Life process class 10 cbse
- 1. Presented By : Ayushman Tiwari
- 2. It can be defined as the basic functions performed by living organisms in order to maintain their lives on earth. These life processes include nutrition, respiration, circulation, excretion, locomotion, control and coordination etc. The life process, allow a living organism to maintain dynamic equilibrium with its surroundings.
- 3. The sum total of all the chemical reaction occurring in a living organism in order to maintain life is known as metabolism. Metabolism includes two types of reactions :- › Anabolism :- The metabolic synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones is called anabolism. It requires an input of energy Example:- Photosynthesis. › Catabolism :- The metabolic breakdown of complex molecule into the simpler ones with the release of energy is called catabolism. Example :- Respiration, breakdown of protein into amino acid.
- 4. Nutrition is the process of intake and utilization of nutrients by an organism. A nutrient can be defined as a substance which an organism obtains from its surroundings and uses it as a source of energy for biosynthesis of its body constituents. We need nutrition to grow, develop, synthesis protein and to maintain state of order in our body. Life on earth is dependent on food sources that are mostly carbon based. Depending on the complexity of these carbon sources, different organism use different modes of nutrition.
- 5. Living organisms uses different modes of nutrition to fulfill their requirements of nutrients based upon these different modes of nutrition, they can be classified as : › Autotrophs :- The organisms which synthesize their own food in the presence of sunlight from inorganic substances are called Autotrophs. › Heterotrophs :- The organisms which cannot synthesize their own food and are dependent on autotrophs or others are called Heterotrophs.
- 6. It is the characteristic of plants and algae which prepared their food by the process of photosynthesis. It is the process by which plant cells containing chlorophyll produce food substances like glucose from carbon dioxide and water, by using light energy. The release oxygen as a byproduct in this process.
- 7. It is the process by which green plants prepare their own food. › During this process, the solar energy is converted into chemical energy and carbohydrates are formed. › Green leaves are the main site of photosynthesis. › The green portion of plants contains chloroplasts, chlorophyll. › The whole process of photosynthesis can be shown by the following equation › 6CO2 + 12H2O ------ C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
- 8. Sunlight Chlorophyll CO2 Water How do the raw material become available to plant (1)Water comes from soil, through xylem tissue in roots and stems. (2)Carbon dioxide comes in the leaves through stomata
- 9. Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll. Conversion of light energy into chemical energy + splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen. Reduction of Carbon dioxide to carbohydrates. Sunlight activates chlorophyll, which leads to splitting of the water molecule. The hydrogen, released by the splitting of water molecule is utilized for the reduction of carbon dioxide. Oxygen is the by-product of photosynthesis Carbohydrate is subsequently converted into starch and is stored in leaves and other storage parts. The splitting of water molecules is a part of light reaction.
- 10. These are tiny pores present in the epidermis of leaf or stem through which gaseous exchange and transpiration occurs. Function of stomata :- › Exchange of gases, O2 and CO2. › Loses a large amount of water (water vapors) during transpiration.
- 12. The opening and closing of stomatal pores are controlled by the turgidity of guard cells. When guard cells uptake water from surrounding cells, they swell to become a turgid body, which enlarges the pore in between (stomatal opening) While, when water is released, they become flaccid shrinking to close the pore (stomatal closing)
- 13. Photosynthesis is the main way through which solar energy is made available for different living beings Green plants are the main producers of food in the ecosystem. All other organisms directly or indirectly depends on green plants for food. The process of photosynthesis also helps in maintaining the balance of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the air.
- 14. Some organism feed on dead and decaying organic matter. This mode of nutrition is called saprophytic nutrition. The food is partially digested outside the body and then it is absorbed. E.g. Fungi are saprophytes.
- 15. Some organisms feed on the expense of another organism and in turn causing it harm. This is called parasitic mode of nutrition. These organisms live on the body or in the body of a host organism and derive the nutrients directly from the body of the host. E.g. Leech is an ectoparasite while Ascaris is an endoparasite. Cuscuta is a parasitic plant.
