Lte Presentation.Ppt
- 1. Long Term Evolution (LTE)By –AbhijitKaulNitin KhannaSahanaMallyaVaibhavMalik
- 2. TopicsIntroduction by NitinKhannaTechnical Architecture by VaibhavMalikBusiness Case by AbhijitKaulConclusion by SahanaMallya
- 3. Introduction Welcome to the world of LTE!
- 4. LTE is the next generation of Mobile broadband technologyData rates of 100 MbpsIt is the next level after UMTS 3G technologyWorks with IP!What is LTE?
- 5. AdvantagesProvides low latencyHigher network throughputIncreased data transfer speedMore cost effectivenessImprovements over 3G network
- 6. LTE v/s Other technologies2G to 4G Evolution and data download rates
- 7. Technical ArchitectureWhat is an LTE Network made up of?
- 8. LTE TechnologiesOFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) for downlinkSC-FDMA (Single Carrier – Frequency Division Multiple Access) for uplinkMIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output)SAE (System Architecture Evolution)
- 9. LTE Architecture Source: Ericsson (2009)
- 10. LTE Network ElementsEvolved Node B (eNB)Supports air interfaceProvides radio resource management functionsServing Gateway (SGW)Provides MobilityResponsible for Routing and Forwarding
- 11. LTE Network Elements (Continued)Packet Data Network Gateway (PDN GW)Provides connectivity to InternetProvides QoS and mobility between 3G and non-3G networksMobility Management Entity (MME)Manages mobility and provides securityOperates in control plane and provides authentication
- 12. Business Case for LTEWhat is the LTE market opportunity and implications for the broaderecosystem, including equipment providers, operators, and devicemanufacturers?
- 13. What are the revenue incentives and investment implications for operators who adopt LTE?
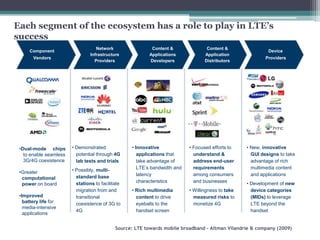
- 14. Each segment of the ecosystem has a role to play in LTE’s success Source: LTE towards mobile broadband – Altman Vilandrie & company (2009)
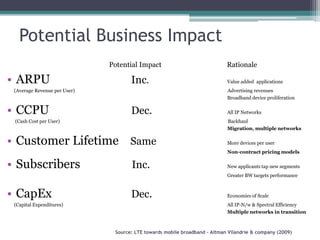
- 15. Potential Business ImpactPotential Impact Rationale ARPU Inc.Value added applications (Average Revenue per User) Advertising revenues Broadband device proliferationCCPU Dec. All IP Networks (Cash Cost per User) BackhaulMigration, multiple networksCustomer LifetimeSameMore devices per userNon-contract pricing modelsSubscribersInc.New applicants tap new segments Greater BW targets performance CapExDec.Economies of Scale (Capital Expenditures) All IP-N/w & Spectral EfficiencyMultiple networks in transition Source: LTE towards mobile broadband – Altman Vilandrie & company (2009)
- 16. ConclusionWhat does the future hold for LTE?
- 17. LTE Future and UsesMass deployment to begin around 2012Devices which are covered under LTE are – Mobile phones, laptops, cameras, camcordersAssured interoperability with older wireless technologies such as GSM, WCDMA/HSPA, CDMA, TD-SCDMA
- 18. LTE AdvancedMobile Communication StandardAs a major enhancement of the 3GPP LTE StandardPeak data rates of 1 Gbps to meet IMT Advanced standards for 4GAbility to leverage advanced topology heterogenous networks such as Picocells and FemtocellsImproves capacity and coverage and provides large bandwidth upto 100 MHz of spectrum
- 19. Conclusion We discussed the topics –What is LTE?Architecture of LTE NetworksMarket growth and evolution of LTEFuture of LTE and LTE Advanced
- 20. Thank You!We’d like to answer any questions that you have…