Indirect Power Saving From Air Conditioner
- 1. S U B M I T T E D B Y SANDIP KUMAR SAHOO INDIRECT POWER SAVING FROM AIR CONDITIONER 1
- 2. TABLE OF CONTENTS Name Page No. 1. Table Of Contents 2 2. Introduction 3 3. Objectives 4 4. Seebeck Effect 5 5. Thermocouple 6 6. Inverter 9 7. Day Night Controller Circuit 11 8. Advantages 13 9. Disadvantages 14 10. Conclusion 15 2
- 3. 1. INTRODUCTION Indirect power saving from Air Conditioner which is called thermoelectricity , is refers to a class of phenomena in which a temperature difference creates an electric potential or an electric potential creates a temperature difference. Thermoelectric power generator is a device that converts the heat energy into electrical energy based on the principles of Seebeck effect . The pioneer in thermoelectric was a German scientist Thomas Johann Seebeck (1770-1831) 3
- 4. 2. OBJECTIVES To utilize the waste heat of air conditioner. To produce electricity from the waste heat. To reduce our electric bill. To gain knowledge about thermocouples and its applications. 4
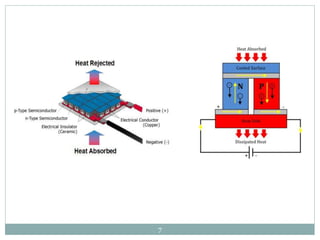
- 5. 3.SEEBECK EFFECT The Seebeck effect is a phenomenon in which a temperature difference between two dissimilar electrical conductors or semiconductors produces a voltage difference between the two substances. The voltages produced by Seebeck effect are small, usually only a few microvolts per Kelvin of temperature difference at the junction. If the temperature difference is large enough, some Seebeck-effect devices can produce a few mill volts (thousandths of a volt) Numerous such devices can be connected in series to increase the output voltage or in parallel to increase the maximum deliverable current. 5
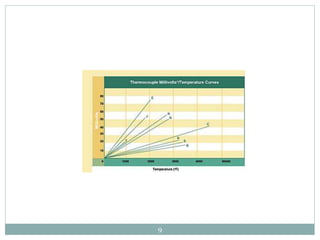
- 6. 4. THERMOCOUPLES A Thermocouple is a sensor used to measure temperature. Thermocouples consist of two wire legs made from different metals. The wires legs are welded together at one end, creating a junction. This junction is where the temperature is measured. When the junction experiences a change in temperature, a voltage is created. The voltage can then be interpreted using thermocouple reference tables to calculate the temperature. 6
- 7. 7
- 8. 5. TYPES OF THERMOCOUPLES 1. Type K Thermocouple (Nickel-Chromium / Nickel-Alumel) 2. Type J Thermocouple (Iron/Constantan) 3. Type T Thermocouple (Copper/Constantan) 4. Type E Thermocouple (Nickel-Chromium/Constantan) 5. Type N Thermocouple (Nicrosil / Nisil) 6. Type S Thermocouple (Platinum Rhodium - 10% / Platinum) 7. Type R Thermocouple (Platinum Rhodium -13% / Platinum) 8. Type B Thermocouple (Platinum Rhodium – 30% / Platinum Rhodium – 6%) 8
- 9. 9
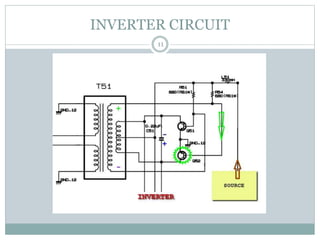
- 10. 6. INVERTER A power inverter, or inverter, is an electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the specific device or circuitry. The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source. 10
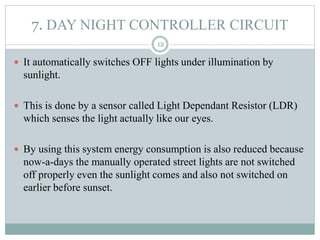
- 12. 7. DAY NIGHT CONTROLLER CIRCUIT It automatically switches OFF lights under illumination by sunlight. This is done by a sensor called Light Dependant Resistor (LDR) which senses the light actually like our eyes. By using this system energy consumption is also reduced because now-a-days the manually operated street lights are not switched off properly even the sunlight comes and also not switched on earlier before sunset. 12
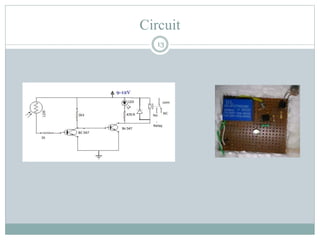
- 13. Circuit 13
- 14. 8. ADVANTAGES Environment Friendly No Noise Easy Maintenance This project doesn't required any land to establish. Efficient use of waste heat. Low maintenance cost Compact and less weight High Reliability 14
- 15. 9. DISADVANTAGES Huge Investment compared to the output. Low efficiency Temperature dependent. Interrupted power generation Poor and middle class people can't afford this and rich people don't require it. 15
- 16. 10. CONCLUSION Air conditioner waste most of its energy by heat, and if somehow we can utilize this heat by using thermocouples we can generate some energy or in one word we can regenerate the waste energy. This thermocouple don't have a great efficiency , the efficiency is maximum 5 to 10% that's why we can't regenerate electricity in a bulk amount. Still if we will take great care when installing thermocouples we can get an average efficiency of 7 to 8%. 16
- 17. 17
- 18. 18
- 19. 19