- 16. Amoeba feeds by holozoic mode of nutrition. It engulfs the food particle using pseudopodia, the process is called phagocytosis. The engulfed food gets enclosed in a food vacuole. As the food vacuole passes through the cytoplasm, digestion, absorption and assimilation take place. When the food vacuole opens to outside, egestion of undigested food takes place.
- 18. › Paramoecium also exhibits holozoic nutrition. › However, they have cilia that help them to engulf the food through the oral groove. › A food vacuole is created enclosing the food. › It moves through the cytoplasm, the process is called cyclosis. › Food digested in the food vacuole is absorbed by the cytoplasm. › Undigested food is given out to a tiny pore called anal pore or cytopyge.
- 20. Humans are omnivores, they can eat plant-based food as well as animal-based food. Being more complex, humans have a very complicated nutrition system. The digestive system has an alimentary canal and associated digestive glands, which together function to nourish the body. There are five stages in human nutrition; Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Assimilation and Egestion. Four stages i.e. ingestion, digestion, absorption and egestion take place in the alimentary canal while assimilation of food takes place in the whole body.
- 21. Alimentary canal in humans is a long tube of varying diameter. It starts with the mouth and ends with the anus. Oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine are the parts of the alimentary canal.
- 22. It is the opening of the alimentary canal and helps in ingestion of food. The buccal cavity which is present behind the mouth is also commonly referred to as the mouth. The buccal cavity has teeth and tongue. The set of teeth helps in the mastication of food. The tongue has taste buds on it and thus helps in tasting the food. The salivary glands open also in the buccal cavity and pour saliva which initiates the process of digestion.
- 23. Teeth are the hard structures present in the buccal cavity. They help us to cut, shear and masticate the food we eat. Vertical section of a tooth shows four layers as enamel, dentine, cement and dental pulp. Enamel is outermost, shiny, highly mineralized and hardest part of the human body. Dentine makes the bulk of the tooth and contains 70% inorganic salts. Cement is present at the lining of a tooth and bony socket. The dental pulp is the central soft part of a tooth and contains nerve endings, blood and lymph vessels along with connective tissue. There are four types of teeth in humans, Incisors, canines, molars and premolars, each with a specific function. Incisors cut the food, canines tear the food while molars and premolars crush it. The dental formula in adult humans is 2:1:2:3.
- 25. The swallowed food passes into the oesophagus. It is a muscular tube, about 25 cm long, with a sphincter (valve/opening) at each end. Its function is to transport food and fluid, after being swallowed, from the mouth to the stomach. Food is pushed down by peristaltic movements.
- 26. The stomach is a thick-walled bag-like structure. Its receives food from the oesophagus at one end and opens into the small intestine at the other end. The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucous, hydrochloric acid and digestive juices. Food is churned into a semi-solid mass in the stomach and is called chyme. Enzymes present in the gastric juice break down the food. Hydrochloric acid helps in partial digestion of proteins and also kills harmful bacteria. Mucus secreted by the wall of the stomach resists the action of HCl on itself.
- 27. The small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal, about 20 feet long in humans. It has regions, duodenum, the region which follows stomach, jejunum is the middle part and ileum is the later region which continues further into the large intestine. The internal surface of the small intestine is folded into finger-like projections called villi. A common pancreatic duct from pancreas and liver opens into the duodenum. Most of the chemical digestion and absorption takes place in the small intestine.
- 28. The large intestine in humans is about 5 feet long. It has two regions, colon ( about 1.5 m) and rectum (10 cm in length in the adult). The region of large intestine after ileum is called colon while the last part is called the rectum. Colon has three regions as, ascending colon, transverse colon and descending colon. At the base of the ascending colon, a small finger-like out-growth is seen and is called an appendix. It houses many useful bacteria required for digestion of food. Rectum opens to outside by anus. The anus has internal and external anal sphincters.
- 30. A constant wave-like movement of the alimentary canal right from the oesophagus to the small intestine is called as peristalsis. Muscles present in the wall of the alimentary canal are responsible for peristalsis. This movement helps to push the food through the alimentary canal.
