LEADERSHIP TRAINING-rappy.pptx
- 1. 21ST CENTURY LEADERSHIP Rappy R. Pejo
- 2. TRAINING AGREEMENTS Be open Show respect Listen to each other One person speaks at a time Silence Cell Phones Participate Share experiences Keep discussion confidential Give feedback in writing
- 4. A leader is one who is followed by others willingly.
- 8. What is leadership? • All leadership has a spiritual context. • By their IDEAS and DEEDS, leaders show the way and influence the behavior of others.
- 9. What is leadership? • Leadership is not magnetic personality. It’s NOT “making friends and influencing people-that is flattery” • Leadership is lifting a person’s vision to a higher standard, the building of personality beyond normal limitations.
- 10. What is leadership? Leadership is getting people do what you want them to do because…. THEY WANT TO.
- 13. • Leaders are responsible for the effectiveness of organizations. • Leaders provide anchors in our lives. • Leaders define cultural and institutional integrity.
- 14. 3 Types of Leaders Teacher Hero Ruler
- 15. 3 Types of Leaders 1. Teachers: -willing to break the rules while following their value code.
- 16. 3 Types of Leaders 2. Heroes -devoted to great causes and noble works.
- 17. 3 Types of Leaders 3. Rulers -motivated to use power to dominate others.
- 18. Leadership Styles: Different approaches for different situations
- 37. “If your actions inspire others to dream more, learn more, do more and become more, then you are a leader.” John Quincy Adams, 6th U.S. President
- 40. When do leaders learn to lead? Experience Example Education
- 41. Can leadership be taught? Definitely yes!
- 42. When do leaders learn to lead? • Learn new responsibilities and risks • Learn to build consensus and trust among groups Everyone can:
- 43. When do leaders learn to lead? • Learn to develop vision for the future • Learn to better communicate that vision Everyone can:
- 44. Not reaching your GOAL is NOT A TRAGEDY -Benjamin Mays
- 45. What is TRAGEDY? NOT HAVING A GOAL
- 46. Vital Requirements of Leaders • Define the mission • Articulate the mission • Empower followers • Empower the enemy • Keep the hope alive
- 47. Enemies of Leadership • Not willing to risk • Succumbing to fear of failure • Believing that one person cannot make a difference
- 48. 3 Basic Needs in Leadership • AUTONOMY- choice made by YOU, not by others • COMPETENCE- you know what you are doing, and getting better at it. • RELATEDNESS- activities connects you in someway to other people
- 50. What is Emotional Intelligence? The ability to monitor one’s own emotions and emotions of others to discriminate among them and use them to GUIDE one’s thinking and actions.
- 51. Domains of Emotional Intelligence 1. Self-Management -ability to control one’s impulses and be able to suspend judgement -thinking before acting
- 52. Domains of Emotional Intelligence 1. Transparency -ability to be honest and open to the group - Sharing the good and the bad - Welcoming feedback from team members
- 53. Think Before You Act Dot Puzzle
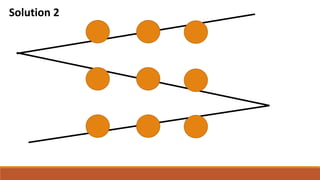
- 54. Connect all the dots by drawing a line (unbroken) with a maximum of 4 strokes
- 56. Solution 1
- 57. Solution 2
- 59. Gather your team in a circle, and have them sit down. Each team member should then put on a provided blindfold. Taking a long rope with its ends tied together, place the rope in each person’s hands so that they all have a hold of it. Leave the circle. Instruct them to form a perfect square out of the rope without removing their blindfolds. Once the team believes they have formed a square, they can remove the blindfolds and see what they’ve accomplished.
- 60. Purpose: This exercise deals with both communication and leadership styles. There will inevitably be team who want to take charge, and others who want to be direction. The team will have to work together to create the square, and find a way to communicate without able to see. By introducing the “muting” feature, you inject the question of trust. Since instructions can’t be vocally verified, the team member calling out has to trust those who cannot talk to do as they are
- 61. What is A Leader? “Leadership at its core, is a very simple process of thinking well or thinking clearly about the situation facing them” »Sean Ruth
- 62. LEADERSHIP STYLE Your style describes HOW you lead. There are many different leadership styles. No one style is correct for all situations. A Leadership Style refers to a leader’s way of providing direction, implementing plans, and motivating people.
- 63. Know how to use the correct leadership style for a given situation. Help individuals recognize and maximize their full potential as team members. Energize and engage people by helping them create a meaningful sense of purpose and direction in their work.
- 65. Definitions: LEADER: A person who has commanding influence (power). FACILITATE: To make easy or possible.
