Introduction to Cryptogamic Botany
- 1. BOTANY 104 Presented by: Fasama Hilton Kollie Lecturer, Department of Biology Mother Patern College of Health Sciences February 4, 2019
- 2. Lesson Outline 1. Overview of Cryptogamic botany 2. Classification of cryptogams 3. General characteristics of cryptogams 4. Phanerogams 5. Classification of Phanerogams
- 3. Lesson Objectives • By the end of this lesson, students should be able to; • Define the term Cryptogamic botany, cryptogams and phanerogams • Identify the classification of cryptogams • Describe the general characteristics of cryptogams • Identify the major groups of phanerogams
- 4. Cryptogamic Botany • Cryptogamae (Greek kryptos, "hidden" + gameein, "to marry") • Lower plants or plant-like organisms that reproduce by spores • They represent the non-seed bearing plants • Other names, such as “Thallophytes", "lower plants", and “Spore plants" are also occasionally used. Spirogyra Ferns Mosses
- 5. Cryptogamic Botany Cont’d… • Cryptogamae as a group are the opposite of the Phanerogamae • Algae, Lichens, Mosses and Ferns are the best known groups of cryptogams • Fungi, Slim molds and Bacteria are also classified as cryptogams Fern Mosses Algae
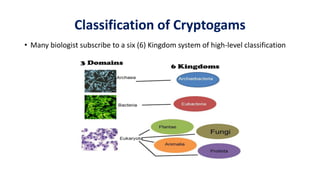
- 6. Classification of Cryptogams • Many biologist subscribe to a six (6) Kingdom system of high-level classification
- 7. Kingdom Representative Group Kingdom Eubacteria Bluegreen bacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Many groups at about the phylum level, of unique prokaryotic organisms Kingdom Protista Algae, Slime molds Kingdom Fungi Basidiomycota, Ascomycota, Lichens, Molds, Yeasts Kingdom Plantae • Bryophytes (Mosses, liverworts and hornworts) • Vascular cryptogams (Ferns, horsetails & Club mosses) • Higher vascular plants ( Conifers, flowering plants) Kingdom Animalia Various invertebrate animal phyla Vertebrate animals Classification Cont’d…
- 8. Classification Cont’d… Kingdom Eubacteria Cyanobacteria Kingdom Protista Slime molds, Algae Kingdom Fungi Basidiomycota, Ascomycota, Zygomycota etc Kingdom Plantae Bryophytes (Moses, Liverworts & Hornworts) Vascular Cryptogams (Ferns, horsetails & club mosses)
- 9. Classification of Plant Kingdom • Along with animals, there are varieties of plant species living and surviving in diverse areas • In 1883, A. W. Eichler proposed a system of classification for the whole plant kingdom • EICHLER classified plants into two sub- kingdoms; ̶ Cryptogamae ̶ Phanerogamae
- 10. Plant Kingdom - Classification • A. W. Eichler
- 11. Cryptogams • Cryptogams are lower plants or plant-like organisms that reproduce by spores • They are also called “flowerless” or “seedless plants” • They are simple plants like algae, mosses and ferns which do not produce flowers, fruits and seeds
- 12. Characteristics of Cryptogams • Cryptogams do not bear flowers and seeds • They reproduce through spores • They need moist environment to survive • Eg: Yeast, Chlamydomonas, Nostoc, Ulothrix, Spirogyra, Ferns, Mosses, Liverworts, hornworts, horsetails etc Thallus spirogyra Horsetails
- 13. Classification of Cryptogams • Cryptogams are divided further into three (3) divisions; 1. Thallophyta 2. Bryophyta 3. Pteridophyta
- 14. Thallophyta: • Commonly called Thyllophytes • Includes plants whose body is not differentiated into roots, stems and leaves • The plant body is called “Thallus” • Thallophyta is sub-divided into; ̶ Algae ̶ Fungi
- 15. 1. Algae: • Characteristically ; • They are mostly found in water or moist place or well-lighted area • They contain chlorophyll • Their cell wall is made up of cellulose • Ex: Volvox, Ulothrix, Spirogyra Volvox
- 16. 2. Fungi: • Characteristically; • Most are multicellular except yeast • They grow in moist and dark places • They lack chlorophyll • Cell wall is made up of fungus cellulose or Chitin • Examples: Mushroom, Mucor, Yeast etc
- 17. Bryophyta • Seedless non vascular plants • Bryophyta are the simples land plants with undifferentiated plant body • They include plants such as mosses, liverworts, hornworts etc
