Introduction To Entrepreneurship
- 2. Objectives • Definition of Entrepreneur • Entrepreneurial Traits • Entrepreneur vs. Manager • Entrepreneur vs. Intrapreneur • The Entrepreneurial decision process • Role of Entrepreneurship in Economic Development • Ethics and Social responsibility of Entrepreneurs • Opportunities for Entrepreneurs in India and Abroad • Woman as Entrepreneur
- 3. What Is An Entrepreneur ?
- 4. Concept of Entrepreneurship • Various views about an ‘Entrepreneur’: • as a risk bearer • as an organizer • as an innovator • Entrepreneurship is related to: • coordination, innovation and performance of the entrepreneur. • a system of creating new business. • referred to the various activities, done for the establishment and operation of an enterprise.
- 5. Definition of Entrepreneurship • “Entrepreneurship is the purposeful activity of an individual or a group of associated individuals, undertaken to initiate, maintain or aggrandize profit by production or distribution of economic goods and services” - A. H. Cole • “Entrepreneurship is based on purposeful and systematic innovation. It included not only the independent businessman but also company directors and managers who actually carry out innovative functions.” - Joseph A. Schumpeter
- 6. Definition of Entrepreneurship • “Entrepreneurs are people who have the abilities to see and evaluate business opportunities , together with the necessary resources to take advantage of them, and to ensure appropriate action to ensure success.” - International Labour Organization • “An entrepreneur is a person who starts a new venture, taking the initiative and risk associated with it and does so by crating something new to provide value to customers.” - David Holt
- 7. Other Definitions of Entrepreneurship • “Entrepreneurship is the process by which individuals pursue opportunities without regard to resources they currently control.” - Stevenson & Jarillo • “Entrepreneurship is the art of turning an idea into a business.” - Fred Wilson
- 8. EntrepreneurialTraits • Innovation - does something new and different, seeking to do something different and unique, try to meet the changing requirements of customers. • Risk – Bearing - must be able to assume the risk involved in the enterprise, needs to be a risk taker not an avoider, should have ability of risk bearing .
- 9. EntrepreneurialTraits (Contd..) • Passion for the Business - This passion typically stems from the entrepreneur’s belief that the business will positively influence people’s lives. • Product/Customer Focus - An entrepreneur’s keen focus on products and customers typically stems from the fact that most entrepreneurs are, at heart, craftspeople. • Execution Intelligence - The ability to fashion a solid business idea into a viable business is a key characteristic of successful entrepreneurs.
- 10. EntrepreneurialTraits (Contd..) • Achievement motivated • Alert to opportunities • Creative • Decisive • Energetic • Has a strong work ethic • Is a networker • Initiative Taker • Lengthy attention span • Optimistic disposition • Persuasive • Responsive to criticism • Self-confident & Self-starter • Tenacious • Tolerant of ambiguity • Visionary
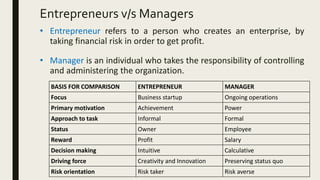
- 11. Entrepreneurs v/s Managers • Entrepreneur refers to a person who creates an enterprise, by taking financial risk in order to get profit. • Manager is an individual who takes the responsibility of controlling and administering the organization. BASIS FOR COMPARISON ENTREPRENEUR MANAGER Focus Business startup Ongoing operations Primary motivation Achievement Power Approach to task Informal Formal Status Owner Employee Reward Profit Salary Decision making Intuitive Calculative Driving force Creativity and Innovation Preserving status quo Risk orientation Risk taker Risk averse
- 12. Intrapreneurs • An Intrapreneur is someone within a company that takes risks in an effort to solve a given problem and is usually is in charge of undertaking innovations in product, service, process etc. • Organizations want to form: • Product Champions: people who take ownership of a product from concept to market. • Skunkworks: a group of intrapreneurs kept separate from the rest of the organization. • New Venture Division: allows a division to act as its own smaller company. • Rewards for Innovation: link innovation by workers to valued rewards.
