Lesson 6 (Other Tissues and Motor Unit).pptx
- 1. OTHER TISSUES AND MOTOR UNIT Lesson 5
- 2. OTHER TISSUES ASSOCIATED WITH BONES, JOINTS AND MUSCLES… Fascia another form of fibrous connective tissue of the body that covers, connects, or supports other tissues a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organ
- 3. FASCIA
- 4. OTHER TISSUES ASSOCIATED WITH BONES, JOINTS AND MUSCLES… Bursa fluid-filled, saclike that functions as a gliding surface to reduce friction between moving tissues of the body a saclike structure that contains bursa fluid and protects muscle, tendon, ligament, and other tissues as they cross the bony prominences
- 6. NORMAL BURSA VS INFLAMED BURSA
- 7. MOTOR UNIT A motor unit is defined as a motor nerve and all the muscle fibers it supplies The structural parts of the motor unit are the motor nerve and the muscle fiber All the motor units together are referred to as the body’s neuromuscular system
- 8. MOTOR UNIT A nerve impulse travels from the spinal cord (or brain) to a dendrite of a spinal nerve, from the dendrite to the nerve’s cell body, and from the cell body over the nerve’s axon to the axon’s end brushes (motor end plate), where a chemical is released as the synapse
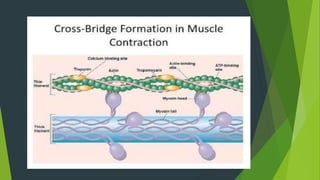
- 10. MOTOR UNIT As the impulse passes from nerve to muscle, calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules within the muscle fibers, two structures closely allied with the actin and myosin protein filaments
- 13. Thank you
Editor's Notes
- The collagen fibers are oriented in a wavy pattern parallel to the direction of pull If ligaments join one bone to bone, tendons join muscle to bone, fascia surround muscles and other structures The fascia from one muscle then connects with the fascia from other muscles, and forms a network of connective tissue that integrates from the top of your head to the tips of your toes
- The fluid inside the bursa looks and feel the same as the egg white
- We have now observed the bones, the ligaments that connect the bones to form articulations, the muscles that cross joints and create movement, the nerves that innervate the muscles and the blood vessels that supply all the these structures.
- The calcium release causes the myosin cross bridges to wiggle or swivel in such a fusion that they contact the actin filaments surrounding them and cause the actin to move toward the center of the sacromere