Inflorescence
- 1. R. NITHYA M. Sc., M. Phil., (Ph. D) ASSISTANT PROFESSOR IN BIOTECHNOLOGY SRI ADI CHUNCAHNAGIRI WOMEN’S COLLEGE, CUMBUM, THENI DT, TAMIL NADU.
- 2. INFLORESCENCE Cluster of flowers attached to peduncle is an inflorescence. Peduncle - The stalk of inflorescence Pedicel - the stalk of individual flowers Sessile - Flower without stalk Bract - the leafy structures in the axil of flowers Involucre - cluster of bracts in a whorl Bracteoles - structures lying between flower and bract. Peduncle of the inflorescence is branched or unbranched.
- 3. TYPES OF INFLORESCENCE Four types Racemose Cymose Mixed Special
- 4. RACEMOSE OR INDEFINITE INFLORESCENCE Peduncle grows continuously. It does not terminate in a flower. Flowers are produced in acropetal order - Younger flowers are at tip Older flowers are at the base
- 5. TYPES OF RACEMOSE INFLORESCENCE Raceme Panicle Spike Compound spike Catkin or Ament Corymb Umbel Spadix Compoundsapdix Head or Capitulum Spike-let of Grass
- 6. RACEME INFLORESCENCE - Unbranched, one pedicellate. - Acropetal succession - Simplest type E.g. Crotalaria
- 7. PANICLE - Compound raceme - Peduncle is branched - Flowers – Acropetal succession - E.g. Yucca, Mangifera
- 9. SPIKE Flowers – Sessile Acropetal succession on the main axis Spike is a modified raceme. E.g. Achyranthes
- 10. COMPOUND SPIKE The main axis is branched with sessile flowers. E.g. Amaranthus spinosus
- 11. CATKIN OR AMENT The peduncle of inflorescence is pendent Bears unisexual flowers Arranged in acropetal order E.g. Acalypha
- 12. CORYMB Main axis of the inflorescence is short Bears pedicellate flower Acropetal succession Pedicel of older flowers are long Younger flower is short. E.g. Cassia.
- 13. UMBEL Main axis become very shortened. All stalked flowers arise at common point. Two types –simple and compound SIMPLE UMBEL Main axis ends in whorl of bracts Flower produced in the axil of each bract. Pedicel of flowers are more or less equal in length. E.g. Allium
- 14. COMPOUND UMBEL The main axis of the inflorescence ends in whorl of involucel of bracts. In the axil of each bract secondary peduncle is formed. It also ends in involucel of bracts. Pedicellate flowers are produced in the axil of the involucel of bracts E.g. Coriandrum.
- 15. SPADIX Peduncle is fleshy and the Sessile flowers are sunk in the Peduncle. The peduncle is enclosed by a large bract known as spathe. E.g. Colocasia
- 16. COMPOUND SPADIX - The main axis is branched - In Cocos nucifera, inflorescence is enclosed by woody bract. - Flowers are sessile, unisexual and arranged on secondary peduncles - Female flowers are few arranged at base - Male flowers are numerous found in the upper part of secondary peduncle.
- 17. HEAD OR CAPITULUM The peduncle ends in a platform like structure called receptacle. The receptacle bears numerous, small sessile flowers. The small reduced flowers – florets. The receptacle bears involucre of bracts at the periphery. E.g. Sunflower
- 18. Sunflower The head is heterogenous Consists two types of florets Disc florets Ray florets The florets at the centre are called disc florets The florets at the periphery – ray florets.
- 19. SPIKE-LET OF GRASS It is a compound spike Each spikelet has Central axis – Rachilla Rachilla bears few bracts – glumes The lower glumes sterile – Lemma Sterile glumes – empty glumes. The upper fertile glumes – palea. The perianth is reduced – Lodicules. Above the lodicules androecium and gynoecium present.
- 20. CYMOSE INFLORESCENCE In cymose the peduncle grows and terminates in a flower. Further flowers are produced laterally. Flowers - basipetal arrangement The central flower is older. The lateral flowers are younger.
- 21. SOLITARY CYME The peduncle grows and terminate in a single flower The lateral flowers do not present E.g. Hibiscus
- 22. SIMPLE CYME It is a cluster of three flowers. Main axis or peduncle ends in a flower(central and older). Two lateral flowers are younger E.g. Jasmine
- 23. MONOCHASIAL CYME The main axis ends in a flower It bears one lateral branch below the terminal flower in the axil of a bract. Two types Monochasial helicoid cyme Monochasial scorpiod cyme
- 24. MONOCHASIAL HELICOID CYME Main axis terminates in a flower and lateral Flowers are produced on the same side. So the flowering branch becomes curved on the side. E.g. Hamelia. This helicoid type of branching is called Dreparium.
- 25. MONOCHASIAL SCORPIOD CYME Main axis ends in a flower and lateral flowers are formed alternately on one side only, So the flowering branch becomes zig-zag in growth. E.g. Heliotropium The scorpioid cyme is called cincinnus.
- 26. DICHASIAL CYME OR BIPAROUS CYME The main axis ends in a flower, which has two opposite bracteoles. Flower arise from each bracteole Each of these flowers again has two bracteoles from this third set of flowers arise. The cluster of flowers can be broken up into small groups of three flowers each. E.g. Clerodendron
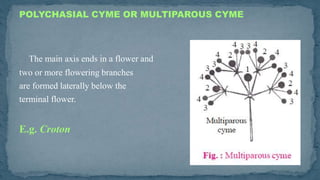
- 27. POLYCHASIAL CYME OR MULTIPAROUS CYME The main axis ends in a flower and two or more flowering branches are formed laterally below the terminal flower. E.g. Croton
- 28. MIXED INFLORESCENCE Mixed inflorescence are partly racemose and partly cymose THYRSUS The main flowering branch is racemose The ultimate branches are cymose. This is a type of panicle E.g. Ocimum
- 29. FASICLE It is a clustered form of inflorescence and the flowers are short and crowded. E.g. Polyalthia
- 30. SPECIAL TYPES OF INFLORESCENCE VERTICILLASTER -Condensed cymose inflorescence - Develops in the axil of pair of opposite leaves. - First order of branching is dichasial further branching are monochasial. E. g. Leucas
- 31. HYPANTHODIUM It is also called syconium, condensed form of cymose inflorescence The inflorescence axis is enlarged Into flask shaped receptacle with a central cavity. Receptacle opens at the top by osltiole guarded by incurved hairs. Numerous small sessile flowers arranged Along the inner wall of receptacle. E.g. Ficus Male flowers are placed towards the top of the cavity Female towards the bottom.
- 32. CYATHIUM - It is condensed inflorescence looks like a flower. - It consists cup like structure formed of involucre of bracts. - Female flower –present at the centre of cup, single, stalked with tri-carpellary ovary. It seen outside the cup. -Male flowers-reduced, five scorpoid cyme surrounds the central female flower. -Single stamen represents the male flower. E.g. Euphorbia hetrophylla