Malone D2
- 1. WASHINGTON STATE SUPERINTENDENTS AND K-12 ONLINE LEARNING: LEADERSHIP PERCEPTIONS, CHALLENGES & OPPORTUNITIES Glenn E. Malone Washington State University April, 2012
- 2. To Examine the Perceptions, Interpretations, and Reactions of K-12 Superintendents in Washington …in Response to the Rapid Growth of Online Learning. Purpose Malone (2012)
- 3. Superintendent Perceptions: Augustine-Shaw (2001) Robison (2007) K-12 Online Learning: Barbour (2009) Literature Reviewed Malone (2012)
- 4. Innovation ~ Recommendations Leadership ~ Purposes Change ~ Issues Leadership Online Learning Innovation Change Disruptive Innovation Theoretical Framework Malone (2012)
- 5. Q1 What are the issues that impede or support the implementation of online learning as perceived by Washington superintendents? Q2 What do Washington superintendents identify as the purposes for online learning? Q3 What recommendations do Washington superintendents suggest for successful implementation of online learning? Q4 How does district size, years of experience, and online status affect superintendent perceptions of the online learning environment? Research Questions Malone (2012)
- 6. Mixed Methods Study ~ Online Survey 39 Closed & 5 Open-ended Survey Items Quantitative Analysis: Descriptive Statistics Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient Qualitative Analysis: Constant Comparative Method Methodology Malone (2012)
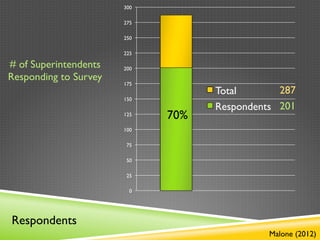
- 7. 300 275 250 225 # of Superintendents 200 Responding to Survey 175 Total 287 150 Respondents 201 125 70% 100 75 50 25 0 Respondents Malone (2012)
- 8. % of Respondents by District Size Less than 100 students 13% 9% 100 – 500 students 11% 22% 501 – 1,000 students 1,001 – 2,500 students 14% 2,501 – 5,000 students 14% 5,001 – 10,000 students 17% 10,000+ students Respondents Malone (2012)
- 9. % of Respondents by Experience 24% 25% 0-3 years 4-7 years 8-11 years 18% 12+ years 33% Respondents Malone (2012)
- 10. % of Respondents by Online Status 19% Not offering Considering 16% Currently offering 65% Respondents Malone (2012)
- 11. Q1 ISSUES: THEMES (P. 67) „ Financial „ Quality „ Regulations Findings Malone (2012)
- 12. Q1 ISSUES: FINANCIAL „ “ We provide online learning to 150-200 students. 50 are from our own district. The others from across the state. We could not offer either without the other. We need 150-200 to break even ... and we still lose money compared to bricks and mortar schools.” „ “I am very skeptical of the motives of private companies and some school districts' purposes. While it is not likely generalizable, my perception is that in some instances there is more interest in making money than with teaching and learning.” „ “I am deeply troubled by districts using online learning to make money.” „ “The motives are overwhelmingly financial.” „ “It is clearly a method for school districts to add additional funds to the district. School districts in Washington State have used this process, knowingly, to pirate students from districts.” „ “With declining resources how can we possibly allocate funds that we don't have to researching these opportunities. They are important but we are just trying to survive right now!” Findings Malone (2012)
- 13. Q1 ISSUES: QUALITY „ “The harm to local districts comes when the parents get sick of baby- sitting and send the student back to the home district and we have to pick up the loss of academic gains.” „ “Students are unsuccessful in online schools and then public school has to clean the mess up.” „ “I have issue with the quality of some of the programs, since these students often end up back in our system with inadequate skills.” „ “We find that students that come back to us from an online program have significant deficits in their learning.” „ “I worry that online programs that may be legally sufficient are not necessarily quality programs that provide an alternative pathway for student success, but they do provide dollars to a district.” „ “I have never heard, in my experience, whether or not these programs make an impact on student learning.” Findings Malone (2012)
- 14. Q1 ISSUES: REGULATION „ “Living in the midst of school districts trying to push the limits of the new laws to bring in FTE, I am a bit jaded at this point.” „ “Online programs have to be regulated to weed out the money grabbers from the legitimate educators.” „ “The ever-changing funding for ALE makes investment risky.” „ “The idea that some schools profit from online courses with FTE, and that other school loose FTE is difficult.” „ “State agencies need to work together to remove road blocks to online learning.” „ “The state taking away 20% of the funding and opening their own online competition is definitely an issue!” Findings Malone (2012)
