritic texture Poikilitic texturePoikilitic texture PhenocrystPhenocryst GroundGround massmass
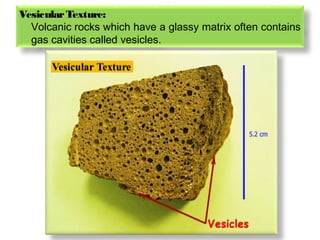
- 7. VesicularTexture: Volcanic rocks which have a glassy matrix often contains gas cavities called vesicles.
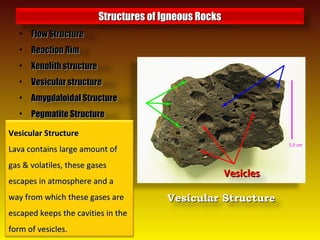
- 8. • Flow StructureFlow Structure • Reaction RimReaction Rim • Xenolith structureXenolith structure • Vesicular structureVesicular structure • Amygdaloidal StructureAmygdaloidal Structure • Pegmatite StructurePegmatite Structure Structures of Igneous RocksStructures of Igneous Rocks VesiclesVesicles Vesicular StructureVesicular Structure Vesicular StructureVesicular Structure Lava contains large amount ofLava contains large amount of gas & volatiles, these gasesgas & volatiles, these gases escapes in atmosphere and aescapes in atmosphere and a way from which these gases areway from which these gases are escaped keeps the cavities in theescaped keeps the cavities in the form of vesicles.form of vesicles.
- 9. Amygdaloidal Structure:Amygdaloidal Structure: The vesicles of volcanic rocks mayThe vesicles of volcanic rocks may subsequently be filled by secondary minerals such as calcite andsubsequently be filled by secondary minerals such as calcite and zeolites, such filled vesicles are called Amygdaloidal Structure.zeolites, such filled vesicles are called Amygdaloidal Structure. Structures of Igneous RocksStructures of Igneous Rocks Amygdaloidal StructureAmygdaloidal Structure
- 10. Xenolith structureXenolith structure: Inner rock fragments are included in to: Inner rock fragments are included in to magma. When it rises up towards the surface, if they are notmagma. When it rises up towards the surface, if they are not digested they remain entrapped within the magma anddigested they remain entrapped within the magma and produces Heterogeneityproduces Heterogeneity Structures of Igneous RocksStructures of Igneous Rocks Xenolith StructureXenolith Structure
- 11. Pegmatite Structure:Pegmatite Structure: The constituent minerals grains exceedsThe constituent minerals grains exceeds several centimeters in the size, the rock is known asseveral centimeters in the size, the rock is known as Pegmatite Structure.Pegmatite Structure. Structures of Igneous RocksStructures of Igneous Rocks Pegmatite StructurePegmatite Structure
- 12. 1)1) Extrusive Igneous BodiesExtrusive Igneous Bodies 2)2) Intrusive Igneous Bodies.Intrusive Igneous Bodies. Forms of Igneous BodiesForms of Igneous Bodies Extrusive Igneous Bodies :Extrusive Igneous Bodies : These are forms when magmaThese are forms when magma reaches to earth surface and get solidification. Example Lavareaches to earth surface and get solidification. Example Lava flowflow Intrusive Igneous Bodies :Intrusive Igneous Bodies : These areThese are formed by the consolidation of magma atformed by the consolidation of magma at some depth below the earth surface. Suchsome depth below the earth surface. Such bodies shows variations in their shape andbodies shows variations in their shape and size.size. These are divided in to two parts.These are divided in to two parts. 1) Discordant bodies 2) Concordant bodies.1) Discordant bodies 2) Concordant bodies.
- 13. Forms of Igneous BodiesForms of Igneous Bodies
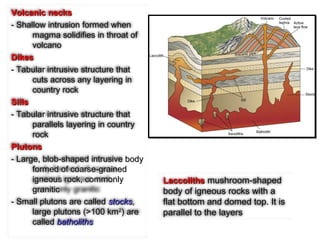
- 14. Forms of Igneous BodiesForms of Igneous Bodies SillSill SillSill DykeDyke Volcanic neckVolcanic neck LaccolithLaccolith
- 15. Volcanic necksVolcanic necks - Shallow intrusion formed when- Shallow intrusion formed when magma solidifies in throat ofmagma solidifies in throat of volcanovolcano DikesDikes - Tabular intrusive structure that- Tabular intrusive structure that cuts across any layering incuts across any layering in country rockcountry rock SillsSills - Tabular intrusive structure that- Tabular intrusive structure that parallels layering in countryparallels layering in country rockrock PlutonsPlutons - Large, blob-shaped intrusive body- Large, blob-shaped intrusive body formed of coarse-grainedformed of coarse-grained igneous rock, commonlyigneous rock, commonly graniticgranitic - Small plutons are called- Small plutons are called stocksstocks,, large plutons (>100 kmlarge plutons (>100 km22 ) are) are calledcalled batholithsbatholiths LaccolithsLaccoliths mushroom-shapedmushroom-shaped body of igneous rocks with abody of igneous rocks with a flat bottom and domed top. It isflat bottom and domed top. It is parallel to the layersparallel to the layers
- 16. Forms of Igneous BodiesForms of Igneous Bodies Mafic dykeMafic dyke
- 17. Forms of Igneous BodiesForms of Igneous Bodies BatholithsBatholiths
- 20. SillsSills are also small igneous intrusions. They are sheets of rock that, unlike dikes, are parallel to pre-existing rocks. Think of magma invading sedimentary rocks by spreading out between rock layers. That magma would cool to form a sill.