- 66. A Facilitative Leader: Facilitative Leaders: Empower others to work together and achieve common goals through relationships, processes and outcomes. They make it easier for people to: •Think, understand, & communicate their thoughts • Work with others and focus on group goals and outcomes
- 67. A Facilitative Leader: •Speak up when there are challenges •Make and carry out decisions •Allow members to develop their own leadership potential •Achieve high quality results through the group’s abilities
- 68. Leadership Is About Having A Vision
- 69. Leadership Is About Inspiring Trust
- 70. Leadership Is About Seeing Possibilities
- 71. Perspective Rectangles Exercise How many rectangles do you see?
- 72. Leadership Is About Seeking New Strategies
- 73. Leadership Is About Quality Communication
- 75. Facilitative Leaders Focus On: SETTING DIRECTION INSPIRING COMMITMENT BUILDING CAPACITY (SKILLS & KNOWLEDGE)
- 76. Facilitative Leaders Practices: Set Direction Share an Inspiring Vision Balance Results, Process and Relationships
- 77. Facilitative Leaders Practices: Inspire Commitment Practice Appropriate Maximum Involvement Create Pathways to Action Facilitate Agreement
- 78. Facilitative Leaders Practices: Build Capacity Coach Others for Success Celebrate Accomplishment
- 79. IMPROVE LISTENING SKILLS 1) Choose to listen 2) Be an effective listener 3) Don’t interrupt unless necessary 4) Listening requires focus. You are paying attention to the story, how it is told, use of language and voice, body language 5) Don’t impose your solutions, you can ask if they are interested.
- 80. **Listening for….** Facts - A true statement that can be proven with evidence. It can be verified. Feelings – Listen for the emotions you hear Values – What core principles or underlying personal driving forces do you hear behind the feelings Adapted from University of Minnesota Extension. NELD North Central 2014 Chicago Workbook. Created by Jody Horntvedt and Toby Spanier
- 81. Encouraging Dialogue vs. Controlling the Conversation Encourages CONFLICT Encourages RESOLUTION CONTROL DIALOGUE
- 82. Supporting DIALOGUE • Ask open ended questions that encourage broad thinking and participation • Use close-ended questions for details • Listen actively • Don’t evaluate • Be comfortable with silence • Be observant of body language • Seek to understand, identify information to resolve conflict • Offer genuine support
- 83. PRACTICE EMPATHY •Recognize emotions in others •Have Fundamental “people skills” •Have awareness of others’ needs/wants •Consider others’ feelings as factors in decision making •Attempt to put yourself in someone else’s shoes to feel & understand the person’s perspective
- 84. PRACTICE ACCEPTANCE ACCEPTANCE IS SIMPLY NON-JUDGMENTAL UNDERSTANDING …NOT AGREEMENT, sanction, compliance, sympathy, encouraging, and the like …is simply seeing something the way it is and saying, “That’s the way it is.”
- 85. How do you measure as a Facilitative Leader?
- 86. Your Development Plan Share an Inspiring Vision: Create and communicate an image of the future and get others engaged in its pursuit. Keep the mission out front. Focus on Results, Process, Relationships: Build a structure for performance and satisfaction that balances what gets done, the way it happens, and how people treat each other. The structure should support continued work when you are gone. Seek Maximum Appropriate Involvement: Leverage the talent & interests of others around you by including them appropriately in the decision making process. Work to increase trust and commitment through engagement. Model Actions that Aid Collaboration: Encourage diversity of opinion and honor individual perspectives. Help team members stay focused on the task at hand through modeling. Design Pathways to Action: Guide others in planning how to solve problems and realize opportunities. Help people see alternatives when executing a plan. Bring out the Best in Others: Coach individuals to do their best. Listen as an ally. Support the expression of others’ ideas. Work to overcome obstacles. Celebrate Accomplishment: Seize the moment to authentically celebrate small successes. Acknowledge individuals and teams for their contributions.
- 87. A Leadership Story: A group of workers and their leaders are set a task of clearing a road through a dense jungle on a remote island to get to the coast where an estuary provides a perfect site for a port.
- 88. The leaders organise the labour into efficient units and monitor the distribution and use of capital assets – progress is excellent.
- 89. The leaders continue to monitor and evaluate progress, making adjustments along the way to ensure the progress is maintained and efficiency increased wherever possible.
- 90. Then, one day amidst all the hustle and bustle and activity, one person climbs up a nearby tree. The person surveys the scene from the top of the tree.
- 91. And shouts down to the assembled group below… •“Wrong Way!” Story adapted from Stephen Covey (2004) “The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People” Simon & Schuster).
- 92. Morale: “Management is doing things right, leadership is doing the right things” (Warren Bennis and Peter Drucker)