Kubernetes on on on on on on on on on on on on on on Azure Deck.pptx
- 1. Maheshkumar R Cloud Solution Architect, Microsoft Azure CKAD, LFCS, MCSE & .NET Geek Azure Kubernetes Service(AKS)
- 2. Content ## Introduction ## Kubernetes on Azure overview ## Why AKS & what's your deal? ## Customer stories ## Resources ## Demo’s and QnA
- 3. Kubernetes momentum For the organizations running Kubernetes today, 77%1 of those with more than 1,000 developers are running it in production. Larger companies are leading the adoption. 77% “By 2020, more than 50% of enterprises will run mission-critical, containerized cloud-native applications in production.” 1Heptio: state of Kubernetes 2018 Src: IDC FutureScape (30 Oct- 2018)
- 4. Kubernetes on Azure overview
- 5. Kubernetes: the industry-leading orchestrator Portable Public, private, hybrid, multi-cloud Extensible Modular, pluggable, hookable, composable Self-healing Auto-placement, auto-restart, auto-replication, auto-scaling
- 6. How Kubernetes works 1. Kubernetes users communicate with API server and apply desired state 2. Master nodes actively enforce desired state on worker nodes 3. Worker nodes support communication between containers 4. Worker nodes support communication from the Internet Kubernetes control API server replication, namespace, serviceaccounts, etc. -controller- manager -scheduler etcd Master node Worker node kubelet kube-proxy Docker Pod Pod Containers Containers Worker node kubelet kube-proxy Docker Pod Pod Containers Containers Internet Internet
- 7. Managed Kubernetes Kubernetes control API server replication, namespace, serviceaccounts, etc. -controller- manager -scheduler etcd Master node Worker node kubelet kube-proxy Docker Pod Pod Containers Containers Worker node kubelet kube-proxy Docker Pod Pod Containers Containers Internet master components node components Azure managed control plane
- 8. How managed Azure Kubernetes Service works • Automated upgrades, patches • High reliability, availability • Easy, secure cluster scaling • Self-healing • API server monitoring • At no charge API server Controller Manager Scheduler etcd Store Cloud Controller Self-managed master node(s) Customer VMs App/ workload definition User Docker Pods Docker Pods Docker Pods Docker Pods Docker Pods Schedule pods over private tunnel Kubernetes API endpoint Azure managed control plane
- 9. From infrastructure to innovation Responsibilities DIY with Kubernetes Managed Kubernetes on Azure Containerization Application iteration, debugging CI/CD Cluster hosting Cluster upgrade Patching Scaling Monitoring and logging Customer Microsoft Managed Kubernetes empowers you to achieve more Focus on your containers and code, not the plumbing of them
- 10. Get started easily > az aks create > az aks install-cli > az aks get-credentials > kubectl get nodes Azure makes Kubernetes easy
- 11. Manage an AKS cluster > az aks list az aks upgrade az aks scale Azure makes Kubernetes easy
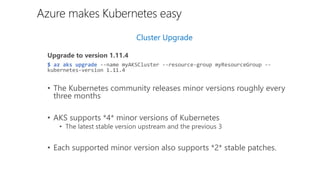
- 12. Cluster Upgrade Upgrade to version 1.11.4 $ az aks upgrade --name myAKSCluster --resource-group myResourceGroup -- kubernetes-version 1.11.4 • The Kubernetes community releases minor versions roughly every three months • AKS supports *4* minor versions of Kubernetes • The latest stable version upstream and the previous 3 • Each supported minor version also supports *2* stable patches. Azure makes Kubernetes easy
- 13. Azure Devops for K8s
- 14. Database tier AKS production cluster Inner loop Test Debug Azure DevSpaces AKS dev cluster Azure Container Registry Azure Pipelines/ DevOps Project Auto-build Business tier Web tier Azure Monitor CI/CD Helm chart Source code control
- 15. Work how you want with opensource tools and APIs Development DevOps Monitoring Networking Storage Security Take advantage of services and tools in the Kubernetes ecosystem Leverage 100+ turn-key Azure services VS Code DevOps ARM Azure VNET Azure Storage Container Registry Azure Active Directory Key Vault Azure Monitor CNAB Virtual kubelet Azure Policy
- 16. Accelerate containerized development Kubernetes and DevOps better together Develop • Native containers and Kubernetes support in IDE • Remote debugging and iteration for multi- containers • Effective code merge • Automatic containerization Deliver • CI/CD pipeline with automated tasks in a few clicks • Pre-configured canary deployment strategy • In depth build and delivery process review and integration testing • Private registry with Helm support Operate • Out-of-box control plane telemetry, log aggregation, and container health • Declarative resource management • Auto scaling Inner loop Test Debug Azure DevSpaces AKS dev cluster Azure Pipelines Source code control Azure Container Registry Helm chart Container image AKS production cluster Azure Monitor Scale Terraform Develop Deliver Operate
