Intro to html
- 1. Intro to HTML The Basics
- 2. HTML HTML means Hyper Text Markup Language . HTML is a language that helps us to create web sites in the Internet . HTML helps to coordinate human and the computer . So we have to use some codes to explain to computer what are we going to do. Therefore we use HTML to give instructions to create web sites.
- 3. Why We Learn HTML?
- 4. Tim Berners-Lee ( CERN physicist) Creator of HTML & WWW CERN is an European Organization for Nuclear Research at Geneva
- 5. HTML is an evolving standard (as new technology/tools are added) HTML 1 (Sir Tim Berners-Lee, 1989): very basic, limited integration of multimedia in 1993, Mosaic added many new features (e.g., integrated images) HTML 2.0 (IETF, 1994): tried to standardize these & other features, but late in 1994-96, Netscape & IE added many new, divergent features HTML 3.2 (W3C, 1996): attempted to unify into a single standard but didn't address newer technologies like Java applets & streaming video Beginning of HTML
- 6. Beginning of HTML (cont.) HTML 4.0 (W3C, 1997): current standard (but moving towards XHTML) attempted to map out future directions for HTML, not just react to vendors HTML 4.01(W3C, 1999): XHTML 1.0 (W3C, 2000): HTML 4.01 modified to conform to XML standards XHTML 1.1 (W3C, 2001): “Modularization” of XHTML 1.0 HTML 5 ( Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group, W3C, 2006): New
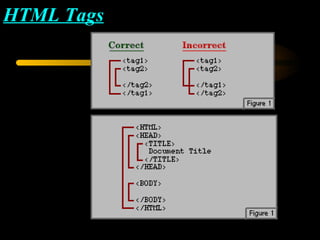
- 7. HTML Tags We use some codes to explain to computer what are we going to do. These codes called as “Tags”. HTML tags must type in the angle brackets(<>) ,it wants to type in a text editor and save with .htm or .html extension. If we use a tag we should close the tag. To close the tag we use closing tags(</>).
- 8. Software & Text Editors What You See is What You Get(Software): Dreamweaver, Microsoft FrontPage, Netscape Composer, Adobe Page Mill, ,Hotdog Word (Save As Webpage) Text Editors Notepad Word pad Code View GEdit Nano Editor
- 9. In HTML we use some essential tags. They are <html> <head> Heading Section <title></title> </head> <body></body> </html> Body Section
- 10. HTML Tags Tag – an HTML code that tells the browser HOW to display something Opening Tag <h3> Closing Tag </h3> Example : < b>This will be bold </b> Tags will not appear in browsers All open tags must have corresponding closing tag.
- 11. Attributes Attributes provide additional display information about a tag Attributes appear within the opening tag brackets Attribute values must be contained in quotes You can have more than one attribute in a tag <font size=“1” color=“green"> This text would be green and smaller </font>
- 12. HTML Tags
- 13. Basic Tags <html></html> Creates an HTML document <head></head> Sets off the title and other information that isn't displayed on the Web page itself <body></body> Sets off the visible portion of the document
- 14. Header Tags <title></title> Puts the name of the document in the title bar Things in the header section do not appear in the browser
- 15. Body Attributes <body bgcolor=?> Sets the background color, using name or hex value <body text=?> Sets the text color, using name or hex value <body background=url> Specifies an image file to be used as background <body vlink=?> Sets the color of followed links, using name or hex value <body alink=?> Sets the color of links on click
- 16. Text Formatting Tags 1 <hl></hl> Creates the largest header <h6></h6> Creates the smallest header <b></b> Creates bold text <i></i> Creates italic text
- 17. Text Formatting Tags 2 <strong></strong> Emphasizes a word (with italic or bold) <font size=“?”></font> Sets size of font <font color=“?”></font> Sets font color, using name or hex value <font face=“?”></font> Set font style like Comic Sans MS