- 31. Several glands produce digestive juices that help in digestion of the food. Salivary glands, Gastric glands, Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas are few to name. Salivary glands secrete saliva which initiates digestion in the mouth itself. Gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach secrete hydrochloric acid and enzyme pepsin. The liver secretes bile which is stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps in digestion of fats. The pancreas secretes many digestive enzymes and its secretion is called as pancreatic juice. Enzymes like trypsin, chymotrypsin, lipase, amylase are present in the pancreatic juice.
- 32. The pancreas is a long, flat gland present behind the stomach in humans. It is one of the major digestive glands and is of mixed nature i.e. endocrine as well as exocrine. As an endocrine organ, it secretes two hormones called insulin and glucagon which maintain the blood sugar level. As an exocrine gland, it secretes pancreatic juice which is nothing but a mixture of many digestive enzymes. The digestive enzymes secreted by the pancreas include trypsin and chymotrypsin and proteases which digest proteins. It also includes amylase which digests the starch content of the food. Pancreatic lipases are the pancreatic enzymes that help in digestion of fats.
- 34. The mode of nutrition in which animals take their food as a whole is called as holozoic nutrition. In holozoic nutrition, food passes through five steps as ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion.
- 35. Mechanical digestion of food takes place in the buccal cavity where teeth masticate the food, saliva gets mixed and it turns into a bolus. Digestion of starch starts in the buccal cavity itself, with the action of salivary amylase present in the saliva. Salivary amylase converts starch into maltose. In the stomach, the churning of food takes place due to the muscular contraction and relaxation of its wall. It breaks down the food into simpler substances. Digestion of proteins starts in the stomach with the action of pepsin. Proteins are broken down into smaller fragments called peptide by the action of pepsin. The bolus after mixing with gastric juice, turn into a fine soluble form known as the chyme. Chyme enters into the small intestine where complete digestion takes place due to the action of various enzymes present in the pancreatic juice, bile and intestinal juice. The digested food is completely absorbed by the villi and microvilli of the small intestine. Undigested food then enters into the large intestine. The colon is responsible for absorption of water and salts whereas rectum stores the undigested food temporarily before defaecation.
- 36. Digestive systems in different animals vary in structure and function. The structure of the digestive system depends on the food habits of the animal. Alimentary canal in herbivores is long as the cellulose content of their plant-based diet takes a long time to digest. On the other hand, the alimentary canal of carnivorous animals is comparatively shorter because meat gets digested faster.
- 37. The alimentary canal in humans is approximately 30 feet (9m) long. It starts with the mouth and ends in the anus. Between these two openings, the alimentary canal is the tube of varying diameter. Oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (divided into three regions as duodenum, jejunum and ileum) and large intestine(having two regions as colon and rectum) are the parts of the alimentary canal. Salivary glands, pancreas and liver act as major digestive glands. Glands present in the wall of the stomach and small intestine also contribute towards digestion of food.
- 38. Hydrochloric acid in the stomach is secreted by the gastric glands present in its wall. pH of the gastric acid is usually between 1.5 to 3.5 This acid serves the following functions: › Converts inactive pepsinogen and pro-rennin into active pepsin and rennin respectively. › Provides acidic medium for protein digestion. › Kills bacteria entered through food and prevents infection. › Prevents putrefaction of food in the stomach. A thick layer of mucus secreted by the mucous glands of the stomach prevent itself from the action of the gastric acid. Excess acid damages gastric mucosa and causes gastric and duodenal ulcers.
- 39. Salivary glands are the exocrine glands that secrete saliva and through a system of ducts, it is poured into the mouth. In humans, three major pairs of salivary glands are present, parotid, submandibular and sublingual. In healthy individuals between 0.5 to 1.5 litres of saliva is produced per day. Saliva serves the following functions in the oral cavity. › It lubricates and protects the soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity › It also gives protection from dental caries › Saliva prevents microbial growth in the oral cavity. › Saliva can encourage soft tissue repair by decreasing clotting time and increasing wound contraction › Saliva contains the enzyme amylase that hydrolyses starch into maltose and dextrin. Hence saliva allows digestion to occur before the food reaches the stomach › Saliva acts as a solvent in which solid particles can dissolve in and enter the taste buds located on the tongue.
