Ions & periodicity
- 1. 1 Periodic Trend of Ionic Charges 18 2 13 14 15 16 17 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 +1 +/- 4 tend to have +2 -2 +3 -1 -3 more than one option +3 + 3 or + 4
- 2. Trends when atoms form Ions Empirical Observation “when forming ions, elements tend to lose or gain electrons to be more like the nearest noble gas”
- 3. Trends when atoms form Ions Empirical Observation “when forming ions, elements tend to lose or gain electrons to be more like the nearest noble gas” Metals tend to lose e-’s
- 4. Trends when atoms form Ions Empirical Observation “when forming ions, elements tend to lose or gain electrons to be more like the nearest noble gas” Metals tend to lose e-’s Nonmetals tend to gain e-’s
- 5. Atomic Radius Definition: Half the distance across a neutral atom
- 6. Atomic Radius Definition: Half the distance across a neutral atom Radius decreases across a period
- 7. Atomic Radius Definition: Half the distance across a neutral atom Radius decreases across a period The electrons are pulled in tighter as the # of protons increases
- 8. Atomic Radius Definition: Half the distance across a neutral atom Radius decreases across a period The electrons are pulled in tighter as the # of protons increases Radius increases down a group
- 9. Atomic Radius Definition: Half the distance across a neutral atom Radius decreases across a period The electrons are pulled in tighter as the # of protons increases Radius increases down a group Each row on the periodic table adds a “shell” or energy level to the atom. This makes atoms larger with each added shell, just like an onion
- 10. Atomic Radius of Diatomic Molecules
- 11. Relative Size of Atoms
- 12. Ionic Radius Definition: Half the distance across an Ion Cations Anions
- 13. Ionic Radius Definition: Half the distance across an Ion Positively charged ions formed when Cations an atom of a metal loses one or more electrons Anions
- 14. Ionic Radius Definition: Half the distance across an Ion Positively charged ions formed when Cations an atom of a metal loses one or more electrons Smaller than the neutral atom Anions
- 15. Ionic Radius Definition: Half the distance across an Ion Positively charged ions formed when Cations an atom of a metal loses one or more electrons Smaller than the neutral atom Negatively charged ions formed when nonmetal atoms gain one Anions or more electrons
- 16. Ionic Radius Definition: Half the distance across an Ion Positively charged ions formed when Cations an atom of a metal loses one or more electrons Smaller than the neutral atom Negatively charged ions formed when nonmetal atoms gain one Anions or more electrons Larger than the neutral atom
- 18. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size
- 19. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals
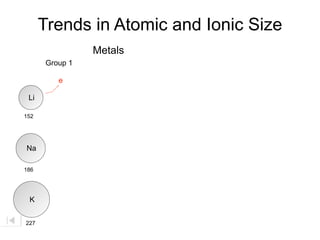
- 20. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1
- 21. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1 Li 152 Na 186 K 227
- 22. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1 e Li 152 Na 186 K 227
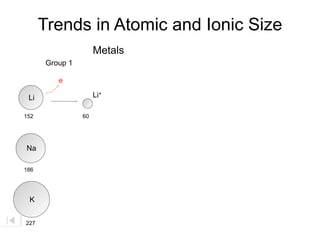
- 23. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1 e Li Li+ 152 60 Na 186 K 227
- 24. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1 e Li Li+ 152 60 e Na 186 K 227
