IMMUNIZATION SCHEDULE
- 1. CREATED BY BRIJESH TYAGI M.Sc. (N) PREVIOUS P. G. COLLEGE OF NURSING JAN VIKAS NYAS GWALIOR
- 2. A popular term of the continuous maintenance of low temperature required for biologicals from the time of manufacture to shipping, warehousing, and storing before administration. OR The maintenance of refrigeration of items from the point of their origin at the manufacturer, through their transportation, unloading, distribution, and cold storage at the site where they will be used.
- 3. WHY IMMUNIZATION ? Key strategy to child survival. Protecting infants from diseases. Lower morbidity and mortality rates in children. Indicator of a strong primary health care system.
- 4. IMMUNIZATION: COMMON TERMS IMMUNIZATION Process Of inducing immunity by stimulating immune system through antigens. OR The fact or process of becoming, as against a disease. IMMUNITY Resistance of a host to a specific agent OR Immunity means exemption or resistance
- 5. CONTI… VACCINE Any preparation of a weakened or killed bacteria or viruses introduced into the body to prevent a disease by stimulating antibodies against it. VACCINATION Administration of antigenic material(the vaccine) to produce immunity to a disease.
- 6. CONTI… FULL IMMUNIZATION: Beneficiary child(12-23 months) -3 doses of DPT and OPV each, 1 dose of BCG & measles each. Mother- two dose or 1 booster dose of tetanus toxoid during her pregnancy. PARTIAL IMMUNIZATION Child-missed any vaccine or one or more dose Mother- received just one dose of primary tetanus toxoid during last pregnancy
- 7. CONTI… NON-IMMUNIZATION Child and/or mother –not received a single dose of vaccine. RING-IMMUNIZATION Vaccination of people in close contact with an isolated infected patient MOP-UP ROUNDS When the final pockets of polio virus transmission have been identified standard surveillance, door to door immunization in high-risk districts.
- 8. CONTI…. CATCH UP ROUND Additional effort besides routine immunization to cover left outs. HERD IMMUNITY Resistance to spread of infectious disease in a group because of few susceptible members, making transmission unlikely. The immunological status of a population, determined by the ratio of resistant to susceptible members and their distribution.
- 9. MILESTONES IN IMMUNIZATION IN INDIA 1978: EPI 1985: UIP, measles vaccine added 1986: Technology mission 1990: Vitamin A 1992: CSSM 1995: Polio National Immunization days 1997: RCH-I 2005: RCH-II and NRHM
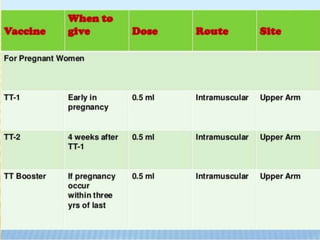
- 12. VACCINATION CHART Sr. No. Time Vaccine Dose Route 1 At Birth BCG, single dose(m) Hep-B 1st dose(m) OPV, 0 dose(m) HPV, single dose(o) (Only for girls) 0.5ml 0.5ml 2 drops 0.5ml I/D I/M PO I/M 2 6 week (1.5 months) Hep-B 2nd dose(m) OPV 1st dose(m) DPT 1st dose(m) HIB 1st dose(o) Pneumococcal 1st dose(o) 0.5ml 2 drops 0.5ml 0.5ml 0.5ml I/M PO I/M I/M I/M 3 10 week (2.5months) Hep-B 3rd dose(m) OPV 2nd dose(m) DPT 2nd dose()m HIB 2nd dose(o) Pneumococcal 2nd dose(o) IPV 1st dose (o) 0.5ml 2 drops 0.5ml 0.5ml 0.5ml 0.5ml I/M PO I/M I/M I/M I/M 4 14 week OPV 3rd dose (m) DPT 3rd dose (m) HIB 3rd dose(o) Pneumococcal 3rd dose(o) IPV 2nd dose (o) 2 drops 0.5ml 0.5ml 0.5ml 0.5ml PO I/M I/M I/M I/M 5 6 months Hep-B booster(m) Rotavirus single dose(o) Influenza (o) 0.5ml 0.5ml 0.5ml I/M I/M I/M 6 9 months Measles (m) 0.5ml S/C 7 12 month(one year) Varicella (m) 0.5ml I/M 8 15 months (1 year 3 months) MMR(m) Pneunococcal booster(o) IPV 3rd dose(o 0.5ml 0.5ml 0.5ml I/M I/M I/M 9 16-24 months Vitamin-A (m) 1 spoon PO 10 18 months(1 rear 6 months) OPV booster 1st dose (m) DPT booster (m) Hib booster(o) 2 drops 0.5ml 0.5ml PO I/M I/M 11 2 year Typhoid (m) Hep-A, single dose 0.5ml 0.5ml I/M I/M 12 24-30 months Vitamin-A 1 spoon PO 13 30-36 months Vitamin-A 1 spoon PO 14 48 months(4 year) MMR (m) 0.5ml I/M 15 60 months(5 year) OPV booster 2nd dose DPT 2 drops 0.5ml PO I/M 16 adult vaccines Influvac once every year for adult of any age Influenza/flu Vaccine 0.5ml I/M 17 one booter dose every 10 year DPT 0.5ml I/M HPV VACCINE for women aged 19 to 26 who did not get vaccinated with HPV during childhood. IMPORTANCE HPV also prevent throat cancer often caused by oral sex.
- 13. BARRIERS TO IMMUNIZATION PHYSICAL BARRIERS -Waiting time -Distance -Discomfort PSYCHOLOGICAL BARRIERS -Discourtesy -Endangered privacy
- 14. REASONS FOR LOW IMMUNIZATION COVERAGE FAILURE TO PROVIDE IMMUNIZATION DROOUTS UN-REACHED POPULATION: Unawareness Socio-economic barriers Geographic area Resistant population Missed opportunities Improper logistics management
- 15. WHAT SHOULD NOT HOLD ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION Minor illnesses such as upper respiratory infections or diarrhoea, mild fever(>38.5 c) Allergy, asthma Prematurity, underweight newborn child Malnutrition Child being breastfed Family history of convulsions Treatment with antibiotics Chronic disease of heart, lung, kidney and liver History of jaundice after birth
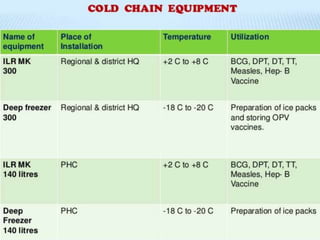
- 16. COLD CHAIN A system of transporting and storing vaccines at recommended temperature from the point of manufacture to the point of use.