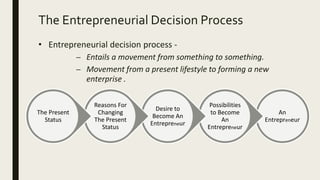
- 14. The Entrepreneurial Decision Process An Entrepreneur Possibilities to Become An Entrepreneur Desire to Become An Entrepreneur Reasons For Changing The Present Status The Present Status • Entrepreneurial decision process - – Entails a movement from something to something. – Movement from a present lifestyle to forming a new enterprise .
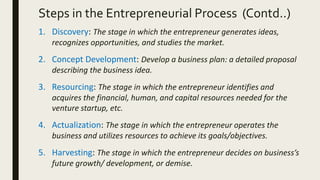
- 15. Steps in the Entrepreneurial Process Discovery Concept Development Resourcing Actualization Harvesting • Once the decision to become an entrepreneur is taken, the entrepreneurial process begins. • The 5 stages of entrepreneurial process are – 1. Discovery 2. Concept Development 3. Resourcing 4. Actualization 5. Harvesting
- 16. Steps in the Entrepreneurial Process (Contd..) 1. Discovery: The stage in which the entrepreneur generates ideas, recognizes opportunities, and studies the market. 2. Concept Development: Develop a business plan: a detailed proposal describing the business idea. 3. Resourcing: The stage in which the entrepreneur identifies and acquires the financial, human, and capital resources needed for the venture startup, etc. 4. Actualization: The stage in which the entrepreneur operates the business and utilizes resources to achieve its goals/objectives. 5. Harvesting: The stage in which the entrepreneur decides on business’s future growth/ development, or demise.
- 17. Role Of Entrepreneurship In Economic Development • Entrepreneurship is one of the most important input in the economic development of a country. • The entrepreneur acts as a trigger head to give spark to economic activities by his entrepreneurial decisions. • The entrepreneur plays a pivotal role not only in the development of industrial sector of a country but also in the development of farm and service sector. • The crucial role played by the entrepreneurs in the development of the Western countries has made the people of underdeveloped countries too much conscious of the significance of entrepreneurship for economic development.
- 18. Role Of Entrepreneurship In Economic Development 1. Promotes Capital Formation 2. Creates Large-Scale Employment Opportunities 3. Promotes Balanced Regional Development 4. Reduces Concentration of Economic Power 5. Wealth Creation and Distribution 6. Increasing Gross National Product and Per Capita Income 7. Improvement in the Standard of Living 8. Promotes Country's Export Trade 9. Induces Backward and Forward Linkages 10. Facilitates Overall Development
- 19. Role Of Entrepreneurship In Economic Development • Promotes Capital Formation • Entrepreneurs promote capital formation by mobilizing the idle savings of public. • They employ their own as well as borrowed resources for setting up their enterprises. • Creates Large-Scale Employment Opportunities • Entrepreneurs provide immediate large-scale employment to the unemployed which is a chronic problem of underdeveloped nations.
- 20. Role Of Entrepreneurship In Economic Development • Promotes Balanced Regional Development • Entrepreneurs help to remove regional disparities through setting up of industries in less developed and backward areas. • The growth of industries and business in these areas lead to a large number of public benefits like road transport, health, education, entertainment, etc. • Reduces Concentration of Economic Power • Industrial development normally lead to concentration of economic power in the hands of a few individuals which results in the growth of monopolies. • In order to redress this problem a large number of entrepreneurs need to be developed.
- 21. Role Of Entrepreneurship In Economic Development • Wealth Creation and Distribution • It stimulates equitable redistribution of wealth and income in the interest of the country to more people and geographic areas, thus giving benefit to larger sections of the society. • Increasing Gross National Product and Per Capita Income • Entrepreneurs are always on the look out for opportunities. • They explore and exploit opportunities,, encourage effective resource mobilization of capital and skill, bring in new products and services and develops markets for growth of the economy. • In this way, they help increasing gross national product as well as per capita income of the people in a country.
