Java virtual machine
- 2. Java Platform. Editions of Java. Big Picture of Java. Java “Fanboi”. What is JVM. What JVM does. Internal Architecture of JVM. Data Types of JVM. Garbage Collection. What is JDK & JRE. Relation among JVM, JDK & JRE. Security Promises of JVM. INDEX
- 3. Java Platform is a suite of programs that facilitate developing & running programs written in java programming language. The platform is not specific to any processor or Operating System. There are multiple platforms each targeting a different class of devices. JAVA PLATFORM
- 4. Java SE: It is the Java Standard Edition that contains basic core java classes. Java EE: It is the Java Enterprise Edition & it contain classes that are beyond Java SE. Java ME: It stands for Java Micro Edition for developing codes for portable devices. EDITIONS OF JAVA
- 5. BIG PICTURE OF JAVA
- 6. Speaking of Java as a language as opposed to the JVM platform, James Gosling, the Father of Java, said "Most people talk about Java the language, and this may sound odd coming from me, but I could hardly care less." He went on to explain, "What I really care about is the Java Virtual Machine as a concept, because that is the thing that ties it all together." JVM “FANBOI”
- 7. Java Virtual Machine is the heart of entire Java program execution process. It’s an abstract machine. It is a specification that provides runtime environment in which java bytecode can be executed. JVM is platform dependent. It is responsible for taking .class file & converting each byte code instructions into the machine language instruction that can be executed by the microprocessor. WHAT IS JVM
- 8. The JVM performs following operation— Loads code. Verifies code. Executes code. Provides Runtime Environment. WHAT JVM DOES
- 9. First of all, it loads .class file into memory. Then it verifies whether all byte code instructions are proper or not. If it finds any instruction suspicious, the execution is rejected immediately. If the byte instructions are proper, then it allocates necessary memory to execute the program. STEPS UNDERTAKEN
- 11. Classloader: Classloader is a subsystem of JVM that is used to load class files. Method Area: Method area is the memory block, which stores the class code, code of the variables, and code of the method in java programs. Heap: It is the runtime data area in which objects are allocated. CONTD.
- 12. Java Stacks: Java stacks are memory area where the java methods are executed. While executing methods, a separate frame will be created in the java stack, where the method is executed. JVM uses separate threads(or process) to execute each methods. PC Registers: These are memory areas which contains memory address of instructions of the methods. CONTD.
- 13. Native Method Stacks: It contains all the native methods used in the applications. Native methods are executed in these stacks. Native Method Interface/Libraries: To execute the native methods, generally native method libraries are required. These header files are located & connected to JVM by a program, called Native method interface. CONTD.
- 14. Execution Engine: Execution engine contains— i. Interpreter. ii. JIT(Just In Time) complier. these are responsible for converting the byte code instructions into machine code so that the processor will execute them. CONTD.
- 15. DATA TYPES OF JVM
- 16. STORAGE & COMPUTATION TYPE INSIDE THE JVM
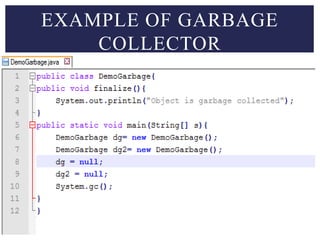
- 17. Each object consumes some memory, of which all there is a limited area. Eventually, the memory allocated to these objects must be reclaimed when they aren’t used. The JVM reclaims these objects automatically through a process called Garbage collection. An object is ready to be garbage collected when it is no longer alive. Garbage collector uses many algorithm but the most commonly used algorithm is mark & sweep. GARBAGE COLLECTION.
- 19. OUTPUT OF ABOVE CODING
- 20. JRE is an acronym for Java Runtime Environment. It is used to provide runtime environment. It is the implementation of JVM. WHAT IS JRE
- 21. JDK is an acronym for Java Development Kit. It physically exists. It contains JRE + development tools. WHAT IS JDK
- 22. RELATION AMONG JVM, JDK & JRE.
- 23. Every object is constructed exactly once before it is used. Every local variable & field is initialized before it is used. Final methods cannot be overridden, & final classes cannot be sub classed. Many More.. The java platform security architecture depends on all the promises & many more.. SECURITY PROMISES OF JVM