- 18. Paragraph Formatting Tags <p></p> Creates a new paragraph <p align=?> Aligns a paragraph to the left, right, or center <br> Inserts a line break <blockquote></blockquote> Indents text from both sides
- 19. Ordered Lists – this is a numbered list, starts with <ol> and ends with </ol>, each new item in list requires the <li> tag HTML Formatting Sample code…. <ol> List Name <li> list item 1 <li> list item 2 <li> list item 3 <li> list item 4 </ol> Browser view… Yankees Starting Lineup 1. Johnny Damon 2. Derek Jeter 3. Bobby Abreu 4. Robbie McGarry
- 20. Un-ordered Lists –bulleted list of items, starts with <ul> tag and ends with </ul> tag, and each list item begins with <li> HTML Formatting Sample code…. <ul> List Name <li> list item 1 <li> list item 2 <li> list item 3 <li> list item 4 </ul> Browser view… Yankees Starting Lineup Johnny Damon Derek Jeter Bobby Abreu Robbie McGarry
- 21. Definition Lists –not a list of items but a list of terms and explanations or definitions Note: inside a definition list (the <dd> tag) you can put paragraphs, line breaks, images, links and other lists HTML Formatting Sample code…. <dl> <dt>Vocab Word 1 <dd>Definition 1 <dt>Vocab Word 2 <dd>Definition 2 </dl> Browser view… Rock hard object, made.. Ball round object….
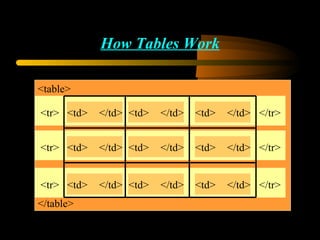
- 22. Table Formatting Tags <table></table> Creates a table <tr></tr> Sets off each row in a table <td></td> Sets off each cell in a row <table border=#> Sets width of border around table cells <table width=“ ? %” or height=“ ? %”> Sets width and height of table - in pixels or as a percentage of document width
- 23. How Tables Work <tr> </tr> <table> </table> <td> </td> <td> </td> </td> <td> <tr> </tr> <td> </td> <td> </td> </td> <td> <tr> </tr> <td> </td> <td> </td> </td> <td>
- 24. Images Img = image src = source of the image alt = stands for alternate and is used to name the image, important for visually impaired users (text to speech) <img src =“nameoftheimage.jpg” alt=“description”> <img src =“nameoftheimage.gif” alt=“description”>
- 25. Images Aligning Images can be done with the “align=“ tag. Place this inside of your image source code. You can only align to the right or to the left with this tag. <img src=“name.jpg” alt=“description” align=“right”> *Note <img….> tag is an empty tag with no </img> tag necessary
- 26. Image as a Link <a href=“url or file name”><img src = “imagefile.jpg” alt=“description”></a> Insert the img src tag in place of the clickable text on a normal link
- 27. Creating Links Two types of links absolute: link to an outside website relative: link to another page within your website HTML uses the <a> (anchor) tag to create a link to another document An anchor can point to any resource on the Web: an HTML page, an image, a sound file, a movie, etc. The correct Syntax of creating an anchor: <a href="url">Text to be displayed</a>
- 28. Creating Absolute Links <a href="url">Text to be displayed</a> Anchor Tag Href attribute used to address the document to link to Where this link will take you Text hyperlink that appears in browser Closing Anchor Tag
- 29. Creating Relative Links <a href=“nameofpage.html">Text to be displayed</a> Anchor Tag href attribute used to address the document to link to Where this link will take you (page within website name Text hyperlink that appears in browser Closing Anchor Tag
- 30. Link Tag Html Links : Html links are defined with the <a> tag Syntax : <a href="http://www.gmil.com">Gmail</a> Example : <html> <body> <a href="http://www.gmail.com">Gmail</a> </body> </html> Gmail O/P : If we click this link it goes to gmail account