- 22. Role Of Entrepreneurship In Economic Development • Improvement in the Standard of Living • Increase in the standard of living of the people is a characteristic feature of economic development of the country. • Entrepreneurs play a key role in increasing the standard of living of the people by adopting latest innovations in the production of wide variety of goods and services in large scale that too at a lower cost. • Promotes Country's Export Trade • Entrepreneurs help in promoting a country's export-trade, which is an important ingredient of economic development.
- 23. Role Of Entrepreneurship In Economic Development • Induces Backward and Forward Linkages • Entrepreneurs like to work in an environment of change and try to maximize profits by innovation. • When an enterprise is established in accordance with the changing technology, it induces backward and forward linkages which stimulate the process of economic development in the country. • Facilitates Overall Development • Entrepreneurs act as catalytic agent for change which results in chain reaction by multiplying their entrepreneurial activities, thus creating an environment of enthusiasm and conveying an impetus for overall development of the area
- 24. Ethics & Social Responsibility Of Entrepreneurs
- 25. What Are Ethics? • Individual values form the basis of ethics, a set of moral principles that govern decisions and actions. • To act ethically is to behave in ways that are in keeping with certain values. • Universal values are values that are shared by all cultures throughout history. • Business ethics are moral principles applied to business issues and actions. • Entrepreneurs have considerable influence on their company’s business ethics.
- 26. Why Practice Business Ethics? • The main reason for behaving ethically, in business or in any area of life is simply that it’s the right thing to do. • Three practical reasons why you should practice business ethics: • Customers are more confident when buying goods and services from an ethical company. • An ethical workplace motivates employees. • Ethical behavior also prevents legal problems.
- 27. Establishing an EthicalWorkplace • Universal values establish a strong foundation for society and are also a good basis for running your business. • To deter unethical behavior, companies try to create transparency, or openness and accountability in business decisions and actions. • To enhance transparency, companies today are using social media, which are interactive electronic forms of communication such as blogs and message boards.
- 28. Ethical Issues for Entrepreneurs • When faced with an ethical decision, it’s best to rely on your own strong personal values to help guide your response. • Intellectual property is artistic and industrial creations of the mind. • Copyright is the exclusive right to perform, display, copy, or distribute an artistic work. • A patent is the exclusive right to make, use, or sell a device or process. • A trademark is a symbol that indicates that the use of a brand or brand name is legally protected and cannot be used by other businesses. • A conflict of interest exists when personal considerations and professional obligations interfere with each other. • Confidentiality involves respecting the privacy of others.
- 29. Corporate Social Responsibility • Corporate social responsibility means that businesses act in ways that balance profit and growth with the good of society. • Corporate social responsibility often translates into profits. This advantage for business is sometimes described as “doing well by doing good.” • One type of socially-responsible corporate behavior is ethical sourcing, which means buying from suppliers who provide safe working conditions and respect workers’ rights
- 30. ResponsibilityToThe Individuals • Corporate social responsibility affects employees, customers, investors, and creditors. • Entrepreneurs have legal obligations to provide a safe workplace and fair employment policies. • Business owners are bound by law to treat customers fairly. • Acting responsibly toward suppliers or vendors results in making the best choices of materials and using them wisely. • Investors and creditors provide the money to start and run a business. They must believe in both the idea behind the business and the entrepreneur.
- 31. ResponsibilityToThe Environment • Sustainable Design - Sustainable products meet the planet’s current needs while preserving resources for future generations. • Alternative Energy - Researchers are working to make fossil-fuel alternatives such as solar, wind, and hydrogen power more efficient. • Organics - Organic produce, grains, and meats make up a small but steadily growing segment of the food market. • Fair Trade - This is a way of doing business based on principles of social and environmental responsibility and promoting sustainable growth.
- 32. The Energy-EfficientWorkplace • Creating an energy-efficient workplace saves money and can draw customers. • Five ways that a business can lower its expenses, while also helping the environment include: • Getting into the recycling loop. • Doing business electronically. • Buying supplies in bulk. • Replacing incandescent light bulbs with fluorescent ones. • Using environmentally friendly transportation.