- 18. Bryophyta Cont’d: • Characteristically • They are found in moist, cool and shady places • They are known as amphibian plants as they need water for reproduction • The plant body is leaf-life Thallus except moss • Examples: liverworts, Moss, Hornworts, Riccia etc
- 19. Bryophyta Cont’d… • Bryophyta is divided into three phyla; • Marchantiophyta (Liverworts) ̶ Eg: Riccia, Marchantia etc • Anthocerophyta (Hornworts) ̶ Eg: Anthoceros • Bryophyta (Mosses) ̶ Eg: Funaria
- 20. Pteridophyta • Known as “Wing-plants” • Seedless vascular plants • They are the most advanced cryptogams • Vascular tissues present in their body • Seedless vascular plants
- 21. Pteridophyta • Examples: Ferns, Azola, Marsilea, Lycopodium, Horsetail etc
- 22. Pteridophyta: • Pteridophyta is divided into four (4) phyla; • Psilotophyta - eg: Psilotum • Lycophyta - eg: Lycopodium, Selaginella • Sphenophyta - eg: Horsetail Equisetum • Pterophyta - eg: ferns, Nephrolepsis, Pteris, Dryopteris etc Lycopodium Psilotum
- 23. Phanerogams: • Greek, phaneros = "visible“ + gameein, "to marry“ • Also called Spermatophyta • They prepare their own food • Bear flowers of different structures and colors and they also bear seed • They have well developed reproductive system
- 25. Gymnosperms: • They are naked-seeded plant as their seed are not enclosed in a fruit • Characteristically; • They do no produce flowers and fruits • They are wood trees and live for many years • The plant body is differentiated into root, stem and leaves • Eg; Cycas, fir, deodar etc
- 26. Gymnosperms Cont’d… • Gymnosperms are generally divided into four distinct division; 1. Cycadophyta – eg: Cycas 2. Coniferophyta – eg: Pinus, Cedrus etc 3. Ginkgophyta – eg: Maidenhair tree 4. Gnetopsida – eg: Gnetum
- 27. Angiosperms: • Angiosperms are the largest group among all the groups of plants • Constitute about 80% of all green plants • Found in varieties of habitats
- 28. Angiosperms Cont’d… • Characteristically; • They are autotrophs • Their seeds are enclosed inside the fruits • Plants of this group grow in different habitats. Some are Hydrophytes, Mesophytes, Xerophytes, and Epiphytes
- 29. Angiosperms Cont’d… • Angiosperms are divided further into two classes; 1. Monocotyledon 2. Dicotyledons
- 30. Monocotyledon: • One cotyledon • Fibrous root system • Long and narrow leaves with parallel venation • They have a weak stem • Examples: Wheat, Rice, Barley, Sugarcane, Maize, Bamboo etc. Rice (Oryza sativa) Maize (Zea mays) Barley
- 31. Dicotyledons • Two seed leaves • Broad leaves with reticulate venation • Tap root system • They have a strong stem • Examples: Beans, Pea, Mustard, Orange, Mango etc
- 32. Reference: • Nabors, Murray W., INTRODUCTION TO BOTANY Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings, 1301 Sansome St., San Francisco, CA 94111. www.aw-bc.com
- 33. Nelson Mandela “It is what we make out of what we have, not what we are given, that separates one person from another”
Editor's Notes
- Hidden marriage signifies that such organism reproductive structures are not visible as compared to other organisms with visible form of reproductive structure
- Cryptogamae as a group are the opposite of the Phanerogamae In contrast, in the seed plants the reproductive organs are easily seen Algae, Lichens, Mosses and Ferns are the best known groups of cryptogams Fungi, Slim molds and Bacteria are also classified as cryptogams
- Along with animals, there are varieties of plant species living and surviving in diverse areas. These organisms differ from one another in different ways EICHLER classified plants into two sub-kingdoms on the basis of flowering and non-flowering features; Cryptogamae Phanerogamae
- They may be aquatic or terrestrial They are the simples and primitive plants
- Commonly called Thyllophytes The most primitive and largest division of cryptogams
- Bryophytes are adapted to grow in water and on land. The more advanced forms only on land Vascular tissues are absent Divided into three classes
- Pteridophytes (pteron=feather, phyton=plant Plants with feather like leaves Also known as Vascular cryptogams. The plant body is differentiated into root, stem and leaves Have feathers-like leaves They are the most developed non-flowering plants
- They are multicellular They are autotrophs