K to 12 Basic Education Curriculum
- 1. Presented by: Joey F. Valdriz
- 3. Republic Act No. 10533 “An Act Enhancing the Philippine Basic Education System by Strengthening Its Curriculum and Increasing the Number of Years for Basic Education, Appropriating Funds Therefor and for Other Purposes” Approved: May 15, 2013 Effective: June 8, 2013
- 5. CORE LEARNING AREAS/DOMAINS FROM K TO 12
- 6. Students do not get adequate instructional time or time on task. Philippine basic education is congested (based on a study of SEAMEO-Innotech). Our high school graduates are not adequately prepared for the world of work. WHY K TO 12?
- 7. The 10-year basic education cycle hinders the recognition of Filipino professional abroad. The Washington Accord prescribes 12 years of basic education as an entry to recognition of engineering professionals WHY K TO 12?
- 8. The Bologna Process also requires 12 years of education for university admission and practice of profession in European countries The Philippines is the only country in Asia and among the three remaining countries in the world that has a 10-year basic education cycle. WHY K TO 12?
- 10. DjiboutiAngola
- 12. During the assessment done by the prestigious organization Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS), they conclude that the problem about the present curriculum in squeezing 12 years of basic education into just 10 is that students are overloaded with subjects which resulted to poor quality of basic education as reflected in the low achievement scores of Filipino students. International tests results like 2003 TIMSS rank the Philippines 34th out of 38 countries in HS II Math and 43rd out of 46 countries in HS II Science; for grade 4, the Philippines ranked 23rd out of 25 participating countries in both Math and Science. In 2008, even with only the science high schools participating in the Advanced Mathematics category, the Philippines was ranked lowest. This quality of education is reflected in the inadequate preparation of high school graduates for the world of work or entrepreneurship or higher education.
- 16. Section 2. Declaration of Policy 1. The State shall establish, maintain and support a complete, adequate, and integrated system of education relevant to the needs of the people, the country and society-at-large. 2. Every graduate of basic education shall be an empowered individual who has learned, through a program that is rooted on sound educational principles and geared towards excellence, the foundations for learning throughout life, the competence to engage in work and be productive, the ability to coexist in fruitful harmony with local and global communities, the capability to engage in autonomous, creative, and critical thinking, and the capacity and willingness to transform others and one’s self. 3. The State shall create a functional basic education system that will develop productive and responsible citizens equipped with the essential competencies, skills and values for both life-long learning and employment. In order to achieve this, the State shall: a) Give every student an opportunity to receive quality education that is globally competitive based on a pedagogically sound curriculum that is at par with international standards; b) Broaden the goals of high school education for college preparation, vocational and technical career opportunities as well as creative arts, sports and entrepreneurial employment in a rapidly changing and increasingly globalized environment; and c) Make education learner-oriented and responsive to the needs, cognitive and cultural capacity, the circumstances and diversity of learners, schools and communities through the appropriate languages of teaching and learning, including mother tongue as a learning resource.
- 17. Guiding Principles and Features of K to 12 Curriculum
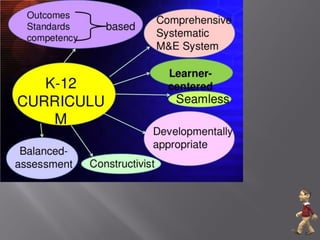
- 20. IMPLEMENTING RULES AND REGULATIONS OF THE ENHANCED BASIC EDUCATION ACT OF 2013 10.2. Standards and Principles a) The curriculum shall be learner-centered, inclusive and developmentally appropriate; b) The curriculum shall be relevant, responsive and research-based; c) The curriculum shall be gender- and culture-sensitive; d) The curriculum shall be contextualized and global; e) The curriculum shall use pedagogical approaches that are constructivist, inquiry-based, reflective, collaborative and integrative; f) The curriculum shall adhere to the principles and framework of Mother Tongue-Based Multilingual Education (MTB-MLE) which starts from where the learners are and from what they already know proceeding from the known to the unknown; instructional materials and capable teachers to implement the MTB-MLE curriculum shall be available. g) The curriculum shall use the spiral progression approach to ensure mastery of knowledge and skills after each level; and h) The curriculum shall be flexible enough to enable and allow schools to localize, indigenize and enhance the same based on their respective educational and social contexts.
