Levels of strategy
- 1. Levels of Strategy PRESENTED BY: HEMANT KUMAR MBA 3rd sem
- 2. Terms Arrange the following terms in a logical hierarchy: Company Division Strategic Business Unit (SBU) Corporation Industry Value Chain Person Department Market
- 3. Terms Arrange the following terms in a logical hierarchy: Industry Value Chain Company Department Person Corporation Division / SBU Company A market refers to the place where goods and services are exchanged.
- 4. Rumelt's Typology of Diversification 1. Single Product: 95% of revenues from a single product line 2. Dominant Product: 70-94% of revenue from a single product line 3. Related Product: Less than 70% of revenue from a single product line and and the remainder of revenues from a related product domain 4. Unrelated Product: Less than 70% of revenue from a single product and remainder of revenues from an unrelated product domain
- 5. Some Levels of Strategy The Impact of IT on strategy is dramatically different depending on the level of strategy. On what level is your paper? Corporate Business Functional Operational
- 6. Corporate Level Strategy What businesses are we in? What businesses should we be in? Four areas of focus Diversification management (acquisitions and divestitures) Synergy between units Investment priorities Business level strategy approval (but not crafting)
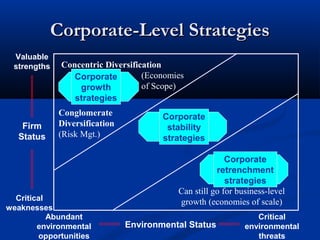
- 7. Corporate-Level Strategies Valuable strengths Firm Status Concentric Diversification (Economies Corporate of Scope) growth strategies Conglomerate Diversification (Risk Mgt.) Critical weaknesses Abundant environmental opportunities Corporate stability strategies Corporate retrenchment strategies Can still go for business-level growth (economies of scale) Environmental Status Critical environmental threats
- 8. The BCG “Portfolio” Matrix Market Share High Stars High Anticipated Growth Cash Cows Rate Low Low Question Marks ? Dogs ? ? ?
- 9. Business Level Strategy How do we support the corporate strategy? How do we compete in a specific business arena? Three types of business level strategies: Low cost producer Differentiator Focus Four areas of focus Generate sustainable competitive advantages Develop and nurture (potentially) valuable capabilities Respond to environmental changes Approval of functional level strategies
- 10. Functional / Operational Level Strategy Functional: How do we support the business level strategy? Operational: How do we support the functional level strategy? An example. Business L.S.: Become the low cost producer of widgets Functional L.S. (Mfg.): Reduce manufacturing costs by 10% Operational (Plant #1): Increase worker productivity by 15%
- 11. A Simple Organization Chart (Single Product Business) Business Level Strategy Research and Manufacturing Development Functional Level Strategy Business Marketing Human Resources Finance
- 12. A Simple Organization Chart (Dominant or Related Product Business) Corporate Level Business Level Multibusiness Corporation Business 1 (Related) Business 2 (Related) Business 3 (Related) Functional Level Research and Manufacturing Development Marketing Human Resources Finance
- 13. An example of an Unrelated Product Business (Note: By itself, an SBU can be considered a related product business) SBU: a single business or collection of related businesses that is independent and formulates its own strategy A (Multi-business) Corporation Strategic Business Unit 1 Company 1 Co. 2 Ex.: G.E. (General Electric Corp.) S.B.U. 2 Co. 3 Division 1 Div. 2 Div. 3
- 14. THANK U