C- language Lecture 7
- 1. Lecture 7 C Language ENG : HATEM ABD EL-SALAM
- 2. • Structure • Unions • Enums Agenda
- 3. Structure • Structure is a collection of variables of different types under a single name • If you want to store some information about a person: his/her name, citizenship number and salary. You can easily create different variables name, citNo, salary to store these information separately. • However, in the future, you would want to store information about multiple persons. Now, you'd need to create different variables for each information per person: name1, citNo1, salary1, name2, citNo2, salary2. • You can easily visualize how big and messy the code would look. Also, since no relation between the variables (information) would exist, it's going to be a daunting task. • A better approach will be to have a collection of all related information under a single name Person, and use it for every person. Now, the code looks much cleaner, readable and efficient as well.
- 4. Structure (Cont.) • Keyword struct is used for creating a structure. • Note: Don't forget the semicolon }; in the ending line. • We can create the structure for a person as mentioned above as:
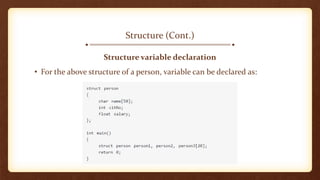
- 5. Structure (Cont.) Structure variable declaration • For the above structure of a person, variable can be declared as:
- 6. Structure (Cont.) Structure variable declaration • Another way of creating a structure variable is:
- 7. Structure (Cont.) Structure variable declaration • In both cases, two variables person1, person2 and an array person3 having 20 elements of type struct person are created. • Note: When a structure is defined, it creates a user-defined type but, no storage or memory is allocated.
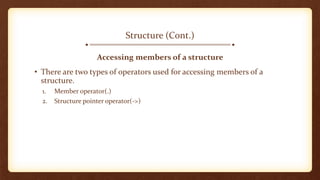
- 8. Structure (Cont.) Accessing members of a structure • There are two types of operators used for accessing members of a structure. 1. Member operator(.) 2. Structure pointer operator(->)
- 9. Structure (Cont.) 1- Member operator(.) • Any member of a structure can be accessed as: • Suppose, we want to access salary for variable person2. Then, it can be accessed as:
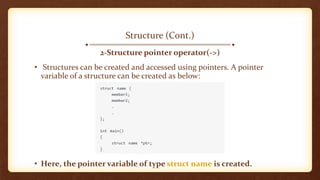
- 11. Structure (Cont.) 2-Structure pointer operator(->) • Structures can be created and accessed using pointers. A pointer variable of a structure can be created as below: • Here, the pointer variable of type struct name is created.
- 12. Structure (Cont.) A structure's member can be accesssed through pointer in two ways: 1. Referencing pointer to another address to access memory 2. Using dynamic memory allocation
- 13. Structure (Cont.) 1- Referencing pointer In this example, the pointer variable of type struct person is referenced to the address of person1. Then, only the structure member through pointer can accessed.
- 14. Structure (Cont.) 1- Referencing pointer Using -> operator • Structure pointer member can also be accessed using -> operator.
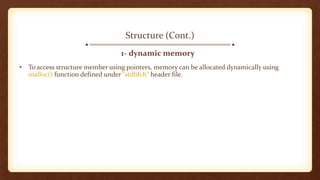
- 15. Structure (Cont.) 1- dynamic memory • To access structure member using pointers, memory can be allocated dynamically using malloc() function defined under "stdlib.h" header file.
- 17. Structure (Cont.) • Structures within structures • Structures can be nested within other structures in C programming. • Suppose, you want to access imag_value for num2 structure variable then, following structure member is used.
- 18. Structure (Cont.) Passing structures to a function There are mainly two ways to pass structures to a function: 1. Passing by value 2. Passing by reference
- 19. Structure (Cont.) Passing by value • A structure variable can be passed to the function as an argument as a normal variable. • If structure is passed by value, changes made to the structure variable inside the function definition does not reflect in the originally passed structure variable.
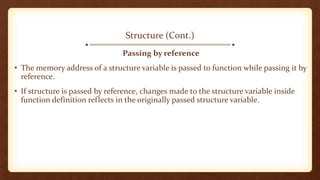
- 21. Structure (Cont.) Passing by reference • The memory address of a structure variable is passed to function while passing it by reference. • If structure is passed by reference, changes made to the structure variable inside function definition reflects in the originally passed structure variable.
- 23. EXERCISES
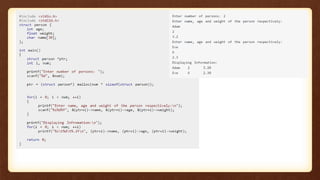
- 24. Exercises • Calculate Difference Between Two Time Period • Store Information of 10 Students Using Structure
- 26. Unions • Unions are quite similar to structures. Like structures, unions are also derived types. • Defining a union is as easy as replacing the keyword struct with the keyword union.
- 27. Unions • Union variables can be created in similar manner as structure variables. OR • In both cases, union variables car1, car2 and union pointer variable car3 of type union car is created.
- 28. Unions Accessing members of a union • Again, the member of unions can be accessed in similar manner as structures. • Using pointer.
- 29. Unions Passing Union To a Function • Union can be passed in similar manner as structures in C programming.
- 30. Unions Difference between union and structure • Though unions are similar to structure in so many ways, the difference between them is crucial to understand • The primary difference can be demonstrated by this example:
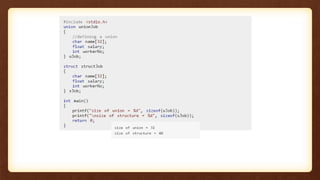
- 32. Unions Difference between union and structure • As seen in the above example, there is a difference in memory allocation between union and structure. • The amount of memory required to store a structure variable is the sum of memory size of all members. • But, the memory required to store a union variable is the memory required for the largest element of an union.
- 33. Unions • only one of its members can be accessed at a time and all other members will contain garbage values.
- 35. Enumeration • An enumeration is a user-defined data type that consists of integral constants. To define an enumeration, keyword enum is used. • Here, name of the enumeration is flag. • And, const1, const2,...., constN are values of type flag. • By default, const1 is 0, const2 is 1 and so on. You can change default values of enum elements during declaration (if necessary).
- 36. Enumeration (Cont.) • When you create an enumerated type, only blueprint for the variable is created. Here's how you can create variables of enum type. • Here, a variable check of type enum boolean is created. • another way to declare same check variable using different syntax
- 37. Enumeration (Cont.) • Changing default values of enum.