- 22. 1. It is learner-centered – The learner is the very reason of the entire curriculum system. Who the learner is in his/her totality, how he/she learns and develops and what his/her needs are were highly considered in the making of the K to 12 curriculum framework. The holistic learning and development of the learner is its primary focus. Teacher creates a conducive atmosphere where the learner enjoys learning, takes part in meaningful learning experiences and experiences success because he/she is respected, accepted and feels safe even if in his/her learning exploration he/she commits mistakes. He/she learns at his/her own pace in his/her own learning style. He/she is empowered to make choices and to become responsible for his/her own learning in the classroom and for a lifetime. The learner-centered K to 12 curriculum gives prime importance to developing self-propelling and independent lifelong learners.
- 23. 2. It is inclusive – The vision statement of DepEd states, “We affirm the right of every Filipino child especially the less advantaged to benefit from such system.” It reaches out to all kinds of learners regardless of ability, condition, age, gender, ethnicity, and social status. It is built on the principle that every child has a right to education and that the education system needs to be flexible to accommodate the learning needs of all learners. The emphasis is on making schools learner-friendly, mainstreaming learners with disability into general schools, and creating a non-discriminatory education system where all learners have equal opportunity to learn.
- 24. 3. It is developmentally appropriate – The K to 12 curriculum considers the various developmental stages of learners. Selection of activities is informed by age-appropriateness, individual differences, and social and cultural diversity. 4. It is standard-based and competency-based – What learners should know and be able to do and the levels of proficiency at which they are expected to demonstrate what they know and can do are clearly stated in the form of standards unpacked into competencies. With a standards- and competencies-based curriculum, learners understand what are expected of them, parents are clear on what are expected of their children, teachers are guided on what to teach and how to teach, and the DepEd is provided with a common reference tool for national assessment.
- 25. 5. It is research-based – The new features of the K to 12 curriculum are backed up by hard data. The use of Mother Tongue as a medium of instruction from K to Grade 3 is supported by a research finding that children learn better and are more active in class and learn a second language even faster when they are first taught in a language they understand. The strengthening of ICT-integration in the basic education curriculum in order to meet the 21st century skills required by employers, the use of the spiral progression approach in the teaching of Math and Science, and the development of alternative delivery modes to provide equal opportunity for all are backed up by the recommendations of the DepEd-commisioned researches conducted by SEAMEO INNOTECH and University of Melbourne. Other research recommendations that were integrated in the K to 12 curriculum are the use of the expanding spiral progression approach in the teaching of Science, Mathematics, Araling Panlipunan, MAPEH and Edukasyon sa Pagpapakatao and the deliberate teaching of the investigatory process in Science as a separate topic by Grade 7.
- 26. 6. It is relevant and responsive – The K to 12 curriculum is aligned with national education and development goals enunciated in the laws of the country and to the ten-point education agenda of the President. It also responds to the Millennium Development Goals and Education for All. As the curriculum framework shows, the K to 12 curriculum is designed to respond to the needs for a nationalistic and productive citizenry who contributes to the building of a progressive, just, and humane society and whose personal discipline is grounded on ethical, moral, and spiritual values. The curriculum likewise addresses the demands of global citizenship and partnership for development that ensures environmental sustainability. In short, the K to 12 curriculum responds to the learning needs of the learner of the 21st century and the local, national and global community.
- 27. 7. It is value laden – The curriculum offers a subject In Values Education with the descriptive title Edukasyon sa Pagpapakatao. This is one of the core and compulsory subjects from Grades 1 to 10. Values and Character Education is also one of the 6 domains in Kindergarten. In the K to 12 curriculum, every teacher is a Values Education teacher as all subject matter is a potent vehicle for values integration. In the K to 12 curriculum, the learner learns and develops in a value-driven environment where everyone is respected and is valued for he/she is.