- 41. When an organism depends on others for food, such a mode of nutrition is called as a heterotrophic mode of nutrition. These organisms depend on autotrophs for their nutritional requirements. E.g. Animals which eat plants as their food are called herbivores. Animals which eat other animals as their food are called carnivores. Holozoic, saprophytic and parasitic nutrition are all types of heterotrophic nutrition.
- 42. Many small glands present in the inner layer of the stomach and intestine take part in the digestion of food. These glands are present in the epithelial lining of the stomach and intestine. The glands present in different regions of the stomach are called gastric glands. They are responsible for the secretion of mucus, hydrochloric acid and enzymes like pepsinogen. The glands present in the epithelial lining of the small intestine and large intestine are called intestinal glands. Glands of the small intestine are responsible for the secretion of intestinal juice also called succus entericus. Intestinal juice contains hormones, digestive enzymes, alkaline mucus, substances to neutralize hydrochloric acid coming from the stomach. Intestinal juice completes the digestion started by the pancreatic juice. Glands of the large intestine are associated with absorption of water and electrolytes.
- 43. Complete digestion and absorption of food take place in the small intestine. Pancreatic juice coming from the pancreas, bile from the liver and intestinal juice secreted by the intestinal glands complete the digestion of food material. All the digested nutrients are absorbed by the long finger-like projections present in the ileum of the small intestine. These small finger-like projections of the inner wall of intestine are called as villi (singular: villus). Each villus has its cell membrane of the lumen side again folded into microscopic processes, called microvilli. Villi increase the internal surface area of the intestinal walls making available a greater surface area for absorption. Digested nutrients pass into the semipermeable villi through diffusion. Villi also help in chemical digestion of food by secreting digestive enzymes.
- 45. The liver is the largest and major digestive gland of humans Liver, in humans, is located in the upper right-hand portion of the abdomen. This organ is dark reddish-brown in colour due to an extensive blood supply. Some of the important functions of the liver are as follows: › It secretes bile that helps in digestion. › It filters the blood coming from the digestive tract before passing it to the rest of the body. › It detoxifies various metabolites and drugs › The liver makes proteins important for blood clotting and other functions. › It stores and releases glucose as needed. › It processes haemoglobin, from the dead and worn out RBCs, for the iron content (the liver stores iron). › Conversion of harmful ammonia to urea takes place in the liver.
- 46. Pancreatic juice, bile and intestinal juice (succus entericus) are collectively called as digestive juices. A common duct from digestive glands pours the secretions into the duodenum. Chyme enters into the small intestine where complete digestion takes place due to the action of various enzymes. In the duodenum, the acidity of chyme is turned to alkalinity by the action of bile coming from the liver. This is necessary for pancreatic enzyme action. Bile also emulsifies the fats into smaller globules. Pancreatic and intestinal amylases break down the carbohydrates into glucose. Trypsin and chymotrypsin are the proteases responsible for the breakdown of proteins finally into amino acids. Lipase is the enzyme which acts on the emulsified fats and breaks them down into glycerol and fatty acids.
- 47. The large intestine is not involved in the digestion of food or absorption of nutrients. The major function of the large intestine is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter and make the stool solid. The large intestine also helps in absorption of vitamins made by bacteria that normally live in the large intestine. The innermost layer of the large intestine also acts as a barrier and protects from microbial infections and invasions. Rectum stores the undigested food temporarily until defaecation.
- 48. Introduction to Respiration › Respiration broadly means the exchange of gases. › Animals and plants have different means of exchange of gases. › At a cellular level, respiration means the burning of the food at the for generating the energy needed for other life processes. › Cellular respiration may take place in the presence or absence of oxygen.
