Introduction to Energy Efficiency, EMS and Energy Audit
- 1. Introduction to EE, EnMS and EA Gyanendra P. Upadhyay, LLTE-Energy Efficiency DCCI Training December 2013
- 2. Energy: Definition Energy is the capacity of a physical system to perform work Units of Energy: Joule Calorie kWh
- 3. Various forms of energy • Potential energy – – – – Chemical Nuclear Mechanical stored energy Gravitational – – – – – Radiant Thermal Motion Sound Electrical • Kinetic
- 4. Primary and Secondary Energy M a jo r p r im a r y a n d s e c o n d a r y s o u r c e s S o u rc e C oal E x tra c tio n O p en o r d eep m in es P ro c e s s in g G ra d in g P rim a r y e n e rg y S e c o n d a ry E n e rg y S te a m C oal p u rific atio n C ok e H yd ro P ower s tatio n N u c le a r M in in g E n ric h m e nt G a s w e ll T re atm e nt N a tu ra l ga s C ra c kin g a n d refin in g P etro l E le c tric ity N a tu ra l ga s LP G P etro le u m O il w e ll D ie s e l/fu e l o ils P etro c h e m ic a l S te a m
- 5. Commercial and Non-commercial Energy • Commercial energy is energy available at price – Examples are electricity, coal, lignite, oil, and natural gas • Non-commercial energy is energy not available in market for a price – Examples are firewood, cattle dung and agricultural wastes, solar energy, animal power, wind energy
- 6. Renewable & Non-renewable Energy
- 7. Energy Conversion Oil burns to generate heat --> Heat boils water --> Water turns to steam --> Steam pressure turns a turbine --> Turbine turns an electric generator --> Generator produces electricity --> Electricity powers light bulbs --> Light bulbs give off light and heat
- 8. Types of Energy/Energy Source Used in Nepalese Industries • Electricity • Hydropower Plant • Diesel generating Plant • Co-generation Plant • Thermal • Bio-mass • Coal • Fuel Oil
- 9. What is Energy Efficiency ? Something is more energy efficient if it delivers more services/output for the same energy input, or the same services/output for less energy input. Energy efficiency is "using less energy to provide the same service/output". Improving energy efficiency can make a real difference. It saves money, reduces carbon emissions and decreases your country's dependence on foreign energy supplies... all at the same time!
- 10. Definition of Energy Management “The judicious and effective use of energy to maximize profits (minimize costs) and enhance competitive positions” “The strategy of adjusting and optimizing energy using systems and procedures so as to reduce energy requirements per unit of output while holding constant or reducing total costs of producing the output from these systems”
- 11. Objectives of Energy Management • To achieve and maintain optimum energy procurement and utilization, through out the organization • To minimize energy costs / waste without affecting production & quality • To minimize environmental effects.
- 12. Definition of Energy Audit • the verification, monitoring and analysis of use of energy including submission of technical report containing recommendations for improving energy efficiency with cost benefit analysis and an action plan to reduce energy consumption
- 13. Need for Energy Audit • Three top operating expenses are energy (both electrical and thermal), labour and materials. • Energy would emerge as a top ranker for cost reduction • primary objective of Energy Audit is to determine ways to reduce energy consumption per unit of product output or to lower operating costs • Energy Audit provides a “ bench-mark” (Reference point) for managing energy in the organization
- 14. Types of Energy Audit • Preliminary energy audit • Targeted Energy Audit • Detailed energy audit • Type of energy audit chosen depends on – Function and type of industry – Depth to which final audit is needed – Potential and magnitude of cost reduction desired
- 15. Preliminary Energy Audit Methodology •Preliminary energy audit uses existing, or easily data obtained Establish energy consumption in the organization •Estimate the scope for saving •Identify the most likely areas for attention •Identify immediate ( no-/low-cost) improvements •Set a ‘reference point’ Identify areas for more detailed study/measurement