- 33. Responsibility to the Community • Businesses support disadvantaged and needy people, either for financial gain or because "It's the right thing to do." • Cause-related marketing is a partnership between a business and a nonprofit group for the benefit of both. It increases sales for the business and raises money and awareness for the nonprofit group. • Sponsorship is when a business sponsors a community event or service in exchange for advertising. • With facilitated giving, a business makes it easier for customers to contribute to a cause. • Philanthropy occurs when business leaders donate money and other resources for socially beneficial causes.
- 34. Opportunities for Entrepreneurs • There is tremendous interest in entrepreneurship all around the world. • India is at a threshold of startup boom, as we are world’s third fastest growing startup eco-system. • With 3,100 startups, India is closely behind UK with 4,000 startups and catching up to US which has 41,500 startups. • E-commerce, in the past few years, has been the flag bearer for entrepreneurship in India with Flipkart, Snapdeal, Zomato, bookmyshow etc. becoming giants in the field within a few years of formation.
- 35. Opportunities for Entrepreneurs • A lot of big venture capitalist firms have shown interest in making investments in India. • Sequoia Capital, the most active venture capital firm of this quarter in the Asia Pacific region has made 13 of its 32 investments in India. • Another global venture capital firm, Tiger Global, has made 9 of its 20 investments in India. • Major initiatives taken by the government regarding improving the entrepreneurial scenario in the manufacturing sector of the country has helped immensely.
- 36. Woman as Entrepreneur • A Woman Entrepreneur is a woman or group of women who initiate, organize and run a business enterprise. • Government of India has defined women entrepreneurs as owning and controlling an enterprise with a woman having a minimum financial interest of 51% of the capital and giving at least 51% of the employment generated in the enterprise to women. • “Women entrepreneurship is based on women participation in equity and employment of a business enterprise.”
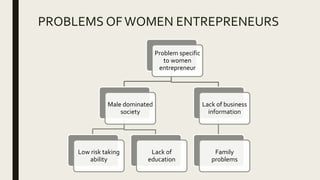
- 37. PROBLEMS OF WOMEN ENTREPRENEURS Problem specific to women entrepreneur Male dominated society Low risk taking ability Lack of education Lack of business information Family problems
- 38. Growth Of Women Entrepreneur’s In India • As per 1991 census, only 1,85,900 women were recorded out of 41,31,112 self employed persons in the country. • Majority of them are engaged in the unorganized sector like agriculture, agro based industries, handicrafts, handlooms, and cottage based industries. • In 1995-96, there were 2,95,680 women entrepreneurs claiming 11.2% of the total 26,40,000 entrepreneurs in India. • As per recent reports, there are 80,50,000 women entrepreneurs out of the total 5,85,00,000 entrepreneurs in India (Roughly approx. 14%).
- 39. Growth Of Women Entrepreneur’s • 21st century is the century of telecom, IT and financial institutions and women’s expertise in all these industries has made them emerge as a force to reckon with. • Many of these industries are headed and guided by women as pioneers and mavericks and have built successful enterprises. • But still in relation to the women population the trend has not been spectacular. • While the Indian startup scene is currently tilted towards the men, Indian women have the potential and passion to catch up to them and transform entrepreneurship into a level playing field in India.
- 40. ThankYou !!
Editor's Notes
- Richard Cantillion in the 18th Century Arranger of musical instruments
- Richard Cantillion in the 18th Century Jean Baptiste Joseph A. Shumpeter
- Academic Definition (Stevenson & Jarillo) Venture Capitalist (Fred Wilson)
- Learning organizations encourage intrapreneurship.
- idea is a concept opportunity is an idea for a new product or service with a market that is willing to pay for that (Observing trends, finding a gap, solving a problem) Innovation is the process of making changes
- A whistle-blower is a term for someone who reports illegal or unethical conduct to superiors or to the public.
- To an environmentalist, “green” means protecting natural resources. To an entrepreneur, being “green” means money.
- A few decades ago, people were not very keen to leave a high-paying job to apply their skills and challenge their destiny in a startup. Entrepreneurship was not so prevalent. If you were an entrepreneur or part of a startup, it was likely a family endeavor or enterprise.
- Make In India, Entrepreneurship & Startup incubation centers Amazon.com lists over 56,000 books dealing with entrepreneurship
- 4.5%