- 28. 8. It is culture-responsive and culture sensitive – to be truly inclusive, the K to 12 curriculum respects cultures and experiences of various ethnic groups and uses these as resources for teaching and learning. Teachers are expected to provide lessons that cater to a culturally diverse population and honor the cultural heritage of all learners. Given the multi-cultural characteristics of Philippine schools, the Mother Tongue-Based Multilingual Education (MTB-MLE) makes the curriculum truly culture-responsive. Learning mother tongue language helps learners retain their ethnicity identity, culture, heritage and values. To make it responsive to Muslim learners, the K to 12 curriculum continues to offer Madrasah education with subjects in Arabic Language and Islamic Values Education (ALIVE) as a vital component of the basic education system.
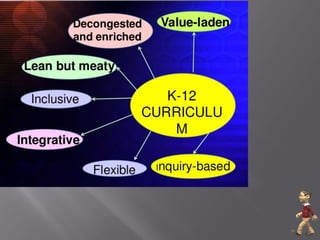
- 29. 9. It is decongested – To allow for mastery of competencies and to give more emphasis to the development of student understanding and on learning how to learn, repetitions of competencies are weeded out. The new curriculum was redesigned in line with the standards and competencies desired of a K to 12 graduate. 10. It is seamless – The K to 12 curriculum consists of a continuum of competencies which provides transition from one grade level to another without unnecessary duplication. The continuum of standards and competencies from the elementary to secondary level is ensured by the unified curriculum framework for each learning area from elementary to high school. The standards and competencies are developed following expanding spiral progression model. This means learning is built upon prior knowledge, skills, values and attitude of students to ensure vertical continuity.
- 30. 11. It is flexible – The flexibility of the curriculum is in keeping with the constitutional mandate of schools “to encourage non-formal, informal, and indigenous learning systems, as well as self-learning, independent, and out- of-school study programs particularly those that respond to community needs” (Article XIV, Section 2(1). 12. It is ICT-based – ICT is taught in the junior high school as one of the Technology and Livelihood Education courses and is now integrated starting Grade 1 not Grade 4 as it is done in the 2002 Basic Education Curriculum. The K to 12 curriculum promotes the use of technology for an engaging, effective, and efficient instruction. 13. It is global – The K to 12 curriculum is benchmarked with curricula of other countries. It meets international standards not merely by adding two years to the 10 years of basic education is equivalent to the 12-year basic education offered in other countries. Graduates of the K to 12 curriculum will be recognized as such in other countries. It expands the local orientedness of the learner to national and global concerns. It enables learners to relate local, national and global events and concerns and builds patterns of interconnectedness which help them make sense of their own lives and the world.
- 31. 14. It is integrative – For holistic learning, subjects are taught using the interdisciplinary and multidisciplinary approach. Learners do not learn isolated facts and theories divorced from their lives. Learning involves change in knowledge, skills, values and attitudes. Learning is organized around the 4 fundamental types of learning: 1) “learning to know”, 2) “learning to do”, 3) “learning to be”, and 4) “learning to live together”. The K to 12 curriculum emphasizes the significant role that co-curricular activities and community involvement play in the holistic development of the learner. They are genuine opportunities for contextualized learning. The co-curricular activities and community involvement programs enable learners to build on their classroom learning and apply the knowledge and skills learned.
- 32. 15. It is broad-based – K to 12 curriculum provides for a broad general education that will “assist each individual in the peculiar ecology of his own society, to (a) attain his potentials as a human being; (b) enhance the range and quality of individual and group participation in the basic functions of society; and (c) acquire the essential educational foundation of his/her development.”
- 33. 16. It is enhanced – The K to 12 curriculum is a product of the collaborative effort of curriculum specialists, subject specialists, practitioners and education stakeholders representing NGOs, business and industry, public and private education institutions, educational institutions, government agencies such as CHED, TESDA, NEDA, DSWD, and DOLE. This curriculum was crafted based on the suggestions from sectoral representatives, college readiness standards formulated by CHED, recommendations from researches and feedbacks from practitioners. The K to 12 curriculum takes pride in the unified frameworks for elementary and high school for all the learning areas.
