Jordan by Sharanya
- 1. Jordan
- 2. Jordan is officially called the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan . Syria lies to the north of Jordan . On the east lies Iraq. The dead sea, Israel an d Egypt lie on the west of Jordan . Saudi Arabia lies to the south east of Jordan. Capital - Amman Language spoken - ArabicReligion - Islam Currency - Jordanian dinarJordanian Kingdom
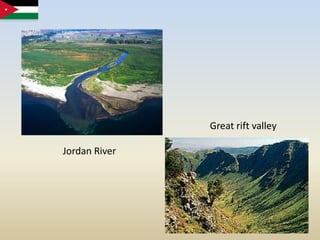
- 3. Relief features of JordanJordan consists mostly of arid desert plateau in the east, with Highland area in the west. The Great Rift Valley of the Jordan River separates Jordan and Israel. The highest point in, while the lowest is the Dead Sea. Aqaba (Red Sea) is Jordan's only port. Other cities include Irbid, Kerak and Zarqa.
- 4. Queen Alia International airport of JordanGulf o Aqaba
- 5. Important cities of JordanGerasa - It is a very ancient city of Jordan, and tourists visiting the city of Gerasa will enjoy the historical sites over there. There are rocky mountains and fertile valleys, found in the city of Gerasa.Amman – It is the largest city in Jordan. Amman, the capital of Jordan is a very ancient city. Tourists mostly visit this city because it serves as the main center of communication, business and cultural life. The city of Amman also features fabulous restaurants, where people enjoy world-class food.
- 6. Important cities of JordanPetra – It is the most spectacular ancient city of Jordan. Petra is also known as “ a rose-red city”. It is located just outside the town of WadiMousa in southern Jordan. Petra, the famous archaeological site draws huge number of tourists every year. Al Karak - The city of Al Karak is situated on the southern part of the city of Amman. Al Karak is well known for the magnificent views of the Red Sea.
- 7. Demography of JordanThe majority of Jordan’s 4.4 million people are Arabs descended from the various tribes that have migrated to the area over the years from all directions. In addition, there are Circassians, descendants of Muslim refugees from the Tsarist Russian invasion of the Caucasus in the 19th century, and a much smaller group of Chechens. Jordan also has a small Armenian population.Jordan values its diverse population, and has consequently provided for the cultural rights of all its citizens. All of Jordan’s ethnic and religious groups have full freedom to form and participate in their own clubs, associations, schools or places of worship. Ethnic groups are also free to teach their own languages. The tradition of tolerance and appreciation for diversity has long been a hallmark of Hashemite Jordan and it has helped to provide a stable social foundation on which to build the country.
- 8. Great rift valleyJordan River
- 9. Climate of JordanThe climate in Jordan is semi-dry in summer with average temperature in the mid 30°C and relatively cold in winter averaging around 13 °C . The western part of the country receives greater precipitation during the winter season from November to March and snowfall in Amman and Western Heights of 500 m. Excluding the rift valley the rest of the country is entirely above 300 m .Spring in AmmanWinter in Amman
- 10. Vegetation & Wildlife Throughout history, the land of Jordan has been renowned for its luxurious vegetation and wildlife. Known as the “land of milk and honey,” the area was described by more recent historians and travellers as green and rich in wildlife. Fortunately, Jordanians have taken great strides in recent years toward stopping and reversing the decline of their beautiful natural heritage. Even now, the Kingdom retains a rich diversity of animal and plant life that varies between the Jordan Valley, the Mountain Heights Plateau and the Badia Desert region.Jordan's national flower, the Black Iris.Arabian Oryx at the Shomari Reserve.Gulf of AqabaArabian HorseSwallow- tail butterfly
- 11. Agriculture of JordanAlthough the agricultural sector's share of GNP declined in comparison with other sectors of the economy, farming remained economically important and production grew in absolute terms. Between 1975 and 1985, total production of cereals and beans rose by almost 150 percent, and production of vegetables rose by more than 200 percent, almost all of the increase occurring between 1975 and 1980.Production of certain cash export crops, such as olives, tobacco, and fruit, more than quadrupled. Because farming had remained labour intensive, by one estimate about 20 percent to 30 percent of the male work force continued to depend on farming for its livelihood.Farmlands of Jordan
- 12. Natural resourcesJordan's mineral wealth and extractive industries constituted a major source of its gross output manufacturing as well as of its total value added in manufacturing. Such natural resources also represented a significant element in Jordan's exports.Phosphate deposits were Jordan's primary natural resource and a major source of export income.Potash was the other major component of Jordan's mining sector. f exploration had resulted in the discovery and exploitation of three oil wells in the Hamzah field in the Wadi al Azraq region west of Amman that yielded only a small fraction of domestic energy requirements.The government was concerned that scarcity of water could ultimately place a cap on both agricultural and industrial development
- 13. King of JordanAbdulla II
- 14. National Animal & EmblemOryx – The national animal of JordanEmblem of Jordan
- 15. Ancient state of JordanOne of the most prominent, ancient states geographically located in what is now the State of Jordan, was the Nabatean Kingdom with their capital at Petra .The Nabataeans developed the North Arabic Script
- 16. The traditional costume of JordanJordanian costume is characterized by its elegance, originality, and practicality. The Jordanian costume is also remarkable for its vast diversity, despite Jordan's relatively small geographical area
- 17. Tourist spots of JordanThe Temple of Artemis at JerashPetra – One of the seven wonders of the world
- 18. The Dead Sea Due to high salt content, one can float in water without trying .. In fact they can recline and read a newspaper !Deep in the Jordan Valley and 55 km southeast of Amman, is the Dead Sea, one of the most spectacular natural and spiritual landscapes in the whole world. It is the lowest body of water on earth, the lowest point on earth, and the world's richest source of natural salts, hiding wonderful treasures that accumulated throughout thousands of years.
- 19. Thank youDone by Sharanya NarayanGrade – 9 B