INTRO.pptx
- 2. A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to accomplish a unique product, service or result.
- 3. •1-
- 4. •The context of project management Project Attributes/Characteristics
- 5. •The context of project management Project Attributes/Characteristics
- 7. •1- •Project Management •Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities in order to meet or exceed stakeholder needs and expectations from a project. – PM is disciple of organizing, staffing, controlling, communicating, coordinating and managing resources to bring about successful completion of project. –Goals of PM •Optimizing use of available resources- time , money. Scope •Planning , scheduling and monitoring progress •Risk management –Characteristics of PM –Manager is the head –Point of convergence –Integrate all efforts and skills –Rewards, results and outcomes –Brings all departments into action
- 8. •Standish group survey(done in 1994 &updated since then) •Project success:completed within time & budget with all functions n feature. • Project challenged: completed & operational but over budget & time with fewer feature n functions. •Project fails: project is cancelled at some time during PLC •1-
- 9. •TCS MAJOR REASONS BEHIND PROJECT FAILURE 1.62% Failed for Schedule 2.49 % Budget Overruns 3.47 % Maintenance cost 4.41 Failed to deliver ROI(return on investment)
- 10. • Approaches of Improving IT Project Success 1.User involvement 2.Executive management support 3.Clear requirements and Business Objectives 4.Proper Planning 5.Realistic expectations 6.Emotional Maturity-Deliver Bad news, accept Criticism 7.Skilled Resources-Competent staff 8.Project Management Expertise-Hard working focused team 9.Standard tools & infrastructure 10.Agile Process
- 12. Concept of 4 P’s
- 13. The effective software project management Focuses on four P’s: The People The Product The Process The Project
- 14. People The following categories of people are involved in the S/W Process. Senior Manager Project Managers Practitioners Customers End Users
- 15. The Process Here the important thing is to select an appropriate process model to develop the software. There are different process models available. They are Water fall model, Iterative water fall model,Prototyping model,Evolutionary model,RAD(Rapid Application Development) model, Spiral model. In practice we may use any one of the above models or a combination of the above models.
- 16. The Product Before a software project is planned, the product objectives and scope should be established. Technical and management constraints should be identified. Without this information it is impossible to define a reasonable cost, amount of risk involved, the project schedule etc. A software project scope must be unambiguous and understandable at the management and technical levels.
- 17. In order to manage a successful software project, we must understand what can go wrong (so that problems can be Avoided) and how to do it right. A project is a series of steps where we need to make accurate decision. Project
- 18. W5HH Principle
- 19. THE W5HH PRINCIPLE In an excellent paper on software process and projects, Barry Boehm states: “you need an organizing principle that scales down to provide simple plans for simple projects.” Boehm suggests an approach that addresses project objectives, milestones, schedules, responsibilities, management and technical approaches, and required resources.
- 20. W5HH Approach Why is the system being developed? The answer to this question enables all parties to assess the validity of business reasons for the software work. Stated in another way, does the business purpose justify the expenditure of people, time, and money? What will be done, by when? The answers to these questions help the team to establish a project schedule by identifying key project tasks and the milestones that are required by the customer.
- 21. Who is responsible for a function? We know that the role and responsibility of each member of the software team must be defined. Where are they organizationally located? Not all roles and responsibilities reside within the software team itself. The customer, users, and other stakeholders also have responsibilities
- 22. How will the job be done technically and managerially? Management and technical strategy must be defined. How much of each resource is needed? Develop estimation. The W5HH is applicable to all software projects regardless of size or complexity.
- 23. Need for Project Management Project management is important because it ensures what is being delivered, is right, and will deliver real value against the business opportunity. Leadership. ... Clear Focus & Objectives. ... Realistic Project Planning. ... Quality Control. ... Risk Management. ... Orderly Process. ... Etc..
- 25. •Phases of PLC
- 27. •1- •Project Management Body of Knowledge
- 28. •Project Management Knowledge Areas Key Knowledge areas 1.Project integration management 2.Project scope management 3.Project time management 4.Project cost management 5.Project quality management
- 29. 6. Project human resource mgmt. 7. Project communication mgmt. 8. Project risk management 9. Project procurement mgmt. Also Project Stake holders mgmt
- 30. Project Integration management is a collection of processes required to ensure that the various elements of the projects are properly coordinated. It involves making trade- offs among competing objectives and alternatives to meet or exceed stakeholder needs and expectations. Project scope management is a process that helps in determining and documenting the list of all the project goals, tasks, deliverables, deadlines, and budget as a part of the planning process.
- 31. Project time management is about using the amount of time allocated to a project wisely in order to meet scheduled deliverables and conclude all work by or before the project completion date is compulsory for a successful project. Project cost management is the process of estimating, budgeting and controlling costs throughout the project life cycle, with the objective of keeping expenditures within the approved budget, for a project to be called successful, it's necessary. Project quality management is the process through which quality is managed and maintained throughout a PLC. This responsibility ensures quality expectations are met.
- 32. Project human resource management involves organizing and managing a project team. The team is usually made up of people with specific skills and responsibilities. Project human resource management processes include human resource planning, acquiring the project team, developing the project team and managing the team. Project communication management is a collection of processes that helps to make sure the right messages are sent, received, and understood by the right people Project Risk management is a process that allows individual risk events and overall risk to be understood and managed proactively, optimizing success by minimizing.
