Lean Startups Steve Blank Eric Ries
- 1. The Lean Startup Low Burn by Design not Crisis Steve Blank and Eric Ries
- 2. The Economy Before • Cash was readily available • Follow on financing was readily available After • Debt markets are tight • IPO & M&A window closed • VC!s deep pessimism Venture fund returns have been on decline for a decade - no end in sight
- 3. State of Startups • High burn rate • Swing for the fences • Full management teams • Assume customer is known • Assume features are known • Assumes growth is by execution Traditional startups are fighting yesterday’s war
- 4. Top Gun dogfight scene
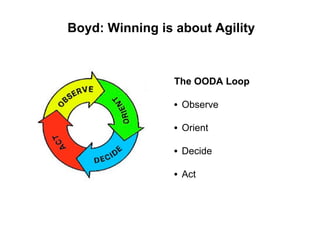
- 6. Boyd: Winning is about Agility The OODA Loop • Observe • Orient • Decide • Act
- 7. Boyd Redefines the Rules to Win • Agility requires a continuous cycle of interactions with the environment • But you can’t do it from a desk
- 8. Winners are Those Who Can Move Faster Than Their Competitors • Winning requires constant assessment of change and ways to mitigate risk • Iterating faster than competitors yields substantial advantage
- 9. Facing Reality at Today’s Startup There is no 2nd Place • Uncertain environment • Rapid, unanticipated changes that lead to disorientation • Constant threats to any initiative • Burn rate (time, fuel, bullets, dollars) limits window of opportunity
- 10. Using OODA to Create “Lean Startups” And Changing the Startup Rules Customer Development Agile Product Development
- 11. Lean Startups Building a New Wave of Companies in Silicon Valley • Continuous customer Customer interaction Development • Revenue goals from day one • No scaling until revenue • Assumes customer and features are unknowns Agile • Low Burn by Design - Not Product Crisis Development
- 12. IMVU
- 13. Founding IMVU • History: - Company founded in April 2004 - Founders audit Steve Blank's B-school class Fall of 2004 • Tactics: - Shipped in 6 months - Charged from Day 1 - No press releases - Ship 20 times a day • Results: - Continuous iteration with customers - 2007 revenues of $10MM • Here's what it looked like to their first venture investors
- 14. IMVU: Q4 2004 • Product 9,000 $8,000 - 3D Instant Messenger (IM) add-on 8,000 hanging out online with friends $7,000 - Piggy-back on existing buddy lists 7,000 $6,000 and IM programs 6,000 • Customer reaction $5,000 - 5,000 Avatar customization is key appeal $4,000 - “Add-on” concept is confusing. They 4,000 actually want a separate buddy list $3,000 3,000 • So we... $2,000 - 2,000 Ditched the IM add-on idea $1,000 1,000 0 $0 Feb-05 Dec-04 Mar-05 Jan-05 Nov-04 May-05 Aug-05 Apr-05 Jul-05 Jun-05
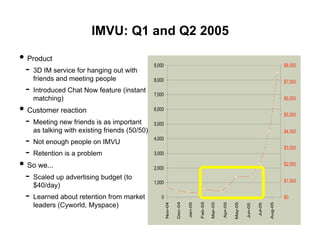
- 15. IMVU: Q1 and Q2 2005 • Product - 9,000 $8,000 3D IM service for hanging out with friends and meeting people 8,000 $7,000 - Introduced Chat Now feature (instant 7,000 matching) $6,000 • Customer reaction 6,000 $5,000 - Meeting new friends is as important 5,000 as talking with existing friends (50/50) $4,000 - 4,000 Not enough people on IMVU $3,000 - Retention is a problem 3,000 • So we... $2,000 2,000 - Scaled up advertising budget (to $1,000 1,000 $40/day) - Learned about retention from market 0 $0 leaders (Cyworld, Myspace) Feb-05 Dec-04 Mar-05 Jan-05 Nov-04 May-05 Aug-05 Apr-05 Jul-05 Jun-05
