Inside Lean Kanban (#lkuk14 keynote)
- 1. Inside Lean Kanban …the humane, start with what you do now approach to change Mike Burrows @asplake @kanbanInside mike@djaa.com
- 3. Understanding FP1: Start with what you do now Agreement FP2: Agree to pursue evolutionary change Respect FP3: Initially, respect current processes, roles, responsibilities and job titles
- 6. CP4: Make policies explicit ~~~ ~~ ~~~~~ ~~ ~~ ~~~ ~~~~~~ ~~~ ~~ ~~~~~ ~~ ~~ ~~~ ~~~~~~ Transparency
- 7. Transparency CP5: Implement feedback loops
- 8. Transparency CP1: Visualize Transparency CP4: Make policies explicit Transparency CP5: Implement feedback loops
- 11. CP3 (expanded): Manage flow, seeking smoothness, timeliness, and good economic outcomes, anticipating customer needs
- 12. CP3 (expanded): Manage flow, Flow seeking smoothness, timeliness, and good economic outcomes, anticipating customer needs
- 13. CP3 (expanded): Manage flow, Flow seeking smoothness, timeliness, and good economic outcomes, Customer focus anticipating customer needs
- 14. Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery Allocate across competing objectives Validate relentlessly
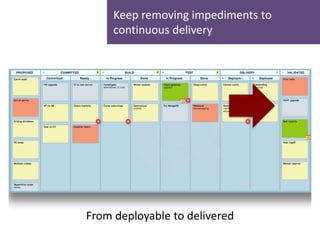
- 15. Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery From deployable to delivered
- 16. Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery From tested to delivered
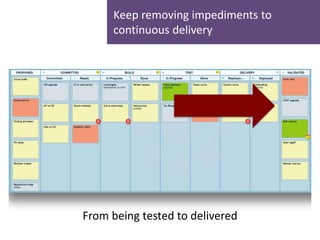
- 17. Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery From being tested to delivered
- 18. Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery From built to delivered
- 19. Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery From being built to Delivered
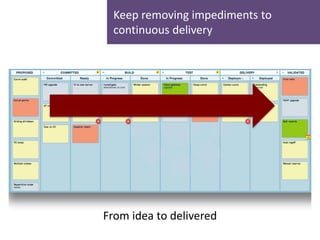
- 20. Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery From idea to delivered
- 21. Allocate across competing objectives Product: the next big thing Product: iterate People, Process Platform Discovery Elaboration Build/Deliver ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
- 22. Allocate across competing objectives Product: the next big thing Product: iterate People, Process Platform Discovery Elaboration Build/Deliver ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ☺ ☺ ☹
- 24. Validate relentlessly feedback, iteration
- 25. Validate relentlessly hypothesis (in)validated
- 26. Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery Allocate across competing objectives Validate relentlessly
- 27. Flow Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery Allocate across competing objectives Validate relentlessly
- 28. Flow Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery Balance Allocate across competing objectives Validate relentlessly
- 29. Flow Keep removing impediments to continuous delivery Balance Allocate across competing objectives Customer focus Validate relentlessly
- 30. Finer-grained objects Disintermediation Distributed cognition Three heuristics Dave Snowden (@snowded)
- 33. Disintermediation Line Manager Engineer Engineer Relationship Manager Engineer Customer
- 34. Disintermediation Line Manager Engineer Engineer Relationship Manager Engineer Customer
- 37. Distributed cognition Across Within Across Within
- 38. Distributed cognition Across Within Across Within
- 39. Finer-grained objects Disintermediation Distributed cognition Three heuristics Dave Snowden (@snowded)
- 40. Flow Finer-grained objects Disintermediation Distributed cognition Balance Three heuristics Dave Snowden (@snowded)
- 41. Flow Finer-grained objects Disintermediation Distributed cognition Balance Collaboration Customer focus Three heuristics Dave Snowden (@snowded)
- 42. Flow Finer-grained objects Disintermediation Distributed cognition Balance Collaboration Customer focus Transparency Leadership Three heuristics Dave Snowden (@snowded)
- 43. I. Kanban through its Values II. Models III. Implementation (STATIK) @KanbanInside ✔ ✔
- 44. Operate kanban systems Increase understanding Pull change through the system
- 45. STATIK 0. Understand the purpose of the system 1. Understand sources of dissatisfaction 2. Analyze demand and capability 3. Model the knowledge discovery process 4. Discover classes of service 5. Design kanban systems 6. Roll out
- 46. Reverse STATIK 0. Understand the purpose of the system 1. Understand sources of dissatisfaction 2. Analyze demand and capability 3. Model the knowledge discovery process 4. Discover classes of service 5. Design kanban systems 6. Roll out
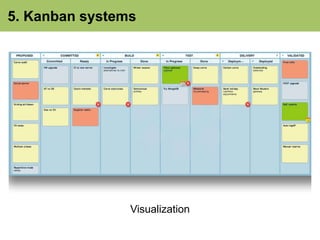
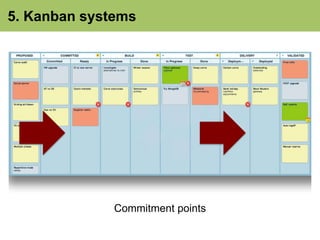
- 48. 5. Kanban systems Visualization
- 49. 5. Kanban systems Policies ~~~ ~~ ~~~~~ ~~ ~~ ~~~ ~~~~~~ ~~~ ~~ ~~~~~ ~~ ~~ ~~~ ~~~~~~
- 50. 5. Kanban systems 4 Limits on work-in-progress (WIP)
- 51. 5. Kanban systems Commitment points
- 52. 5. Kanban systems Feedback loops
