check basin , furrow and border strip method
- 1. DESIGN ASPECTS IN BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION, CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION & FURROW IRRIGATION METHOD PREPARED BY - TILVA RAJ KOYANI UMANG JADEJA DEVRATSINH DODIYA RAVI CHAROLA ANAND
- 3. BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION WHAT IT IS ? Borders are long, uniformly graded strips of land , seperated by earth bunds.
- 4. BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION WHAT IT IS ? In contrast to basin irrigation these bunds are not to contain the water for ponding but to guide it as it flows down the field. In contrast to furrows these bunds are prevents lateral movement of water within the bunds where as furrows are provided for lateral percolation of the water in the sub soil directly.
- 5. BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION WHEN it USED ? Larger merchanized farms Where machines operations are involved in agriculture Less suited to small scale farms involving hand labour or animal powered cultivation methods. Uniform slope(min. 0.05% and max. 2% slope) Deep homogenous loam or clay of medium infiltration rate. For close growing crops
- 6. BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION DESIGN ASPECTS Border layout The dimensions and shape of borders are influenced by the soil type, stream size, slope, irrigation depth and other factors such as farming practices and field or farm size.
- 9. BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION IRRIGATING BORDERS BORDERS ARE IRRIGATED BY DIVERTING A STREAM OF WATER FROM THE CHANNEL TO THE UPPER END OF THE BORDER. ON CLAY SOILS(INFLOW STOPPED AT 60% OF THE BORDER) ON LOAMY SOILS(IT IS AT 70% - 80% OF BORDER) ON SANDY SOILS(ENTIRE BORDER COVERED)
- 10. BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION INFILTRATION RATE & STREAM SIZE(BORDER SIZE) STREAM SIZE TOO SMALL
- 11. BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION INFILTRATION RATE & STREAM SIZE(BORDER SIZE) STREAM SIZE TOO LARGE
- 12. BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION CROSS-SLOPE OF BORDER if the land is not properly graded and there is a cross-slope,the irrigation water will not spread evenly over the field. it will flow down the slope always seeking the lowest side of the border.(as shown in fig.)
- 13. BORDER STRIP IRRIGATION MAINTENANCE OF BORDERS BORDERS ARE KEPT FREE FROM WEEDS. UNIFORMLY SLOPED BORDERS FREQUENT BUND REPAIRATION CHANNEL AND DRAINS ARE TO BE WEEDED REGULARLY
- 15. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION WHAT IT IS ? Check basins are rectangular or square small plots surrounded by levees or checks.
- 16. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION WHEN It USED ? Crops roots which required submergence in water for periods longer than 24 hours. i.e.Potatoes,beet,carrots,rise,citrus,banana,clover, tobacco. The flatter the land surface,the easy to construct basins. It is also possible to construct basins on sloping land,even when the slope is quite steep.
- 17. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION DESIGN ASPECTS BASIN LAYOUT Basin layout not only refers to the shape and size of the basins but also to the shape and size of the bunds. ♠ What is the shape of the basin : Square,rectangular or irregular ? ♠ How high should be the bund be : 10,50 or 100cm? ♠ What is the shape of bund?
