LIFE PROCESSES ( Part-1)
- 1. LIFE PROCESSES Class 10 Science ~Shubhika Chenna
- 2. LIFE PROCESSES The processes which maintains body functions and necessary for survival are called life process. • All the processes which together perform tasks to maintain the body and keep the organism alive. • There are seven essential processes in common: movement, respiration, sensitivity, growth, reproduction, excretion and nutrition. • The four main processes are: - -Nutrition -Respiration -Transportation/Circulation -Excretion
- 3. NUTRITION The process of taking nutrients from food is called nutrition. It is a critical part of health and development. Modes of Nutrition: -Autotrophic -Heterotrophic Autotrophic- The organism which produce their own food from simple inorganic material (water and carbon dioxide) in the presence of sunlight. Ex: Plants, algae, bacteria. Heterotrophic- The organism which depends upon another organism to live. Ex: Human beings, Amoeba, Animals.
- 4. NUTRITION IN PLANTS • Photosynthesis- The process in which green plants convert simple inorganic material (water, carbon dioxide) into complex organic material (6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 ) in the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight. • Order of Events: - Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll. - Conversion of light energy into chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into Hydrogen and Oxygen - Reduction of Carbon dioxide into Carbohydrates. • Chloroplasts- These are the small organelles found in plant cell. It contains chlorophyll, which absorb sunlight for photosynthesis.
- 5. HETEROTROPHIC NUTRITION Saprophytes- They obtain food from dead or decaying organic matter. Ex- Bacteria, Fungi etc. Parasitic- They obtain food from another organism without killing them. Ex- Mosquito, Leeches, Ticks, Tice etc. Holozoic- The mode of nutrition which involves ingestion, digestion, absorption and assimilation of liquid or solid organic material. Ex- Animals, Human beings etc.
- 6. NUTRITION IN HUMAN • Mouth- Intake of food • Teeth- Breaks the food • Tongue- Tasting and rolling the food • Glands- Saliva contains enzyme (salivary amylase) that breaks down starch (food) to simple sugar. Oesophagus • Taking food from mouth to stomach by Peristaltic movement. • Stomach is large organ, it expands when food enters it. • Gastric Glands- It releases Gastric Juice which contains ; HCL, Pepsin and Mucus. • HCL- Makes medium acidic kill the harmful bacteria of food. • Pepsin- Breaks down proteins into amino acids. • Mucus- Protects inner lining of stomach.
- 7. Stomach • It is a site of complete digestion. • Liver- It produces Bile Juice and salt. • Bile Juice- It makes the food alkaline (breaks down into simpler). • Bile salt- Breaks the large fat globules. This is called emulsification. • Gall bladder- Stores Bile juice and salt • Pancreas: Tripsin- Break down protein into amino acid. Lipase- It breaks down emulsified fat. Small Intestine • Villi -Finger like projections -Increase in surface area of absorption -Supplies food to blood vessels • Then blood vessels take the food to each cell of the body
- 8. Large Intestine • Unabsorbed food is sent. • Its walls absorb more water from the material. • Rest of the material is removed from the body via Anus. This process starts in the long tube called the Alimentary canal from mouth to anus.
- 9. RESPIRATION The process in which cells of an organism obtains energy by consuming oxygen and glucose is called Respiration. It involves breathing. • There are two types: Aerobic- Producing energy in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic- Producing energy in the absence or lack of oxygen. GLUCOSE Anaerobic – Absence of Oxygen: Ethanol (C2H5OH) + Carbon Dioxide + Energy Ex: Yeast Lack of Oxygen: Lactic acid (C3H6O3 ) + Energy Ex: Muscle cells Presence of Oxygen: Water + Carbon Dioxide + Energy Ex: Living Beings (takes place in Mitochondria)
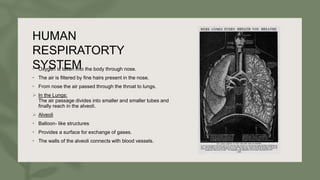
- 10. HUMAN RESPIRATORTY SYSTEM • Oxygen is taken into the body through nose. • The air is filtered by fine hairs present in the nose. • From nose the air passed through the throat to lungs. In the Lungs: The air passage divides into smaller and smaller tubes and finally reach in the alveoli. Alveoli • Balloon- like structures • Provides a surface for exchange of gases. • The walls of the alveoli connects with blood vessels.
- 11. • Then, oxygen dissolves in Haemoglobin from alveoli and is carried from lungs to cells to all the body parts. • The blood brings Carbon Dioxide from the cells releases into Alveoli.