- 34. The K to 12 curriculum builds on the previous curricular reforms. The 1957 2-2 Plan for secondary education and 1958 revised elementary education curriculum provided for the preparation of students in the world of the academe or the world of work. However, it limited the students to only two choices – college or vocational education. The K to 12 curriculum affords the student more choices after graduation, at least four (4) – employment, entrepreneurship, middle level skills development, or higher education.
- 37. 1. Constructivist. Teaching of all the subjects is anchored on the belief that the learner is not an empty receptacle who is mere recipient of instruction. Rather, the learner is an active constructor of knowledge and a maker of meaning. The role of the teacher becomes one of a facilitator, a guide on the side” rather than a dispenser of information, the “sage on stage”. The student becomes the active “meaning-maker” not the teacher imposing meaning. This means that learners construct their own knowledge and understanding of what is taught out of their experiences.
- 38. 2. Inquiry-based. The curriculum ensures that the learners have the opportunity to examine concepts, issues and information in various ways and from various perspectives. It provides them opportunities to develop skills of creative and critical thinking, informed decision- making, and hypothesis building and problem solving. The learners are encouraged to become active investigators by identifying a range of information, understanding the sources of information and evaluating the objectivity of information. They are thus better able to draw meaningful conclusions which are supported by evidence. Rather than examining an issue from any one perspective, the learners are challenged to explore other possibilities by applying higher order thinking skills in their decision-making endeavors.
- 39. 3. Reflective. Reflective teaching means making the learners look at what they do in the classroom, think about why they do it, and think about if it works. Reflective teaching encourages learners to engage in a process of self-observation and self-evaluation. By collecting information about what goes in their classroom, and by analyzing and evaluating this information, they identify and explore their own practices and underlying beliefs. This may then lead to changes and improvements in their learning.
- 40. 4. Collaborative. Learning is a social activity and so must be collaborative. Learning is intimately associated with connection with other human beings-classmates, teachers, peers, family as well as community. The teaching-learning process is a rich opportunity to teach what it means to “live together”, the fourth pillar of learning. The teaching-learning process should be interactive and must promote teamwork.
- 41. 5. Integrative. Subject matter is taught using interdisciplinary and multidisciplinary approaches. Science is taught in relation to Math and vice versa. The content in Science, Health, Art, and Physical Education may become a reading material in English or the content in Araling Panlipunan and Edukasyon sa Pagpapakatao serves as reading material in Filipino. What is taught in Science is reinforced by the lessons in Health. With the thematic approach, within each subject itself, the connectedness of topics taught is shown. Co-curricular activities and community involvement complement teaching-learning in the classroom. They are real life opportunities for contextualized and integrative learning. Learning is contextual. Learning cannot be divorced from their lives. Learners do not learn from isolated facts and theories separate from the rest of their lives. Every end of the quarter is an opportunity to integrate learning by way of a culminating activity.
- 42. The K to 12 curriculum has a balanced assessment program. Assessment in the K to12 curriculum is, in the words of Cronbach, comprehensive and involves multifaceted analysis of performance that uses a variety of techniques which has primary reliance on observations of performance and integration of diverse information. It makes appropriate use of both traditional and authentic assessment tools. It practices self-assessment (assessment as learning), formative assessment (assessment for learning) and summative assessment (assessment of learning).
