Imf ppt
- 1. PRESENATATION ON IMF AND FINANCIAL ENVIRONMENT Presented by finance group
- 2. Contents Introduction Establishment Problem Objectives Functions Where the IMF gets its money Special drawing rights Membership Success & failures IMF & India Conclusion
- 3. Introduction The IMF is an intergovernmental institution established by an international treaty in 1945 to create a framework for international economic cooperation focusing on balance of payment problems and the stability of currencies. IMF headquarters is in Washington D.C , U.S.A
- 4. In the beginning ( 1945-2003 ) 29 member countries but In 2007, the number of member countries of IMF was 185.
- 5. Establishment of IMF IMF was founded on 27th december,1945. During the closing years of World War Second, different countries realized that there must be a common International Forum for achieving economy cooperation, promoting International Trade and providing help to needy nations during emergency. So IMF was formed for this purpose.
- 6. World War Second has its adverse effect on global economy. To remedy the situation, an international monetary conference was convened in 1944, at Bretton Woods in America. It was attended by the represenatives of 44 countries. India also participated therein. It was decided in this Conference to set up IMF for the economic development of all countries.
- 7. PROBLEMS Three main problems are : ☻Economic order and piece. ☻Reconstruction of economies ☻Stable world piece
- 8. Objectives Of IMF 1) To Promote International Monetary Cooperation 2) To Establishment a System of Multilateral Payments 3) To Maintain Stability in the Rate of Exchange
- 9. 4) To Provide Aid to Members during emergency 5) To reduce Disequilibrium in Balance of Payments 6) To promote balanced economic development
- 10. FUNCTIONS OF IMF 1) The funds provide a mechanism for improving short-term BOP Position 2) Fund provides a machinery for international consultationS 3) Technical Assistance 4) Imparts Training
- 11. 5) Facilities during emergency 6) It serves as a short-term credit institutions 7) Determining Exchange Rate for every Country
- 12. Where the IMF gets its money Most comes from the quota subscriptions the money each member contributes when joining the IMF. The Capital resources of the fund are subscribed by the various member countries by way of their respective quotas. Each Member country is required to subscribe its quota partly in gold and partly in its own national currency. Each Member country is required to subscribe its quota partly in gold and partly in its own national currency. General Arrangements to Borrow (1962) line of credit set up with several governments and banks throughout the world
- 13. Special Drawing Right (SDRs) SDR is an invented currency its value is based on the worth of the world’s five major currencies US Dollar, French Franc, Pound Sterling, Japanese Yen, Deutsche Mark Countries add SDRs to their holdings of foreign currencies keep available for need of payments that must be made in foreign exchange
- 14. MEMBERSHIP There are two types of members of the Fund 1) ORIGINAL MEMBERS- All those countries whose representatives took part in Bretton Woods Conference and who agreed to be the member of the fund prior to 31st December,1945, are called Ordinary Members
- 15. 2) ORDINARY MEMBERS- All those countries who became its member subsequently are called Ordinary Members. Any country can cease to be its member after giving a notice in writing to that effect . Fund can terminate the membership of such a country which does not observe its rules. In 1945, the number countries was in 44, in year 2007 the number of member countries was 185.
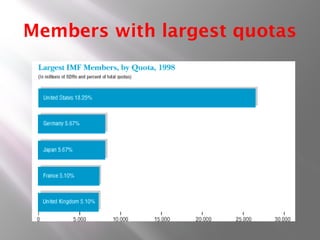
- 16. Members with largest quotas
- 17. SUCCESS OF IMF 1) International Monetary Cooperation 2) Reconstruction of European Countries 3) Multilateral System of Foreign Payments 4) Increase in International Liquidity 5) Increase in International Trade
- 18. 6) Special Aid to Developing Countries 7) Providing Statistical Information 8) Helpful in Times of Difficulties 9) Easiness & Flexibility in Making International Payments
- 19. FAILURES OF IMF 1) Lack of Stability in Exchange Rate 2) Lack of Stability in the Price of Gold 3) Inability to Remove Restrictions on Foreign Trade 4) Rich Nations Club 5) No help for development projects
- 20. 6) No Solution of International Liquidity 7) Interference in Domestic Economies 8) Inability to tackle the Monetary Crisis of August 1971 9) Less Aid for Developing Countries 10) High Rate of Interest
- 21. IMF AND INDIA India is a founder member of IMF. Earlier India was made a permanent Executive Director of the Board of Directors. At present India is no longer a permanent director. India is now an elected member of IMF. India’s rank is 13th among 185 member nations.
- 22. ADVNANTAGES FROM MEMBERSHIP OF IMF TO INDIA 1) Facility of Foreign Exchange 2) Freedom from British Pound 3) Membership of the World Bank 4) Importance of India in International Sector 5) Economic Consultation
- 23. 6) Help during Emergency 7) Financial help for five Year Plans 8) Special Drawing Rights 9) Help in Foreign Exchange Crisis 10) Profit from Sale of Gold
- 24. conclusion The IMF works to foster global growth and economic stability. It provides policy advice and financing to members in economic difficulties and also works with developing nations to help them achieve macroeconomic stability and reduce poverty
- 25. Thank you.. Thank you..
Editor's Notes
- <number>