- 33. Project procurement management is to establish and maintain relationships with vendors of goods and services during the project life cycle. This unique function is an essential part of project management, which is concerned with overseeing designated sets of temporary operations Project Stakeholder management is the project manager's responsibility to manage and even influence key stakeholders' expectations as well as requirements. Suppose if key stakeholders aren't happy, the project is a failure. This is why project stakeholder management is crucial for project success.
- 36. Phase 1: Conceptualize and Initialize Define Project Goal Provides business value to organization How will we know if the project is successful given the time, money, and resources invested? ⮚Deliverable : Business Case
- 37. �Business case is a deliverable that documents projects goal as well several alternatives �Cost feasibility,benefits, risks �Organisation funds �strategic
- 38. Project Charter: how project organized and how approved alternative will be implemented. Project plan is tactical details concerning who will carry out work n when who is manager? team? scope? cost? time? Resources? Technology? ⮚Deliverable : Project Charter and plan
- 39. �Phase 3: Execute and Control the Project using approach such as the SDLC oAnalysis oDesign oCoding oTesting oMaintenance �Phase 4: Close Project �Deliverable : oFinal project report and documentation
- 40. �Phase 5: Evaluate Project Success ◦Post mortem by project manager and team of entire project ◦Evaluation of team members by project manager ◦Evaluate project’s organizational value
- 41. Business Case ⮚It provides the 1st deliverable in the IT Project Life Cycle. ⮚Definition : • Business Case provides an analysis of the organizational value, feasibility, costs, benefits and risks of several proposed alternatives. ⮚It is not a budget or project plan. ⮚Attributes of a good Business Case ▪Details all possible impacts, costs, benefits ▪Clearly compares alternatives ▪Objectively includes all pertinent information ▪Systematic in terms of summarizing findings
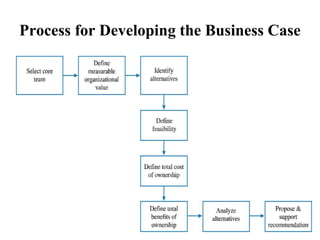
- 42. Process for Developing the Business Case
- 43. Step I: Select the Core Team A core team is recruited. ⮚The core team includes: •Managers •Business Specialist •IT Specialist •Other stakeholders that are affected by the project or involved in its delivery. ⮚Advantages: -Credibility -Alignment with organizational goals -Access to the real costs -Ownership -Agreement -Bridge building
- 44. Step II: Define Measurable Organizational Value (MOV) ⮚The Project’s overall goal and measure of success is referred as the Project’s overall Measurable Organizational Value . ⮚Aligns IT project with the organization and supports the Organization’s goal, mission and objectives. ⮚The MOV must: ✔Be measurable ✔Provides value to the organization ✔Must be agreed upon ✔Must be verifiable at the end of the project
- 45. Step III: Identify Alternatives ⮚Options identified in the Business Case are the strategies for achieving the MOV. ⮚Base Case Alternatives: •It describes how the organization would perform if it maintained the status quo- i.e. if it did not pursue any of the options described in the business case. ⮚Possible Alternative Strategies •Change existing process without investing in IT •Adopt/Adapt systems from other organizational areas •Reengineer Existing System •Purchase off-the-shelf Applications package •Custom Build New Solution
- 46. Step IV: Define Feasibility and Asses Risk Feasibilty: Focuses on whether a particular alternative is doable and worth doing. Types: i.Economic feasibility:Cost/Benefit Analysis of alternatives ii.Technical feasibility:Focuses on existing technical infrastructure iii.Organizational feasibility:Considers the impact on the organization iv.Other feasibilities:Issues like operational,legal and ethical feasibility
- 47. Risk: ⮚An uncertain event that has a positive or negative effect on the project’s objective. ⮚It focuses on what can go wrong and what must go right. ⮚Risk deals with: oIdentification: What can go wrong ?What must go right? oAssessment: What is the impact of each risk? oResponse: How to avoid or minimize the risk?
- 48. Step V: Define Total Cost of Ownership(TCO) ⮚It refers to the total cost of acquiring ,developing, maintaining and supporting the application system over its useful life. ⮚TCO includes costs as: 1.Direct/Up-Front costs- Initial purchase of h/w , s/w & telecom equipments installation cost etc. 2.Ongoing cost- Salaries ,training,upgrades,maintenance etc. 3.Indirect Cost- time lost by users when the system is down,quality assurance etc. ⮚TCO goes beyond the original purchase or development costs.
- 49. Step VI: Define Total Benefits of Ownership(TBO) ⮚It should address the benefits of an alternative over the course of its useful life. ⮚It must include all of the direct,ongoing and indirect benefits associated with each proposed alternative. ⮚Benefits can arise from: oIncreasing high-value work oImproving accuracy and efficiency oImproving decision-making oImproving customer service
- 50. Step VII: Analyze Alternatives using Financial models and Scoring models •All the Alternatives are compared with each other consistently. •The most common ways are :