- 50. The human respiratory system involves the nose, nasal cavities, pharynx, larynx, trachea/windpipe, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli. Bronchioles and alveoli are enclosed in a pair of lungs. The rib cage, muscles associated with the rib cage and diaphragm, all help in inhalation and exhalation of gases. Exchange of gases takes place between an alveolar surface and surrounding blood vessels. Alveoli provide a large surface area for exchange of gases.
- 51. Breathing in humans is facilitated by the action of internal intercostal and external intercostal muscles attached to the ribs and the diaphragm. When the dome-shaped diaphragm contracts and becomes flattened and the rib cage is expanded due to the action of intercostal muscles, the volume of the lungs increases, pressure there drops down and the air from outside gushes in. This is inhalation. To exhale, the diaphragm relaxes, becomes dome-shaped again, chest cavity contracts due to the action of intercostal muscles, the volume inside the lungs decreases, pressure increases and the air is forced out of the lungs. Inhaled air increases the concentration of oxygen in the alveoli, so oxygen simply diffuses into the surrounding blood vessels. Blood coming from cells has more concentration of carbon dioxide than outside air and thus carbon dioxide simply diffuses out of the blood vessels into the alveoli. Thus, breathing takes place due to the combined action of intercostal muscles and diaphragm while the exchange of gases takes place due to simple diffusion.
- 53. The process of taking in air rich in oxygen is called inhalation. Similarly, the process of giving out air rich in carbon dioxide is called exhalation. One breath comprises one inhalation and one exhalation. A person breathes several times in a day. The number of times a person breathes in one minute is termed as his/her breathing rate.
- 54. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from high concentration area to the low concentration area without spending any energy.
- 56. Cellular respiration is set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). › Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. These can be divided into two categories: › Catabolism – the process of breaking molecules to obtain energy. › Anabolism – the process of synthesizing all compounds required by the cells. › Therefore, respiration is a catabolic process, which breaks large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy to fuel cellular activities. › Glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport chain are the important processes of the cellular respiration.
- 58. Aerobic respiration is a process in which the food i.e. glucose is converted into energy in the presence of oxygen. › The general equation of aerobic respiration as a whole is as given below- › Glucose + oxygen ⇒Carbon-dioxide + Water + Energy › This type of respiration takes place in animals, plants and other living organisms.
- 59. Lower animals lack a sophisticated respiratory system like lungs, alveoli etc. Respiration in them takes place by simple exchange mechanisms. Animals like earthworms take in gases through their skin. Fishes have gills for gaseous exchange. Insects have a tracheal system, which is a network of tubes, through which air circulates and gaseous exchange takes place. Frogs breathe through their skin when in water and through their lungs when on land.
- 60. Respiration in muscles can be anaerobic when there is not enough oxygen. Glucose gets broken down to carbon dioxide and lactic acid. This results in the accumulation of lactic acid that makes the muscles sore. This type of anaerobic respiration is also known as lactic acid fermentation.
- 61. It is the energy currency of the cell. ATP stands for Adenosine Tri-Phosphate. This molecule is created as a result reaction like photosynthesis, respiration etc. The three phosphate bonds present in the molecule are high energy bonds and when they are broken, a large amount of energy is released. Such released energy is then used for other metabolic reactions.
- 63. Unlike animals and humans, plants do not have any specialized structures for gaseous exchange They have stomata (present in leaves) and lenticels (present in stems) which are involved in the exchange of gases. Compared to animals, plant roots, stems, and leaves respire at a very lower rate.
- 64. Transpiration is a biological process in which water is lost in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plants. This process occurs mainly through the stomata where the exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) occurs. Transpiration helps in the transportation of water from roots to upper parts of plants and this is explained by ‘transpirational pull theory’. Loss of water, especially from leaves, acts as a straw effect and pulls water upwards from roots. Transpiration also acts as an excretory mechanism in plants as it helps to get rid of excess water.