- 25. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1 e Li Li+ 152 60 e Na+ Na 95 186 K 227
- 26. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1 e Li Li+ 152 60 e Na+ Na 95 186 e K 227
- 27. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1 e Li Li+ 152 60 e Na+ Na 95 186 e K+ K 133 227
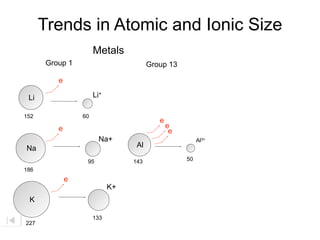
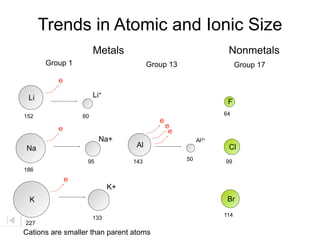
- 28. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1 Group 13 e Li Li+ 152 60 e e e e Na+ Al3+ Na Al 95 143 50 186 e K+ K 133 227
- 29. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Group 1 Group 13 e Li Li+ 152 60 e e e e Na+ Al3+ Na Al 95 143 50 186 e K+ K 133 227 Cations are smaller than parent atoms
- 30. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Nonmetals Group 1 Group 13 e Li Li+ 152 60 e e e e Na+ Al3+ Na Al 95 143 50 186 e K+ K 133 227 Cations are smaller than parent atoms
- 31. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Nonmetals Group 1 Group 13 Group 17 e Li Li+ 152 60 e e e e Na+ Al3+ Na Al 95 143 50 186 e K+ K 133 227 Cations are smaller than parent atoms
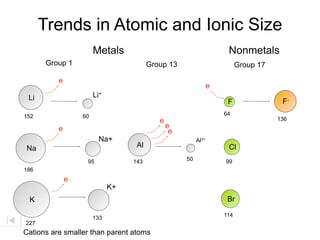
- 32. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Nonmetals Group 1 Group 13 Group 17 e Li Li+ F 152 60 64 e e e e Na+ Al3+ Na Al Cl 95 143 50 99 186 e K+ K Br 114 133 227 Cations are smaller than parent atoms
- 33. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Nonmetals Group 1 Group 13 Group 17 e e Li Li+ F F- 152 60 64 e 136 e e e Na+ Al3+ Na Al Cl 95 143 50 99 186 e K+ K Br 114 133 227 Cations are smaller than parent atoms
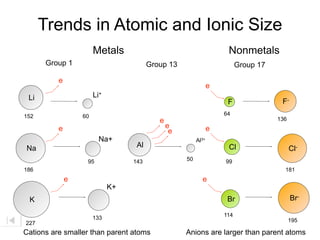
- 34. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Nonmetals Group 1 Group 13 Group 17 e e Li Li+ F F- 152 60 64 e 136 e e e e Na+ Al3+ Na Al Cl Cl- 95 143 50 99 186 181 e K+ K Br 114 133 227 Cations are smaller than parent atoms
- 35. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Nonmetals Group 1 Group 13 Group 17 e e Li Li+ F F- 152 60 64 e 136 e e e e Na+ Al3+ Na Al Cl Cl- 95 143 50 99 186 181 e e K+ K Br Br- 114 133 195 227 Cations are smaller than parent atoms
- 36. Trends in Atomic and Ionic Size Metals Nonmetals Group 1 Group 13 Group 17 e e Li Li+ F F- 152 60 64 e 136 e e e e Na+ Al3+ Na Al Cl Cl- 95 143 50 99 186 181 e e K+ K Br Br- 114 133 195 227 Cations are smaller than parent atoms Anions are larger than parent atoms
- 38. Periodic Properties • How does the size of an atom change when electrons are added or removed?
- 39. Periodic Properties • How does the size of an atom change when electrons are added or removed? As an Atom loses 1 or more electrons (becomes positive), it loses an orbit or energy level and therefore, its radius decreases.
- 40. Periodic Properties • How does the size of an atom change when electrons are added or removed?
- 41. Periodic Properties • How does the size of an atom change when electrons are added or removed? As an Atom gains 1 or more electrons (negative), it fills its outermost energy level, therefore, its radius increases.
- 43. Electron Shielding CORE electrons are closer to the nucleus and therefore have a stronger attraction to the positive nucleus. This “shields” valence electrons from feeling as strong of a pull from the positive nucleus.
