IPA for DNA analysis
- 1. Interval position analysis (IPA) Common order g=1.0308 ACCTTCATCCCCAACAAC CACCACCATTACCACCAT g=1.0462 g=1.0586 CACCACCATTACCACCTA H=1.4591 IPA characteristics' values sensitive to the order of elements in contrast to the characteristics of Information theory (Claude Shannon)
- 2. Interval position analysis (IPA) Special order CT AGCT AGCT AGCT AGCT AGCT AGCT AGCT AG 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 H=2 g≈2 L→∞ g→H If the special order of items in the sequence the values of the characteristics of the IPA are approximately equal to values of simular characteristics in Information theory (Claude Shannon)
- 3. Ribosomal RNA Shpynov S. N. (Proffessor, PHD) http://goo.gl/0XWsj № Organism g № Organism g 1 M.musculus 1,4174 16 Rattus norvegicus 1,4703 2 C.crocodylus 1,4186 17 Crocodylus niloticus 1,4784 3 C.familiaris 1,4280 18 I.persulcatus 1,4830 4 G.gallus 1,4284 19 Zebrias zebra 1,4907 5 Sus scrofa 1,4405 20 Kareius bicoloratus 1,4936 6 Amia calva 1,4409 21 O.moubata 1,4958 7 Homo sapiens 1,4429 22 P.humanus cap 1,5031 8 Th.thermophilus 1,4483 23 M.domestica 1,5110 9 Thermotoga thermarum 1,4483 24 S.pyogenes 1,5164 10 Gallus gallus 1,4557 25 B.anthracis 1,5221 11 Bos taurus 1,4607 26 B.burgdorferi 1,5222 12 Erinaceus europaeus 1,4636 Candidatus Nitrosopumilus 1,5239 13 Homo sapiens 1,4638 27 maritimus 14 Mus musculus 1,4656 28 M.pneumoniae 1,5329 15 Cricetulus griseus 1,4682 29 Neisseria gonorrhoeae 1,5353
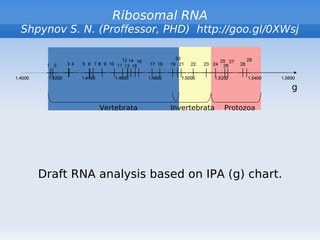
- 4. Ribosomal RNA Shpynov S. N. (Proffessor, PHD) http://goo.gl/0XWsj g Vertebrata Invertebrata Protozoa Draft RNA analysis based on IPA (g) chart.
- 5. Phylogenetic trees made with ClustalW and method based on IPA (g) IPA based method ClustalW
- 6. Local g profile Local g profiles for 3 different organisms (Ribosomal RNA) RNA length ≈ 1800 CACCACCATTACCACCAT window size = 100 step = 2 nucleotide
- 7. Evaluation of DNA segmentation based on the law Heaps Gnomic: A dictionary of genetic codes Pareto distribution http://goo.gl/PWu8B Trifonov E, Brendel, V http://goo.gl/dZxJo Zipf’s Law http://goo.gl/Sjeum Bradford’s law http://goo.gl/bdNjG Heaps law http://goo.gl/u6H2F CACCACCATTACCACCAT
- 8. Rank distribution ln(nr) ln(Gr) 2 1 I II 3 ln(r ln(r ) )
- 9. Interval position analysis (IPA) IPA characteristic based on distance between simular elements N M M N V M V V N M N V A L L A B L B B A L A B F G G F H G H H F G F H 1 2 2 1 3 2 3 3 1 2 1 3 1 - - 1 - - - - 1 - 1 - ∆11 ∆12 ∆13 ∆14
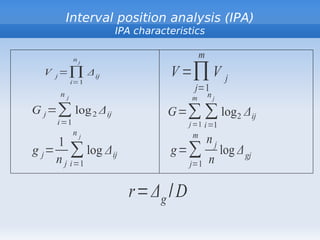
- 10. Interval position analysis (IPA) IPA characteristics nj m V j =∏ Δ ij V =∏ V j i=1 j=1 nj m nj G j =∑ log 2 Δ ij G=∑ ∑ log 2 Δ ij i =1 j =1 i=1 nj m 1 nj g j = ∑ log Δ ij g =∑ log Δ gj n j i=1 j=1 n r= Δ g / D