- 65. In unicellular organisms like an amoeba exchange of gases takes place through a general body surface by osmosis. In lower animals like an earthworm, the gaseous exchange takes place through their moist skin. The requirement of oxygen is sufficiently met by these ways. But as the animal starts becoming more and more complex, for example, human, the requirement of oxygen cannot be met alone by diffusion. Moreover, diffusion will not be able to supply oxygen to the deep- seated cells. This difficulty has led to the evolution of a more complex mechanism of gaseous exchange and that is the development of lungs. The alveoli present in the lungs provide a large surface area required for the necessary gas exchange.
- 66. Transportation › All living organisms need a few necessary components like air, water, and food for their survival. › On our regular basis, animals ensure these elements by breathing, drinking and eating. › The required elements are transported to their body cells and tissues by a transportation system. › In plants, the vascular tissue is responsible for transporting the substances.
- 67. Transportation in humans is done by the circulatory system. The circulatory system in humans mainly consists of blood, blood vessels and heart. It is responsible for the supply of oxygen, nutrients, removal of carbon dioxide and other excretory products. It also helps to fight the infections.
- 68. The muscular organ which is located near the chest slightly towards the left in the thoracic region. The heart is the main pumping organ of the body. The human heart is divided into four chambers which are involved in the transportation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. The upper two chambers are called atria whereas the lower two chambers are called as ventricles.
- 71. Blood vessels carry blood throughout the body. There three types of blood vessels; arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood. Gaseous exchange takes place between blood and cells at capillaries.
- 72. Difference between Arteries and Veins
- 74. The pressure exerted by the blood when it flows through the blood vessels is called blood pressure. › There are two different variants of blood pressure; the systolic and the diastolic blood pressure. › The pressure exerted on the walls of arteries when the heart is filling with blood is called diastolic pressure. It constitutes the minimum pressure on arteries. › The normal range of diastolic blood pressure should be 60 – 80 mm Hg. › The pressure exerted on the walls of arteries when the heart is pumping the blood is called systolic pressure. It constitutes the maximum pressure applied on the arteries. › The normal range of systolic blood pressure should be 90 – 120 mm Hg.
- 75. Bleeding occurs when the blood vessels rupture. Bleeding is stopped by the platelets that help in the clotting of blood at the site of the injury. Blood Clotting is the process of forming a clot in order to prevent excess loss of blood from the body. It is a gel-like mass which is formed by the platelets and a fibre-like protein in the blood.
- 76. In the human body, blood circulates through the heart twice. Once it goes through the heart during pulmonary circulation and second time during systemic circulation. Hence, circulation in human beings is called double circulation.
- 78. Transportation is a vital process in plants. The process involves the transportation of water and necessary nutrients to all parts of the plant for its survival. Food and water transportation takes place separately in plants. Xylem transports water and phloem transports food.
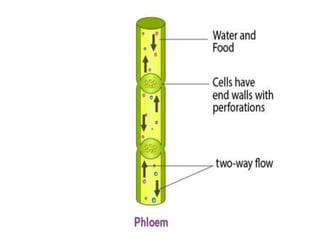
- 80. The phloem is responsible for translocation of nutrients and sugar like carbohydrates, produced by the leaves to areas of the plant that are metabolically active. Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma cells are the components of this tissue The flow of material through phloem is bidirectional.
- 82. Transport of food in the plant through phloem via a process such as mass flow is called as translocation. Photosynthates i.e. sugars and organic molecules such as amino acids, organic acids, proteins and inorganic solutes like potassium, magnesium, nitrate, calcium, sulfur and iron from source tissues (mature leaves) to the sink cells (areas of growth and storage) are transported through the phloem. Material like sucrose is loaded from leaves to phloem using the energy of ATP. Such a transfer increases the osmotic pressure causing movement of water from nearby cells into in phloem tissue and the material gets transported through the phloem. The same pressure is also responsible for the transfer of substances from phloem to tissues where food is required. Thus the bulk flow of material through phloem takes place in response to an osmotically generated pressure difference.
- 84. Xylem tissue transports water in plants from root to all other parts of the plant. Xylem tissue is made up tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma. The flow of water and minerals through xylem is always unidirectional.