- 53. 4. Classes of service 5. Kanban systems Review: • The visibility of work items and where they sit • Policies • WIP limits and other controls on WIP • Commitment points • Feedback loops 6. Roll out
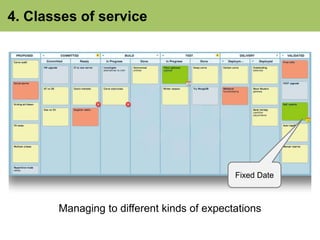
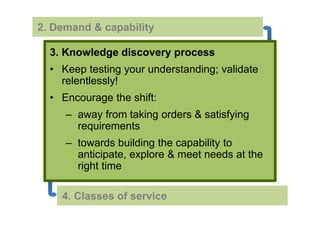
- 54. 4. Classes of service Managing to different kinds of expectations
- 55. 4. Classes of service Fixed Date Managing to different kinds of expectations
- 56. 4. Classes of service Expedited Fixed Date Managing to different kinds of expectations
- 57. 4. Classes of service Expedited Intangible Fixed Date Managing to different kinds of expectations
- 58. 4. Classes of service Standard Expedited Intangible Fixed Date Managing to different kinds of expectations
- 59. 3. Knowledge discovery process 4. Classes of service • Recognise different kinds of customer expectation • Organise: qualitative categories before any quantitative ranking • Make explicit both internally and externally • Select (prioritise) and risk-manage items accordingly 6. Kanban systems
- 60. 3. Knowledge discovery process
- 61. 3. Knowledge discovery process hypothesis (in)validated
- 62. 2. Demand & capability 3. Knowledge discovery process • Understand what kind of knowledge is acquired at each stage of the process and aim to acquire it quickly • Implement through customer validation, customer collaboration, policies, allocations 4. Classes of service
- 63. 2. Demand & capability 3. Knowledge discovery process • Keep testing your understanding; validate relentlessly! • Encourage the shift: – away from taking orders & satisfying requirements – towards building the capability to anticipate, explore & meet needs at the right time 4. Classes of service
- 64. 2. Demand & capability Demand • How work arrives • How frequently • From whom • Of what types • In what sizes • etc Capability • How work leaves • Batches • Lead time(s), delivery rate • Predictability • Flow efficiency • etc Are these in balance?
- 65. 2. Demand & capability Demand • Weekly calls with business managers • Ad-hoc meetings with user reps • Mostly business-driven work; some market-driven, regulatory and infrastructure change • Typically 2-10 days development work per item Capability • Releases every 6 weeks • But ~18 week lead time • Flow efficiency percentage in single digits • (5 days in 18 weeks is 4%) Outline example
- 66. 1. Sources of dissatisfaction 2. Demand & capability • Attend to both sides of this equation • Internal and external perspectives • Expect changes at the boundaries to impact system design, and vice-versa 3. Knowledge discovery process
- 67. 1. Sources of dissatisfaction Internal External
- 68. 1. Sources of dissatisfaction Internal (self awareness) External (empathy) Source: Markus Andrezak @markusandrezak #lascot14
- 69. 0. Purpose 1. Sources of dissatisfaction • Two perspectives (at least!) • Assumes a system scope and a boundary – Both of these are potential sources of dissatisfaction in their own right • Sources are much easier to identify & address when there is already some transparency 2. Demand & capability
- 70. 0. Purpose What Who WHY
- 71. Reverse STATIK 0. Understand the purpose of the system 1. Understand sources of dissatisfaction 2. Analyze demand and capability 3. Model the knowledge discovery process 4. Discover classes of service 5. Design kanban systems 6. Roll out
- 72. Sustained, purposeful change with Kanban 0. Understand the purpose of the system 1. Understand sources of dissatisfaction 2. Analyze demand and capability 3. Model the knowledge discovery process 4. Discover classes of service 5. Design kanban systems 6. Roll out Agreement Respect Balance Flow Customer focus Transparency Collaboration Leadership
- 73. Operate kanban systems Increase understanding Pull change through the system
- 74. Inside Lean Kanban …the humane, start with what you do now approach to change Mike Burrows @asplake @kanbanInside mike@djaa.com
Editor's Notes
- Ken Power, last thing tomorrow
- Ken Power, last thing tomorrow
- Ken Power, last thing tomorrow
- Ken Power, last thing tomorrow
- Ken Power, last thing tomorrow
- Ken Power, last thing tomorrow
- Patrick Steyeart this afternoon talks by Alan Kelly & Martin Aspeli tomorrow afternoon
- Patrick Steyeart this afternoon talks by Alan Kelly & Martin Aspeli tomorrow afternoon
- Kev Murray & Imran Younis before lunch tomorrow
- Kev Murray & Imran Younis before lunch tomorrow
- Kev Murray & Imran Younis before lunch tomorrow
- Morton Hansen David Logan
- Morton Hansen David Logan
- A repeatable way to introduce kanban impactfully
- A way to understand and improve the effectiveness of existing kanban implementations
- A way to understand and improve the effectiveness of existing kanban implementations
- Operate kanban systems Increase understanding Pull change through the system