Adoption, Diffusion & Scaled Impacts - Using what we know in extension practice
- 1. MEAS Symposium 2015 June 4 “Leading Issues in Extension and Rural Advisory Services” Adoption, Diffusion & Scaled Impacts - Using what we know in extension practice - Brent M. Simpson Senior Agricultural Officer, Investment Center, United Nations Food & Agriculture Organization
- 2. Adoption of Innovations ADOPTION PROCESS • Awareness • Interest • Evaluation • Trial (adaptation) • Adoption Source: Rogers, 1964
- 3. Technology Characterists INNOVATION CHARACTERISTICS • Perceived advantage • Complexity • Riskiness • Trialability (lumpiness) • Observability Source: Rogers, 1963
- 4. Time in reaching Scale ? Source: Rogers, 1995
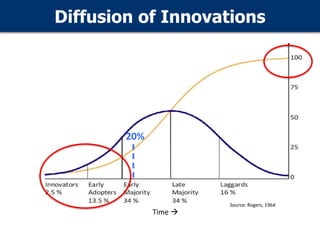
- 5. Diffusion of Innovations Time 20% Source: Rogers, 1964
- 8. The nature of scale No change is permanent – it’s a process Every innovation has its natural scale of utility – its never 100% of farmers
- 9. Going Forward • Start with good innovations • Be careful in targeting where innovations are promoted • Be purposeful in outreach activities • Matching methods, messages and messengers to the 5-phases of adoption • Make sure innovations are actionable • Using different methods for different technologies • Allow farmers to tryout and make adaptations • Understand that it will take time – set appropriate targets and timeframes, design supportive M&E systems to monitor progress, be patient
- 10. MEAS Technical Note Simpson, B.M. 2015. Planning for Scale: Using what we know about human behavior in the diffusion of agricultural innovation and the role of agricultural extension. MEAS Technical Note. Urbana- Champaign, Ill: University of Illinois.
- 11. Disclaimer This presentation was made possible by the generous support of the American people through the United States Agency for International Development, USAID. The contents are the responsibility of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID or the United States Government.