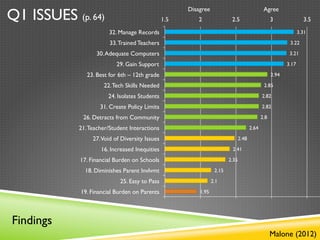
- 15. Q1 ISSUES (p. 64) Disagree Agree 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 32. Manage Records 3.31 33. Trained Teachers 3.22 30. Adequate Computers 3.21 29. Gain Support 3.17 23. Best for 6th – 12th grade 2.94 22. Tech Skills Needed 2.85 24. Isolates Students 2.82 31. Create Policy Limits 2.82 26. Detracts from Community 2.8 21. Teacher/Student Interactions 2.64 27.Void of Diversity Issues 2.48 16. Increased Inequities 2.41 17. Financial Burden on Schools 2.35 18. Diminishes Parent Invlvmt 2.15 25. Easy to Pass 2.1 19. Financial Burden on Parents 1.95 Findings Malone (2012)
- 16. Q2 PURPOSES: THEMES (P. 76) „ Flexibility „ Individualization „ Options Findings Malone (2012)
- 17. Q2 PURPOSES: FLEXIBILITY „ Scheduling Flexibility (M=3.23) „ “The purpose of online learning is to provide flexible opportunities for students in a system that is traditionally not flexible.” „ “Online Learning allows us to provide students with an opportunity to fulfill graduation requirements when they need to accrue credits.” „ “It gives students options and opportunities in a variety of situations young students get themselves into.” Findings Malone (2012)
- 18. Q2 PURPOSES: INDIVIDUALIZATION „ Meeting Individual Student Needs (M=3.13) „ “Not all students learn the same way. Online learning gives those students an opportunity for an education who may not be able to attend a brick and mortar school for specific reasons.” „ “Online learning seems best suited to meeting unique, individual needs rather than serving large numbers of students.” Findings Malone (2012)
- 19. Q2 PURPOSES: OPTIONS „ Expanding Course Options (M=3.11) „ “Online learning is a tool used in creating a continuum of services to meet the mission of ensuring the learning of all our children, not a whipping post for legislators and short sighted educators who may be afraid of change.” „ “The purpose is to provide a wider variety of opportunities for students to take courses.” „ “It is beneficial to have a variety of choices for students to engage in high quality learning environments.” Findings Malone (2012)
- 20. Q2 PURPOSES: CONCERNS „ “I do not believe the purposes of online learning align with the practice.” „ “I believe districts rip off the system and have lost site of the purpose.” „ “There is a considerable gap between the stated potential for online learning and its actual implementation, which is profit-driven.” Findings Malone (2012)
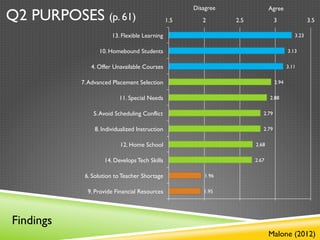
- 21. Disagree Agree Q2 PURPOSES (p. 61) 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 13. Flexible Learning 3.23 10. Homebound Students 3.13 4. Offer Unavailable Courses 3.11 7. Advanced Placement Selection 2.94 11. Special Needs 2.88 5. Avoid Scheduling Conflict 2.79 8. Individualized Instruction 2.79 12. Home School 2.68 14. Develops Tech Skills 2.67 6. Solution to Teacher Shortage 1.96 9. Provide Financial Resources 1.95 Findings Malone (2012)
- 22. Q3 RECOMMENDATIONS: THEMES (P. 77) „ Blending „ Individualization „ Regulations „ Examination Findings Malone (2012)
- 23. Q3 RECOMMENDATIONS: BLENDING „ “Face-to-face contact remains critical to maintaining an effective and sustained online learning program.” „ “Traditional and online learning together produce the best results.” „ “Strong face-to-face student-to-teacher relationships and interactions are essential as the mainstay of K-12 education.” „ “Teachers are still an important component of online learning. The human connection is critical.” „ “Online learning and blended classrooms are the future of education. We as educators must have the vision to allow these programs in our existing schools to support and enhance our more traditional academic programs.” Findings Malone (2012)
- 24. Q3 RECOMMENDATIONS: INDIVIDUALIZATION „ “Online learning provides an opportunity for students who do not fit in the traditional classroom setting.” „ “I am very satisfied to have online learning available to the few learners who need the option but not on a widespread basis.” „ “Online learning should continue to be very limited to meet unique needs of individual students but not a replacement for the strong and good work being done with face-to-face instruction in schools.” Findings Malone (2012)