- 16. Detailed Energy Audit • Evaluates all energy using systems, equipment and includes detailed energy savings and costs • Carried out in 3 phases – Pre-audit Phase – Audit Phase – Post-Audit
- 17. Ten Step Methodology of Detailed Audit S tep No P L A N O F A C T IO N PU R PO SE / RESULTS P h ase I – P re A u d it P h ase S tep 1 P lan an d o rgan ise W alk th ro u gh A u d it In fo rm al In terv iew w ith E n ergy M an ager, P ro d u ctio n / P lan t M an ager R eso u rce p lan n in g, E stab lish /o rgan ize a E n ergy au d it team O rgan ize In stru m en ts & tim e fram e M acro D ata co llectio n (su itab le to typ e o f in d u stry.) F am iliarizatio n o f p ro cess/p lan t activ ities F irst h an d o b serv atio n & A ssessm en t o f cu rren t lev el o p eratio n an d p ractices S tep 2 C o n d u ct o f b rief m eetin g / aw aren ess p ro gram m e w ith all d iv isio n al h ead s an d p erso n s co n cern ed (2 -3 h rs.) B u ild in g u p co o p eratio n Issu e q u estio n n aire fo r each d ep artm en t O rien tatio n , aw aren ess creatio n
- 18. S te p 3 S te p 4 P h a se II – A u d it P h a se P rim a ry d a ta g a th e rin g , P ro c e ss F lo w D ia g ra m , & E n e rg y U tility D ia g ra m C onduct m o n ito rin g su rv e y and H isto ric d a ta a n a lysis, B a se lin e d a ta c o lle c tio n P re p a re p ro c e ss flo w c h a rts A ll se rv ic e u tilitie s syste m d ia g ra m (E x a m p le : S in g le lin e p o w e r d istrib u tio n d ia g ra m , w a te r, c o m p re sse d a ir & ste a m d istrib u tio n . D e sig n , o p e ra tin g d a ta a n d sc h e d u le o f o p e ra tio n A n n u a l E n e rg y B ill a n d e n e rg y c o n su m p tio n p a tte rn (R e fe r m a n u a l, lo g sh e e t, n a m e p la te , in te rv ie w ) M e a su re m e n ts : M o to r su rv e y, In su la tio n , a n d L ig h tin g su rv e y w ith p o rta b le in stru m e n ts fo r c o lle c tio n o f m o re a n d a c c u ra te d a ta . C o n firm a n d c o m p a re o p e ra tin g d a ta w ith d e sig n d a ta .
- 19. S te p 5 C onduct of d e ta ile d tria ls /e x p e rim e n ts fo r s e le c te d e n e rg y g u z z le rs T ria ls /E x p e rim e n ts : 2 4 h o u rs p o w e r m o n ito rin g (M D , P F , k W h e tc .). L o a d v a ria tio n s tre n d s in p u m p s , fa n c o m p re s s o rs e tc . B o ile r/E ffic ie n c y tria ls fo r (4 – 8 h o u rs ) F u rn a c e E ffic ie n c y tria ls E q u ip m e n ts P e rfo rm a n c e e x p e rim e n ts e tc S te p 6 A n a lys is o f e n e rg y u s e E n e rg y and M a te ria l lo s s /w a s te a n a lys is S te p 7 Id e n tific a tio n a n d d e v e lo p m e n t o f E n e rg y C o n s e rv a tio n (E N C O N ) o p p o rtu n itie s Id e n tific a tio n & C o n s o lid a tio n ENCON m e a s u re s C o n c e iv e , d e v e lo p , a n d re fin e id e a s R e v ie w th e p re v io u s id e a s s u g g e s te d b y u n it p e rs o n a l R e v ie w th e p re v io u s id e a s s u g g e s te d b y e n e rg y a u d it if a n y U se b ra in s to rm in g and v a lu e a n a lys is te c h n iq u e s C o n ta c t v e n d o rs fo r n e w /e ffic ie n t te c h n o lo g y S te p 8 S te p 9 C o s t b e n e fit a n a lys is R e p o rtin g & P re s e n ta tio n to th e T o p M a n a g e m e n t b a la n c e & e n e rg y A ssess te c h n ic a l fe a s ib ility, e c o n o m ic v ia b ility and p rio ritiz a tio n of ENCON o p tio n s fo r im p le m e n ta tio n S e le c t th e m o s t p ro m is in g p ro je c ts P rio ritis e by lo w , m e d iu m , lo n g te rm m e a s u re s D o c u m e n ta tio n , R e p o rt P re s e n ta tio n M a n a g e m e n t. to th e to p
- 20. S tep10 P hase III – P ost A udit phase Im plem entation and F ollow up A ssist and Im plem ent E N C O N recom m endation m easures and M onitor the perform ance A ction plan, S chedule for im plem entation F ollow -up and periodic review