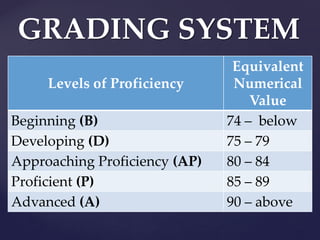
- 43. Levels of Proficiency Equivalent Numerical Value Beginning (B) 74 – below Developing (D) 75 – 79 Approaching Proficiency (AP) 80 – 84 Proficient (P) 85 – 89 Advanced (A) 90 – above GRADING SYSTEM
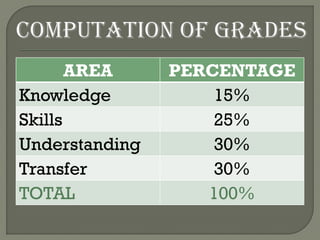
- 44. AREA PERCENTAGE Knowledge 15% Skills 25% Understanding 30% Transfer 30% TOTAL 100%
- 45. 1.Quizzes 2. Periodical Examinations Paper and pencil test using multiple choice, true or false, matching type Paper and pencil test using constructed response type like essay tests, fill in the blanks, performance tasks 3. Participation
- 46. 1.Quizzes 2. Periodical Examinations Paper and pencil test involving case analysis 3. Role Play
- 47. 1.Quizzes 2. Periodical Examinations 3. Recitation Explain/justify something based on facts/data, phenomenon or evidence Tell/retell stories Make connections of what was learned Apply what has been learned in real life situations
- 48. 1.Authentic Performance Task Transfer is assessed thru product and performance Performance includes participation in group activities/projects Products include projects, homework, experiments, formal and informal themes, portfolio, and other outputs
- 50. • CMO 11, series of 2011, “Policies and Standards for the Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics (Ph. D Mathematics) Program” • CMO 10, series of 2011, “Policies and Standards for the Master of Science in Mathematics (M. Sc. Mathematics) Program” • CMO 19, series of 2007, “Minimum Policies and Standards for Bachelor of Science in Mathematics and Bachelor of Science in Applied Mathematics”
- 51. CMO 19, series of 2007,“Minimum Policies and Standards for Bachelor of Science in Mathematics and Bachelor of Science in Applied Mathematics” ARTICLE IV COMPETENCY STANDARDS Section 6 Competency Standards Graduates of a BS Mathematics/Applied Mathematics program are expected to: a. Develop an appreciation of the power of mathematical thinking and achieve a command of the ideas and techniques in pattern recognition, generalization, abstraction, critical analysis, problem- solving and rigorous argument; b.Acquire and develop an enhanced perception of the vitality and importance of mathematics in the modern world; c.Apply analytical and critical reasoning skills to express mathematical ideas with clarity and coherence; d. Know how to use problem-solving approaches to investigate and understand mathematical content; e. Formulate and solve problems from both mathematical and everyday situations; f. Communicate mathematical ideas orally and in writing using clear and precise language; g. Make and evaluate mathematical conjectures and arguments and validate their own mathematical thinking; h. Determine the truth or falsity of mathematical statements using valid forms of argument; i. Appreciate the concept and role of proof and reasoning and demonstrate knowledge in reading and writing mathematical proofs; j. Show an understanding of the interrelationships within mathematics; and, k. Connect mathematics to other disciplines and real-world situations.
- 52. CMO 10, series of 2011, “Policies and Standards for the Master of Science in Mathematics (M. Sc. Mathematics) Program” ARTICLE IV COMPETENCY STANDARDS Graduates of M.Sc. Mathematics are expected to: Demonstrate success in teaching and possess the ability to work with undergraduates in research; Achieve a certain level of fluency in advanced mathematics; Be able to pursue various career options such as research, teaching, and other professional practice.
- 53. ARTICLE IV COMPETENCY STANDARDS Section 3. A graduate the of the Ph.D. in Mathematics program is expected to: acquire the requisite knowledge and skills in mathematics and move beyond the relatively passive role of receiving knowledge to become active and self-motivated scholar; develop a commitment to the professional standards and practices of mathematics; attain a level of training and knowledge suitable for advanced and independent research; possess the competence to sit as a member of a panel in a thesis/dissertation defense; have the ability to referee or review a research article in his/her field of specialization for possible publication in a journal; demonstrate a commitment to the continued improvement of teaching that utilizes research-based practices; participate in course and curriculum development and provide public or professional service; and have the maturity and desire to conduct research and direct or advise graduate students.
- 54. As teachers, we are all like pencils. We go through a lot of sharpening. We are used and sometimes abused. No matter what, we will always leave a mark.
- 55. Thank You!