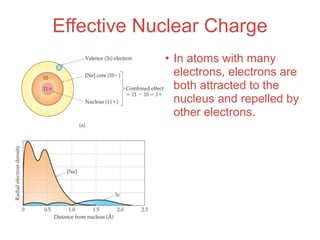
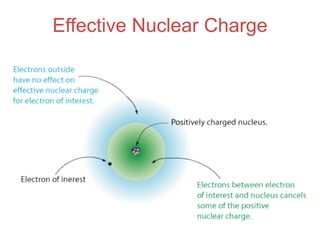
- 45. Effective Nuclear Charge • In atoms with many electrons, electrons are both attracted to the nucleus and repelled by other electrons.
- 46. Effective Nuclear Charge • In atoms with many electrons, electrons are both attracted to the nucleus and repelled by other electrons. • Opposite charges attract. Like charges repel.
- 47. Effective Nuclear Charge • In atoms with many electrons, electrons are both attracted to the nucleus and repelled by other electrons. • Opposite charges attract. Like charges repel. • The nuclear charge that an electron experiences depends on how close it is to the nucleus and how many other electrons are around it.
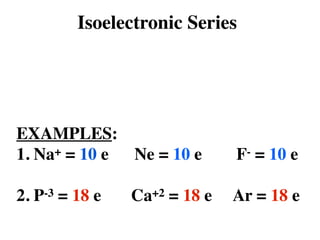
- 49. Isoelectronic Series EXAMPLES: 1. Na+ = 10 e Ne = 10 e F- = 10 e 2. P-3 = 18 e Ca+2 = 18 e Ar = 18 e
- 50. Isoelectronic Series •Atoms and Ions with the SAME # of electrons EXAMPLES: 1. Na+ = 10 e Ne = 10 e F- = 10 e 2. P-3 = 18 e Ca+2 = 18 e Ar = 18 e
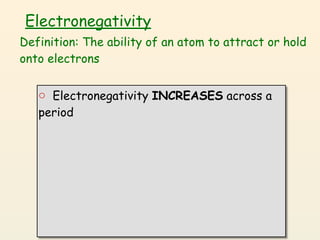
- 51. Electronegativity Definition: The ability of an atom to attract or hold onto electrons
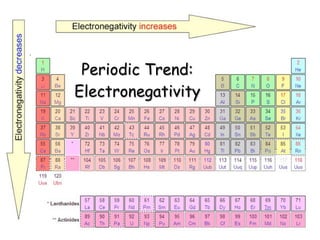
- 52. Electronegativity Definition: The ability of an atom to attract or hold onto electrons o Electronegativity INCREASES across a period
- 53. Electronegativity Definition: The ability of an atom to attract or hold onto electrons o Electronegativity INCREASES across a period o WHY? As the atomic radius decreases, electrons get closer to the atom’s nucleus
- 54. Electronegativity Definition: The ability of an atom to attract or hold onto electrons o Electronegativity INCREASES across a period o WHY? As the atomic radius decreases, electrons get closer to the atom’s nucleus o Electronegativity tends to DECREASE down a group
- 55. Electronegativity Definition: The ability of an atom to attract or hold onto electrons o Electronegativity INCREASES across a period o WHY? As the atomic radius decreases, electrons get closer to the atom’s nucleus o Electronegativity tends to DECREASE down a group o WHY? As the atomic radius increases, electrons are farther from the atom’s nucleus
- 58. Ionization Energy • Amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
- 59. Ionization Energy • Amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom. First ionization energy is that energy required to remove first electron.
- 60. Ionization Energy • Amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom. First ionization energy is that energy required to remove first electron. Second ionization energy is that energy required to remove second electron, etc.
- 61. Trends in First Ionization Energies
- 62. Trends in First Ionization Energies • Down a GROUP, ionization energy decreases • For atoms in the same group, Zeff is essentially the same, but the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. • Across a PERIOD, ionization energy increases
Editor's Notes
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n
- \n