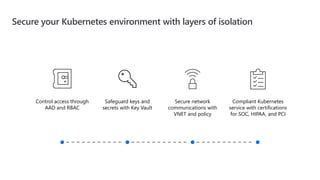
- 17. Secure your Kubernetes environment with layers of isolation Safeguard keys and secrets with Key Vault Secure network communications with VNET and policy Control access through AAD and RBAC Compliant Kubernetes service with certifications for SOC, HIPAA, and PCI
- 18. Scale applications on the fly Built-in auto scaling Global data center to boost performance and reach Geo-replicated container registry for low latency image serving Elastically burst from AKS cluster using ACI
- 19. Microsoft innovations on K8s
- 20. * August, 2018 bi-annual CNCF survey Microsoft drives community-led innovations for Kubernetes 68% 11K
- 21. Virtual Kubelet https://github.com/virtual-kubelet/virtual-kubelet It allows Kubernetes Nodes to be backed by other services, such as serverless container platforms.
- 22. VM Pods VM Pods VM Pods VM Pods Kubernetes control pane Azure Container Instances (ACI) Pods ACI Connector Application Architect Infrastructure Architect Deployment/t asks Bursting with the ACI Connector/ Virtual Kubelet
- 23. Run anything, anywhere Your choice of… Container Linux Windows Environment IoT Edge Public cloud Azure Stack Azure Government (coming soon) Region 20+ regions worldwide
- 24. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) support for Windows Server Containers • Lift and shift Windows applications to run on AKS • Seamlessly manage Windows and Linux applications through a single unified API • Mix Windows and Linux applications in the same Kubernetes cluster—with consistent monitoring experience and deployment pipelines Now you can get the best of managed Kubernetes for all your workloads whether they’re in Windows, Linux, or both
- 25. Kubernetes is built and maintained by the community 30,000 contributors 150,000 commits #1 GitHub project Kubernetes collects wisdom, code, and efforts from hundreds of corporate contributors and thousands of individual contributors Microsoft is part of this vibrant community and leads in the associated committees to help shape the future of Kubernetes and its ecosystem CNCF platinum member CNCF technical oversight committee CNCF governing board Kubernetes steering committee Linux Foundation board member AKS is certified Kubernetes conformant, ensuring portability and interoperability of your container workloads
- 26. Packaging & distribution Scalability & control Kubernetes developer tooling Helm CNAB Virtual Kubelet Open Policy Agent Draft Brigade VS Code Kubernetes Extensions Duffle Containerd KEDA Service Mesh Interface Microsoft contributions to the community
- 27. Microsoft contributions to the community Top code contributor to Windows support in Kubernetes 68% of Kubernetes users prefer Helm 55,000 monthly downloads of Helm 1of 3 top corporate contributors 3x growth of employee contributors within three years Created the Illustrated Children’s Guide to Kubernetes, now part of CNCF
- 28. Top scenarios for Kubernetes on Azure Cost saving without refactoring your app Lift and shift to containers Performance Low latency processing Machine learning Portability Build once, run anywhere IoT Agility Faster application development Microservices Automation Deliver code faster and securely at scale Secure DevOps
- 29. AKS cluster Dev Spaces 1. The “Integration” dev space is running a full baseline version of the entire application 2. John and Sanjay are collaborating on FeatureX; it is setup as a dev space and running all the modified services required to implement a feature 3. Code is committed to the master source control 4. A CI/CD pipeline can be triggered to deploy into “Integration,” which updates the team's baseline Sanjay John Lisa John namespace Sanjay namespace Lisa namespace FeatureX namespace Integration namespace Production namespace Dev Spaces enabled git commit git push Container registry helm upgrade --install values.test.yaml helm upgrade --install values.prod.yaml 'up' or F5 debug values.dev.yaml 5. The same Helm assets used during development are used in later environments by the CD system Dev Spaces is enabled per Kubernetes namespaces and can be defined as anything. Any namespace in which Dev Spaces is NOT enabled runs *unaffected*. CI/CD pipeline Source control