- 18. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION SHAPE AND SIZE OF BASINS ♠ BASIN WIDTH Main limitation of basin width is land slope. (Steep slope then narrow basins) Factors affect basin width 1)depth of fertile soil 2)method of basin construction 3)agricultural practices
- 19. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION SHAPE AND SIZE OF BASINS ♠ BASIN SIZE Main limitation of basin width is land slope. (Steep slope then narrow basins) Factors affect basin SIZE 1)soil type 2)available water flow to the basin 3)land slope
- 20. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION SHAPE AND SIZE OF BASINS
- 21. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION WHAT IS BUNDS ? Bunds are earth embankments which contain irrigation water within basins. They are sometimes called ridges,dykes,or levees. The height is governed by 1) irrigation depth 2) free board
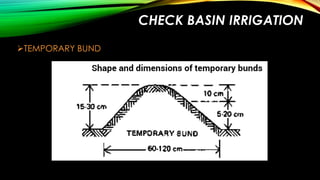
- 22. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION TEMPORARY BUND
- 23. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION PERMANENT BUND
- 24. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION BASIN CONSTRUCTION 1) SETTING OUT OF THE MARKERS
- 25. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION BASIN CONSTRUCTION 2) MARKING A CONTOUR LINE
- 26. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION BASIN CONSTRUCTION 3) MAKING THE BUNDS BY WOODEN FRAME & SMOOTHING THE LAND
- 27. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION IRRIGATING BASINS 1) DIRECT METHOD
- 28. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION IRRIGATING BASINS 2) CASCADE METHOD
- 29. CHECK BASIN IRRIGATION MAINTENANCE OF BASINS Erosion control is made which may be caused by rainfall,flooding or the passing of people when used as footpaths Rats may dig holes in the sides of the bunds. Levelling of basins also required at regular time.
- 31. FURROW IRRIGATION WHAT IT IS ? Furrows are small,parallel channels,made to carry water in order to irrigate the crop. The crop is usually grown on the ridges between the furrows.
- 32. FURROW IRRIGATION WHEN IT USED ? Furrow irrigation is suitable for many crops,especially row crops. Crops that would be damaged if their stems or crown should be irrigated by furrows. I.E. Maize,sunflower,sugarcane,soybean,tomatoes,wheat, Vegetables,potatoes,citrus,grapes Land slope does not exceed 0.5%.
- 33. FURROW IRRIGATION DESIGN ASPECTS FURROW LAYOUT ♠ FURROW LENGTH ( CLAY: 300 TO 400 m SAND: 60 to 300 m ) 1) SLOPE 2) SOIL TYPE 3) STREAM SIZE 4) IRRIGATION DEPTH 5) FIELD LENGTH
- 34. FURROW IRRIGATION FURROW LENGTH
- 35. FURROW IRRIGATION FURROW LENGTH
- 36. FURROW IRRIGATION DESIGN ASPECTS ♠ FURROW SHAPE STABLE Shape is either u-shaped, V-shaped, Parabolic shaped or Trapezoidal shaped
- 37. FURROW IRRIGATION DESIGN ASPECTS ♠ FURROW SHAPE LATERAL INFILTRATION IS HIGH
- 38. FURROW IRRIGATION DESIGN ASPECTS ♠ FURROW SIZE For low permeability of soils wide and shallow furrow is preferred. For highly permeable soils narrow and deep furrows is provided. Furrows of 75mm to 125 mm depth are provided for ROW crops.
- 39. FURROW IRRIGATION DESIGN ASPECTS FURROW LAYOUT ♠ FURROW SPACING 1) SOIL TYPE SANDY (30-60 cm, 30 cm for coarse and 60 cm for sand) CLAY (75-150 cm) Normally 1 m-2 m is provided
- 40. FURROW IRRIGATION FURROW CONSTRUCTION
- 41. FURROW IRRIGATION FURROW CONSTRUCTION
- 42. FURROW IRRIGATION WETTING PATTERNS
- 43. FURROW IRRIGATION IDEAL WETTING PATTERN
- 44. FURROW IRRIGATION SPACING OF FURROWS
- 45. FURROW IRRIGATION STREAM SIZE 1) STREAM SIZE TOO SMALL
- 46. FURROW IRRIGATION STREAM SIZE 1) STREAM SIZE TOO LARGE
- 47. FURROW IRRIGATION PLANTING TECHNIQUES
- 48. FURROW IRRIGATION PLANTING TECHNIQUES
- 49. FURROW IRRIGATION PLANTING TECHNIQUES
- 50. FURROW IRRIGATION MAINTENANCE OF furrows water should be reach the d/s end of all furrows is regularly checked. There should be no dry places or spots where water stays ponding. Overtopping of ridges should not occur. Field channels and drains should be kept free from weeds.
- 51. Thank you