- 21. Energy Conservations Vs Energy Efficiency E n e rg y E ffic ie n t E q u ip m e n t u s e s le s s e n e rg y fo r s a m e o u tp u t a n d re d u c e s C O 2 e m is s io n s C o m p a c t f lu o r e s c e n t L a m p 15 W In c a n d e s c e n t L a m p 60 W C O 2 E m is s io n – 6 5 g /h r C O 2 E m is s io n – 1 6 g /h r Figure 1.14
- 22. What is an Energy Management System? Definition Energy Management System = Set of interrelated or interacting elements of an organization to establish energy policy and objectives and to achieve those objectives. Overall aim: improve energy performance 22
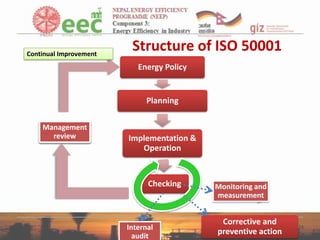
- 23. Energy Management Standard ISO 50001 ISO 50001 • • • • International Standard Since June 2011 International Energy Management Standard Specifies requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and improving an Energy Management System • It does not prescribe specific performance criteria 23
- 24. Continual Improvement Structure of ISO 50001 Energy Policy Planning Management review Implementation & Operation Checking Internal audit Monitoring and measurement Corrective and preventive action 24
- 25. ISO 50001 ENERGY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MANAGEMENT PLAN • Policy/Objectives/ Targets (4.3, 4.4.6) • Resources (4.2.1) DO • Training (4.5.2) • Communication (4.5.4) • Documentation (4.5.4) • Operational Control (4.5.5) CHECK • Internal Audit (4.6.3) • Corrective / Preventive action (4.6.4) ACT • Management review (4.7) Management System For Energy ACT CHECK TECHNICAL PLAN • Energy Review (4.4.3) • Energy baseline (4.4.4) • Energy Performance Indicators (4.4.5) PLAN DO • Design (4.5.6) • Energy Purchasing (4.5.7) DO CHECK • Monitoring (4.6.1) • Measurement (4.6.1) • Verifying action plans results (4.4.6) ACT • Energy Performance and EnPls Review (4.7.2) 25
- 26. Cycle of Energy Policy Understand Energy Aspects Set out Energy Policy Legal and best practice obligation Opportunity for improvement Review 26
- 27. Energy Planning Process Planning Inputs Past and present energy uses Energy Review A. ANALYSE ENERGY USE AND CONSUMPTION Planning Outputs • ENERGY BASELINE • EnPI( s) Relevant variables affecting significant energy use • Performance B. IDENTIFY AREAS OF SIGNIFICANT ENERGY USE AND CONSUMPTION • OBJECTIVE S • TARGETS • PERSONAL Legal requirements and other requirements C. IDENTIFY OPPORTUNITIES FOR IMPROVING ENERGY PERFORMANCE • ACTION PLANS 27
- 28. General steps to certification Initiate contact to certifier Certification & beyond Meet assessment team Onsite Assessment Advisory services (training if required) Preliminary review 28
- 29. Benefits of implementing EnMS Improves efficiency and productivity by reducing energy variation, inefficiency & energy losses Reduces energy cost / increases profitability Reduces GHG/carbon footprint/protect environment Improves employee motivation and involvement Secures energy supply Helps to confirm to new & stricter legislation Increasing focus on corporate responsibility – improves reputation at clients 29
- 30. Compatibility of ISO 50001 with other standards Occupational Health & safety Quality ISO 9001 Environment OHSAS 18001 ISO 14001 ISO 50001 Energy 30
- 31. Energy Auditor: Skill Requirement • • • • • • Reading Comprehension Active Listening Writing Speaking Critical thinking Judgment and decision making • Mathematics • • • • • • • • Monitoring System analysis Problem solving Time Management Coordination Persuasion Science System evaluation
- 32. Data Collection format (General) • • • • • • • • • Name of Business Type of Business Location Address and Contact Person Products Production Capacity ? ? ?
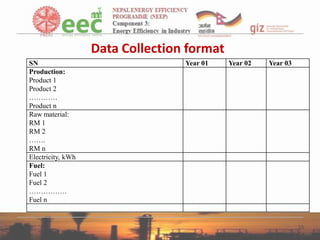
- 33. Data Collection format SN Production: Product 1 Product 2 ………… Product n Raw material: RM 1 RM 2 ……. RM n Electricity, kWh Fuel: Fuel 1 Fuel 2 ……………. Fuel n Year 01 Year 02 Year 03 33
- 34. Data Collection format Month Energy in units (kWh) T1 T2 T3 Total Demand in kVA Energy T1 T2 Total Demand T3 34
- 35. Data Collection format S. N. Equipment kW kVA P.F. kVAR Remarks Reference 35