Kinds of companies
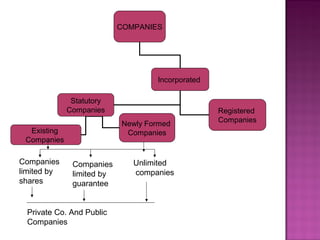
- 2. COMPANIES Incorporated Statutory Companies Registered Companies Existing Companies Newly Formed Companies Companies limited by shares Companies limited by guarantee Unlimited companies Private Co. And Public Companies
- 3. 1. Statutory Companies – Companies created by a special act of the legislature. These are mostly concerned with public utilities. Reserve Bank of India, LIC, GIC, Railways, Tramways, NHAI. 2. Registered Companies – Which are formed & registered under the companies act, 1956. BHEL, SAIL, GAIL, BEML, ONGC, OIL and RNRL.
- 4. 1. Companies with limited liability: (A). Companies limited by shares. The liability of the members limited only up to face value of the share. It may be public or a private company. (B). Companies limited by guarantee – Liability of the member is limited to a fixed amount which the member undertake to contribute to the assets of company in the event of winding up.
- 5. 2. Unlimited companies – Section 12 specifically provides that any 7 or more persons ( 2 or more in case of a private company ) may form an incorporated company, without limited liability. In case of such a company, every member is liable for the debts of the company.
- 6. 1. Private Company : A company which has a minimum paid up capital of Rs. 1,00,000 or higher paid up capital as may be prescribed, and by its Articles-(prohibits any invitation to public) A) restricts the right to transfer its shares, if any. This restriction is meant to preserve the private feature of the company. Limits the members to 2-50. Donot accept deposits accept from members, also no subscription from members
- 7. 2. Public Company- means a company which (a) Is not a private company and members 7- unlimited (b) Has min paid up capital of Rs. 5,00,000. (c) It may be :- Listed public company Unlisted public company Diff between both When does pvt co becomes public and vice versa
- 8. 1. Holding company :- a company is holding of another company if it has control over that other company. 2. Subsidiary :- a company is known as subsidiary of another when the control is exercised by latter. I.e. controlling BOD, majority of shares, subsidiary of another subsidiary
- 9. 1. Govt. company:- it means any company in which not less than 51% of paid up capital is held by central, state or partly by central & partly by state. Rules- appointment of auditor and audit reports to comptroller, also annual report to parliament 2. Non- govt. company:- it is controlled & operated by private capital
- 10. It means any company incorporated outside India which has established its place of business in India , where a minimum of 50% of the paid up share capital( equity or Preference) /Mix is held by one or more citizens of India or one or more body corporates incorporated in India.
- 11. This is the company in which one man holds practically the whole of the share capital of the company & in order to meet the statutory requirements of min members, some dummy members who are mostly his relations or friends hold just 1 or 2 shares each. E.g- A private company is registered with a share capital of Rs 5,00,000 divided into 5000 shares of 100 each. Of these shares 4999 shares are held by A and one share is held by A’s Wife, B. This is a one man Company.
- 12. THANK YOU