Lightening
- 1. LIGHTENING Presented by Md Asif Hasan
- 2. Introduction Lightening is the occurrence of a natural electrical discharge of very short duration and high voltage between a cloud and the ground or within a cloud, accompanied by a bright flash. More simply, it is the meeting of negative charges with positive charges
- 3. Some Facts about Lightening Duration of one stroke of lightning, 1/5th of second. Lightning can travel at speeds of 60,000 m/sec. Lightning containing an average charge of 30 to 50 lakhs volts During lightening heat exceeds 50,000 degrees F (3 times hotter than the surface of the sun)
- 4. Mechanism of Lightning The lightning occurs in phases. The scientists discovered that the lightning occurs in three main phases- The first phase: A negative charge descends from the cloud toward the ground in part of a second. The second phase: The positive charge on the ground meets with that negative charge. The third phase: As a result, a strong electric spark generates and goes toward the cloud. The returned electric charge and that is the lightning beam, all of these four phases happens in 25 Millisecond.
- 6. Occurrence Tall objects such as trees and skyscrapers are commonly struck by lightning. Mountains also make good targets. The reasons for this is their tops are closer to the base of the storm cloud. However, this does not always mean tall objects will be struck.it all depends on where the charges accumulate. Lightning can strike the ground in open field even if the tree line is close by.
- 7. Damage due to lightning Lightning striking a structure can result in damage to the structure itself and to its occupants and contents, including failure of equipment and especially of electrical and electronic systems. It injuries or sometimes even kills animals and people instantly. It can cause fire and shatter buildings resulting in lot of destruction and damage. It can burn trees and also causes forest fire
- 8. Safety Measures Take shelter in a building or car Stay about 15 feet away from each other Do not lie flat on ground Stay away from all types of water bodies because water is an excellent conductor of electricity It is safer to use mobile phones and cordless phones during lightning Do not take baths and showers during storms, as water is an excellent conductor of electricity.
- 9. Lightening in Bangladesh Fig: Statistics Of Lightning-related Fatalities in Bangladesh 1990-2017 Fig: Gender Variation Of Lightning- related Fatalities in Bangladesh
- 10. Fig: Socioeconomic Conditions Affecting Activities Of Lightning Fatalities
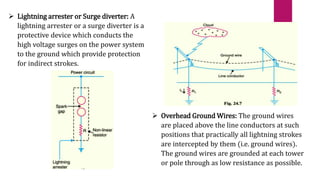
- 11. Lightning Protection System Lightening Conductor: A lightning conductor is fixed on the top of tall buildings to protect them from damage due to the lightning
- 12. Overhead Ground Wires: The ground wires are placed above the line conductors at such positions that practically all lightning strokes are intercepted by them (i.e. ground wires). The ground wires are grounded at each tower or pole through as low resistance as possible. Lightning arrester or Surge diverter: A lightning arrester or a surge diverter is a protective device which conducts the high voltage surges on the power system to the ground which provide protection for indirect strokes.
- 13. The Earthing Screen: It consists of a network of copper conductors (generally called shield or screen) mounted all over the electrical equipment in the sub-station or power station. The shield is properly connected to earth on at least two points through a low impedance. On the occurrence of direct stroke on the station, screen provides a low resistance path by which lightning surges are conducted to ground. The limitation of this method is that it does not provide protection against the travelling waves which may reach the equipment in the station