- 25. Q3 RECOMMENDATIONS: REGULATIONS „ “OSPI needs to create reasonable reporting requirements and funding formulas.” „ “Regulate the funding of online learning very carefully from OSPI. Make an effort to limit abuse from revenue generating interests.” „ “Provide via statewide model so districts are not competing for students.” „ “Online programs, if offered to the public, should be offered and controlled 100% by OSPI.” „ “Develop stronger policies that discourage fly-by-night providers that create a churn in student enrollments for profit.” „ “Vetted courses should be made available at no cost to districts, funded by the state, so that access to educational services does not become even more inequitable.” Findings Malone (2012)
- 26. Q3 RECOMMENDATIONS: EXAMINATION „ “Good grief, how many more hours should a young person spend in a virtual versus actual experience?” „ “Online programs exacerbate the problems of regular schools, rather than solve them.” „ “In general, online learning is not a meaningful learning experience.” „ “We cannot afford to bury our heads in the sand on this issue. Technology will continue to infuse itself into education; we can embrace it or get choked by it.” „ “The decision to offer online programming should be based on student need, not the administrative prejudices or limitations of the adults in the system.” „ “We are all convinced that the breakthrough strategy for improving the quality of instruction that students receive, and for improving the quality of professional learning for teachers, is the meaningful collaboration of teachers who share students and content. This is not a feature of online instruction, and in fact online programs are a step backward toward isolation of practice and norms of autonomy vs. the norms of collaboration we have been working to establish.” Findings Malone (2012)
- 27. Q4 DEMOGRAPHIC AFFECT FACTORS (P. 48) „ Experience „ District Size „ Online Status Findings Malone (2012)
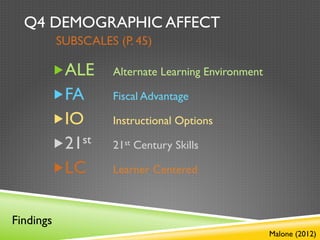
- 28. Q4 DEMOGRAPHIC AFFECT SUBSCALES (P. 45) „ ALE Alternate Learning Environment „ FA Fiscal Advantage „ IO Instructional Options „ 21st 21st Century Skills „ LC Learner Centered Findings Malone (2012)
- 29. Q4 DEMOGRAPHIC: CORRELATIONS Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient by Factor and Subscale (p. 54) Subscale District Size Experience Online Status Fiscal Advantage (FA) -0.083 0.042 -0.051 Instructional Options (IO) 0.092 -0.066 0.111 21st Century Skills (21) 0.017 0.037 .171* Learner-Centered (LC) 0.137 0.107 0.107 Alternate Learning (ALE) .157* -0.025 .280** * Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed) ** Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed) Findings Malone (2012)
- 30. Q4 DEMOGRAPHIC: EXPERIENCE Superintendent Perceptions by Experience (p. 57) 3.1 3.05 3.01 3.02 Agree 2.93 2.9 2.7 2.57 2.51 ALE 2.5 2.46 FA 2.34 IO 2.3 21 LC Disagree 2.1 2.03 1.97 1.9 1.88 1.73 1.7 0-3 years 4-7 years 8-11 years 12+ years Findings Malone (2012)
- 31. Q4 DEMOGRAPHIC: DISTRICT SIZE Superintendent Perceptions by District Size (p. 55) 3.3 3.19 Agree 3.1 2.99 3.02 2.98 2.9 2.92 2.7 ALE 2.61 2.55 2.56 FA 2.5 2.45 IO 2.36 21 2.3 LC 2.1 Disagree 1.97 1.96 1.9 1.89 1.85 1.83 1.7 < 1000 1001-2500 2501-5000 5001-10000 10000+ Findings Malone (2012)
- 32. Q4 DEMOGRAPHIC: ONLINE STATUS Superintendent Perception by Online Status (p. 58) 3.1 3.02 3.03 Agree 2.96 2.9 2.88 2.84 2.7 2.63 2.53 2.5 2.49 ALE FA 2.3 2.29 IO 21 Disagree LC 2.1 1.99 1.9 1.9 1.91 1.7 Not Offering Considering Currently Offering Findings Malone (2012)
- 33. RECOMMENDATIONS (P. 85) „ Regional Adaptive Dialogic Work „ Statewide Superintendent Forums „ Accountability Legislation „ Blended Online Learning „ Common Core Standard Alignment „ Disseminate These Results Recommendations Malone (2012)
- 34. FUTURE RESEARCH (P. 86) „ Case Study of Specific Superintendents „ Online Learning Effectiveness „ Equitable Access „ Longitudinal Study of Students „ Student Perceptions „ Funding Models w/out Charter Future Research Malone (2012)
- 35. FINAL THOUGHTS (P. 84) „ Underlying assumption that online learning should be implemented more broadly. „ Online learning may not be “the” way but “a” way to improve student learning. „ The privatization of public education is at the center of the debate. „ Superintendents’ perceptions are suspicious, leery and jaded. „ This study suggests some superintendents consider some colleagues as part of the problem. Conclusion Malone (2012)