- 30. Open-source component jointly built by Microsoft and RedHat • Event-driven container creation & scaling Allows containers to “scale to zero” until an event comes in, which will then create the container and process the event, resulting in more efficient utilization and reduced costs • Native triggers support Containers can consume events directly from the event source, instead of routing events through HTTP • Can be used in any Kubernetes service This includes in the cloud (e.g., AKS, EKS, GKE, etc.) or on-premises with OpenShift—any Kubernetes workload that requires scaling by events instead of traditional CPU or memory scaling can leverage this component. Kubernetes-based event-driven auto-scaling (KEDA) Kubernetes cluster External trigger source KEDA AKS cluster Scaler Controller Metrics adapter
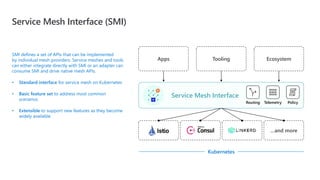
- 31. SMI defines a set of APIs that can be implemented by individual mesh providers. Service meshes and tools can either integrate directly with SMI or an adapter can consume SMI and drive native mesh APIs. • Standard interface for service mesh on Kubernetes • Basic feature set to address most common scenarios • Extensible to support new features as they become widely available Service Mesh Interface (SMI) Apps Tooling Ecosystem …and more Service Mesh Interface Routing Telemetry Policy Kubernetes
- 32. Announcing Dapr • Open source, portable, event-driven runtime helps to build resilient, microservice stateless and stateful applications that run on the cloud and edge • Embraces the diversity of all programming languages & frameworks • Accessed by standard HTTP or gRPC APIs • Agnostic -> you can run your applications locally, on any Kubernetes cluster, and other hosting environments that Dapr integrates with. https://dapr.io/ An event-driven, portable runtime for building microservices on cloud and edge.
- 33. Announcing OAM (Rudr) - allow users to deploy and manage applications easily on any Kubernetes cluster with separation of concerns of application developer and operator. https://openappmodel.io/ THE OAM WAY A New Application Model 1.Manage your apps like you manage your teams - with roles and scopes for apps, free of infrastructure. 2.An opinionated workflow that separates the concerns of App developers, App operators, and Infra Operator 3.Runs anywhere - a unified approach that works across cloud platforms and edge devices.
- 34. Additional references, 1. aka.ms/LearnKubernetes 2. https://github.com/virtual-kubelet/virtual-kubelet 3. https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/virtual-nodes-portal 4. https://openappmodel.io/ 5. https://dapr.io 6. https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/resources/kubernetes-up-and- running/ 7. https://aksworkshop.io/
- 35. Key Takeaways 1) Azure Dev spaces-> a private share on the K8s cluster for dev and testing. Kind of isolation for each dev without jumping into others work 2) Tooling and flexibility-> integrated with Azure services, tools like VSCode, AAD, ACR, Visual Studio 3) Offer first-of-its serverless k8s (Virtual Kubelet) - Unique project by MS, donated to CNCF. Helps to handle sudden spike in the load by bursting ACI's. We called it as “AKS – Virtual Nodes” 4) Azure DevOps Project- fully functional CI/CD for k8s in few clicks 5) Mixing Windows and Linux nodes on AKS 6) MS leading numerous K8s related projects like Draft, Helm, Brigade, CNAB and Virtual Kubelet 7) Dapr & OAM - new announcements. Microsoft is the #4 contributor to the core Kubernetes project 8) SMI - https://smi-spec.io/ - Service Mesh Interface is a specification that covers the most common service mesh capabilities. KEDA - https://github.com/kedacore/keda (Kubernetes-based Event Driven Autoscaling) 9) Fully managed environment, AKS is a 100% upstream, Enterprise grade support, Most comprehensive set of compliance offerings of any cloud service provider 10) Azure Arc – preview (ignite announcement)
- 36. Demo – Azure Virtual Node (refer recording)
- 37. MahesKBlr
Editor's Notes
- #8: Kubernetes is made of a central manager (aka master) and some worker nodes. Master is the Control plane and is responsible to keep the Kubernetes cluster running The manager runs an API server, a scheduler, various controllers and a storage system to keep the state of the cluster, container settings, and the networking configuration.
- #9: A Kubernetes cluster is typically made up of Master nodes for system components like the API server, etcd store, and scheduler Agent nodes for user container workloads Managing the cluster involves: Monitoring the API server Ensuring HA/DR for the etcd store Safely managing upgrades across Kubernetes versions Safely scaling the cluster in and out Patching master and agent VM nodes And on and on… This is complex, error-prone, and expensive A managed service like AKS moves those tasks to the cloud provider