- 87. Conduction of water through the xylem, from roots to upper parts of plants, is due to many forces acting together. One of the forces responsible for this is root pressure. Root pressure is osmotic pressure within the cells of a root system that causes sap to rise through a plant stem to the leaves. Root pressure helps in the initial transport of water up the roots.
- 88. Water is absorbed by the roots and is transported by xylem to the upper parts of the plant. Imbibition, osmosis, root pressure and transpiration are the forces that contribute towards the upward movement of water, even in the tallest plants. › Imbibition is a process in which water is absorbed by the solids. E.g. seeds take up water when soaked. › Osmosis is a process where water moves from the area of its lower concentration to the area of its higher concentration. › At the roots, the cells take up ions by an active process and this results in the difference of concentration of these ions. › It leads to movement of water, in the root cells, by osmosis. › This creates a continuous column of water that gets pushed upwards. This is root pressure. › Transpiration contributes to the upward movement of water by creating a staw effect. › It pulls the water column upwards as there is a continuous loss of water from leaves. › All these forces act together for water transport through the xylem
- 89. Excretion › Excretion is the process of removal of metabolic waste material and other non-useful substances. Organisms like animals have an advanced and specialized system for excretion. But plants lack a well-developed excretory system like that in animals. They do not have special organs for excretion and thus excretion in plants is not so complex.
- 90. In unicellular organisms such as amoeba and bacteria, the waste product is removed by simple diffusion through the general body surface. Unicellular organisms like the amoeba, paramecium excrete excess through tiny organelles called contractile vacuoles. Undigested food in unicellular animals is excreted when the food vacuole merges with the general body surface and opens to outside.
- 91. The excretory system in humans includes › a pair of kidneys, › a pair of ureters, › a urinary bladder and › urethra. It produces urine as a waste product.
- 93. Paired kidneys are the main excretory organs of the body. They are basically the filtration units of the human body. Each kidney is made up many tiny filtration units called nephrons. Kidneys perform crucial functions like: › Filtering waste materials, medications, and toxic substances from the blood. › Regulation of osmolarity i.e. fluid balance of the body. › Regulation of ion concentration in the body. › Regulation of pH. › Regulation of extracellular fluid volume. › Secreting hormones that help produce red blood cells, promote bone health, and regulate blood pressure
- 94. Nephrons are the structural and functional unit of kidney. › Each kidney has millions of nephrons and it forms the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. › Each nephron has two parts: Malpighian body and renal tubule. › Malpighian body is made up of cup-like structure called Bowman’s capsule which encloses a bunch of capillaries called glomerulus. › They together filter waste materials along with many useful substances. › Renal tubule has regions called proximal convoluted tubule, Loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule. › These regions absorb back useful substances into the blood and also filter remaining waste substances. › The output from nephrons is called urine.
- 96. › When the kidneys fail, it results in a lot of complications and to compensate this situation a technology called dialysis has been developed. › It uses a machine filter called a dialyzer or artificial kidney. › This is to remove excess water and salt, to balance other electrolytes in the body and remove waste products of metabolism. › Blood from the body is removed and flowed through a series of tubes made up of a semipermeable membrane. › A dialysate flows on the other side of the membrane, which draws impurities through the membrane.
- 98. The cellular respiration, photosynthesis, and other metabolic reactions produce a lot of excretory products in plants. Carbon dioxide, excess water produced during respiration and nitrogenous compounds produced during protein metabolism are the major excretory products in plants. Plants produce two gaseous waste products i.e. oxygen during photosynthesis and carbon dioxide during respiration. Excretion of gaseous waste in plants takes place through stomatal pores on leaves. Oxygen released during photosynthesis is used for respiration while carbon dioxide released during respiration is used for photosynthesis. Excess water is excreted by transpiration. Organic by-products generated by the plant are stored in different forms in different parts. The gums, oils, latex, resins, etc. are some waste products stored in plant parts like barks, stems, leaves, etc. Eventually, plants shed off these parts. Few examples of the excretory products of plants are oil produced from orange, eucalyptus, jasmine, latex from the rubber tree, papaya tree, and gums from acacia. Sometimes plants even excrete into the soil.