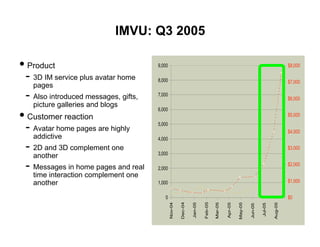
- 16. IMVU: Q3 2005 • Product 9,000 $8,000 - 3D IM service plus avatar home 8,000 $7,000 pages - Also introduced messages, gifts, 7,000 $6,000 picture galleries and blogs 6,000 • Customer reaction $5,000 - Avatar home pages are highly 5,000 $4,000 addictive 4,000 - 2D and 3D complement one $3,000 3,000 another - Messages in home pages and real $2,000 2,000 time interaction complement one $1,000 another 1,000 0 $0 Feb-05 Dec-04 Mar-05 Jan-05 Nov-04 May-05 Aug-05 Apr-05 Jul-05 Jun-05
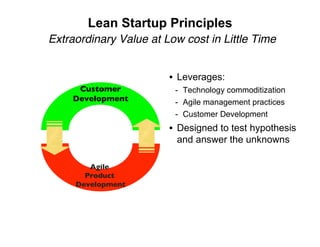
- 17. Lean Startup Principles Extraordinary Value at Low cost in Little Time • Leverages: Customer - Technology commoditization Development - Agile management practices - Customer Development • Designed to test hypothesis and answer the unknowns Agile Product Development
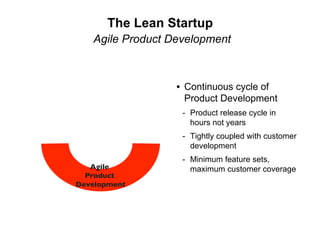
- 18. The Lean Startup Agile Product Development • Continuous cycle of Product Development - Product release cycle in hours not years - Tightly coupled with customer development - Minimum feature sets, Agile maximum customer coverage Product Development
- 19. What has changed? Technology Lean Startups Leverage Commoditized Technology Licensed Software/ Open Source/ Proprietary Hardware Commodity Technology
- 20. Product Development a la Microsoft Unit of progress: Advance to Next Stage Waterfall Problem: known Solution: known
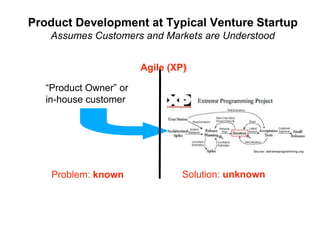
- 21. Product Development at Typical Venture Startup Assumes Customers and Markets are Understood Agile (XP)! “Product Owner” or in-house customer Solution: unknown Problem: known
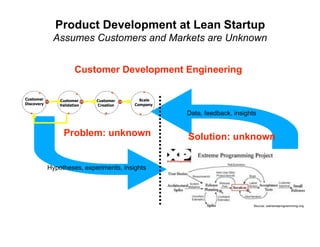
- 22. Product Development at Lean Startup Assumes Customers and Markets are Unknown Customer Development Engineering Customer Scale Customer Customer Discovery Company Validation Creation Data, feedback, insights Problem: unknown Solution: unknown Hypotheses, experiments, insights
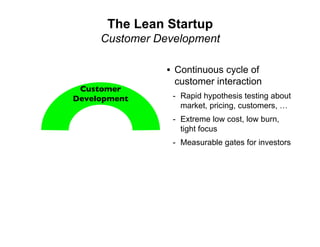
- 23. The Lean Startup Customer Development • Continuous cycle of customer interaction Customer - Rapid hypothesis testing about Development market, pricing, customers, … - Extreme low cost, low burn, tight focus - Measurable gates for investors
- 24. The Lean Startup Customer Development Parallels Agile Development Agile Development Concept / Continuous Agile Continuous Business Plan Test Development Ship Customer Development Customer Company Customer Customer Discovery Building Validation Creation
- 25. Customer Development Turns Market Risk/Product Fit Hypothesis into Facts Customer Company Customer Customer Discovery Building Validation Creation • Discovery - Test hypotheses I.e. problem and product concept • Validation - Build a repeatable and scalable sales process • Creation - Create end-user demand and fill the sales pipeline • Building - Scale via relentless execution
- 26. Lean Startup Advantages Customer Development • Builds low-burn companies by design - Low cost market risk testing Agile • Organized around learning and Product Development discovery • Right model for current conditions The next wave of capital efficient startups