Introduction To Usability
- 2. User Experience IDEO video
- 5. User Experience If the user can’t find it, th F th ’t fi d it the Function is not there… ti i t th
- 8. User Experience ATM Bank Bk E Mail Postal Mail Yahoo mail Rediffmail Blue Line bus Metro Rail
- 10. User Experience
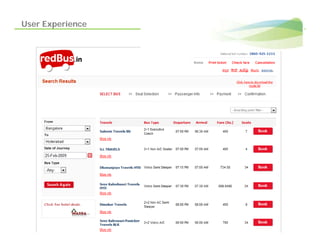
- 11. User Experience
- 12. User Experience
- 14. Overview 1. Overview of Usability and User Centred Design 2. 2 Benefits of Usability to business of an organisation 3. Knowing your users and creating personas 4. Introduction to Navigation, Information Architecture and Task Flow 5. UCD methodology 6. Home Page design 7. Web 2.0
- 15. Overview of Usability How to define Usability History of Usability Hiring the right people Challenges of UCD
- 16. Design What is Design Design is NOT about decoration. Its about communication and Problem Solving “Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.” – Steve Jobs “Like all forms of design, visual design is about problem solving, not about personal preference or unsupported opinion” – Bob Baxley
- 17. Usability Usability = Use + Ability • Learnability • Efficiency • Memorability • Errors • S ti f ti Satisfaction
- 18. Reading the Words beam chap list later wage smog pot jolt duck start trout big job lot cold tape Mayor dusk else wade
- 19. Reading the Words FBIPHDTWAIBM FBI PHD TWA IBM
- 20. Human Memory In psychology, memory is an organism's ability to store, retain, and subsequently retrieve information. There are two kinds of memories 1. Short Term Memory • Short-term memory allows one to recall something from several seconds Short term to as long as a minute without rehearsal. • George Miller in his paper ‘The magical number 7 +/- 2’ suggested that the store of Short term memory was 7 +/- 2 items. • Memory capacity can be increased through a process called chunking. 2. Long Term Memory • Long-term Long term memory can store much larger quantities of information for potentially unlimited duration (sometimes a whole life span). • Short-term memory is supported by transient patterns of neuronal communication, dependent on regions of the frontal lobe and the parietal lobe. Long-term memories, on the other hand, are maintained by more stable and permanent changes in neural connections widely spread throughout the brain
- 21. Visual Memory Find the amount 1,25
- 22. Usability Usability is the “effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction with which a specified set of users can achieve a specified set of tasks in a particular environment.” – International Standards Organization It ti l St d d O i ti A Usable product • Is easy to learn. • Is hard to forget. • Minimizes burden burden. • Reduces Workload. • Anticipates and forgives mistakes. • Does what the user wants and when the user wants it. • Always provides feedback. • Satisfying and probably fun to use.
- 23. Importance of Usability If website is difficult to use..................................... people leave If the homepage fails to clearly state what a company offers and what users can do on the ff d ht d th site......................................................................... people leave If users get lost on a website................................. they leave If a website's information is hard to read or doesn't answer users' key questions..................... they leave The first law of e-commerce is that if users cannot find the product, they cannot buy it either. For intranets, usability is a matter of employee productivity. Time users waste being lost on your intranet or pondering difficult instructions is money you waste by paying them to be at work without getting work done. Current best practices call for spending about 10% of a design project's budget on usability.
- 24. Benefits of Usability Users can • Find what they need. • Learn what else is there. • Use the tool to its fullest. • Do it all without help •L Leave f li th i time is well spent. feeling their ti i ll t Developers / Designers can • Focus on maintenance, improvement and the next project. • Reduce time / budget lost to • Helpdesk mails • Revision to changes.
- 27. Hiring the Right people Usability professionals help design products based on what people • Are like physically intellectually and cognitively physically, cognitively. • Can and Can’t do. • Do well and Don’t do well. • Expect and Don’t expect. • Like and Don’t like.
- 28. Usability Professional and Graphic Designer Usability Professional Graphic Designer • Usability professional gathers data and requirements of the target audience. • Designer conceptualizes and creates the initial prototype. • Usability Professional refines the design in accordance to user behavior and conducts Usability t di U bilit studies on that design. th t d i
- 29. Usability Professional job titles Human Factors Specialist Information Architect User Interface Designer Human F t H Factors Engineer Ei Usability Engineer User Experience Designer
- 30. Usability Problem – Process Problem The problem is • Focusing exclusively on functions, data and technology. • But not focusing on user experience.
- 31. Usability Problems • Management and other teams do not understand the importance of User Research. • Time to market is low and hence timelines do not allow User Centered Design. •D i Designers work on th i gut and personal preference often f k their t d l f ft forgetting th t tti that they are not the users of the product. • Agile Software Development Process vs. User Centered Design Methodology. Methodology
- 32. How do you ensure Usability • Include Usability early in the design / development process process. • Include users in the design process through testing. • Set measurable usability goals early. • Allow usability and user needs to drive design.
- 33. Making Usability Routine Routine Usability requires an Organization to change • You need strong and visionary management • You need infrastructure • You need a staff of Usability Professionals. • You need to make it routine.
- 34. If you bring user in to use your product and they have problems, it's not because they're dumb, but we were dumb with the design.
- 35. Exercise 1
- 36. Thank You