Introduction of flower
- 1. Faculty of Pharmacy Beni Suef University
- 2. Definition:- Highly modified & specialized stem or a branch of a stem carrying appendages (a crowded modified leaves known as floral leaves) each of the floral leaves concerned with special function in the process of fertilization for the production of the fruits & seeds. A typical flower is usually formed of 4 sets4 sets of floral leaves arranged on expanded apex of shortened axis called receptaclereceptacle.
- 3. These floral leaves are attached to the receptacle in the following sequences:- Calyx: composed of sepals. Corolla: composed of petals. Androecium: composed of stamens (filament & anther). Gynoecium: composed of carpels (stigma, style & ovary). When the outer floral leaves (calyx & corolla) are not differentiated, they are known as Perianth. Outer floral parts
- 10. Bract: is a leafy structure from the axis of which the flower arises. Bracteole: scale like leaf found on the floral stalk. Involucre: is a group of bracts arranged in one or more whorls surrounding a group of florets. Pedicellate flower: when the flower is carried on a stalk or pedicel. Sessile flower: flower without pedicel.
- 11. Scheme of flower 1-Origin: Part used, Genus name (1st letter in capital), species name (1st letter in small) & Family (1st letter in capital). 2-Condition: entire, powder, fresh, dry. 3-Shape: 4-Size: 5-Color: 6-Touch: 7-Odour: 8-Taste: 9- Kind of flower: Solitary or Inflorescence. 10- Receptacle: hollow, solid, convex, flat. 11- Insertion: Pedicellate or sessile.
- 12. 12- Kind of flower: 1- According to presence or absence of any of the floral parts:- A- Complete: All floral parts are present. B- Incomplete: one of them are absent. 2-According to symmetry of the floral leaves:- A- Actinomorphic: when the flower can be divided by a number of radial longitudinal cuts into equal halves.
- 13. B- Zygomorphic: when the flower can be divided by only one planes into equal halves. C- Irregular or asymmetric: the flower can’t be divided into equal halves by any plane.
- 14. 3-According to presence or absence of both sexual parts:- A-Hermaphrodite (Bisexual): when both androecium & gynoecium are present. B- Sterile: when both male & female organs are absent or not functioning. C- Unisexual: when only one of the sexual organs is present & functioning. Staminate(♂): when flowers have only the androecium. Pestillate(♀): when flower have only the gynoecium.
- 16. 13-Calyx:- 1-Cohesion of sepals: Polysepalous, Gamosepalous. 2-Insertion: Hypogenous, Perigynous, Epigenous.
- 17. 3- No. Of sepals: ………… 4- Pecularities: More description of calyx such as shape, color. Forms of gamosepalous calyx:- 1- Tubular: having nearly parallel sides.
- 18. 2-Campanulate or Bell shaped. 3-Bilabiate: irregular or Bilipped. 4-Globose: spherical in shape.
- 19. 14-Corolla:- 1-Cohesion of petals: Polypetalous, Gamopetalous. 2-Insertion: Hypogenous, Perigynous, Epigenous. 3- No. Of petals: ………… 4- Pecularities: More description of Corolla. Forms of Gamopetalous corolla:- 1- Tubular: when united in tube like structure.
- 20. 2-Ligulate: strap-shaped with short tubular base. 3-Bilabiate: irregular or Bilipped. 4-Campanulate or Bell shaped.
- 21. 15-Androecium 1-
- 23. 2- No. Of stamens: ………… 3-Insertion: oEpipetalous: when the filaments fused with petal. oWhen androecium arise from receptacle as calyx & corolla they described as:- 1- Hypogenous 2- Perigynous 3- Epigenous
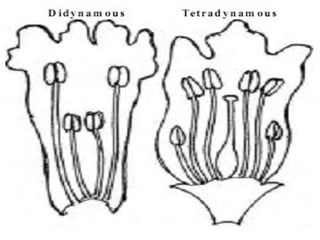
- 24. 4-Filaments: long, short. 5-Anther:…………. 4-Pecularities: More description of androecium as, Didynamous & Tetradynamous. Didynamous Tetradynamous
- 26. 16-Gynoecium:- 1-Cohesion of carpels: Apocarpous, Syncarpous.
- 27. 2-Insertion: Superior or Inferior. 3- No. Of carpels: ………… 4- Ovary: no. of locules. 5- Style: size, shape, color. 6- Stigma: pointed, bifid.
- 28. Placentation