Malvaceae
- 1. Family: Malvaceae Dr. Vasanta I. Kahalkar Assistant Professor Department of Botany M. G. Arts, Science & Late N. P. Commerce College, Armori
- 2. Characters of Malvaceae • Stellate hairs on the young parts, leaves alternate, stipulate, multicostate reticulate; inflorescence solitary or cyme; flower actinomorphic, hermaphrodite, hypogynous, pentamerous, with epicalyx, calyx free or united, corolla free; stamens indefinite, monadelphous; anthers monothecous, stamens united to form a tube; gynoecium many often five, syncarpous, ovary multilocular, superior, axile placentation.
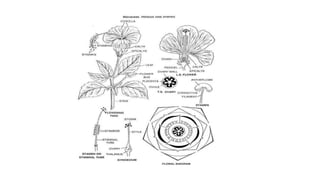
- 3. Hibiscus rosa-sinensis • Habit and Habitat: An ornamental shrub, cultivated in tropics; perennial. • Root:Tap, branched and deep. • Stem: Erect, branched, cylindrical, solid, woody, glabrous. • Leaf: Alternate, simple, petiolate, stipulate, ovate, serrate margin, acute apex, glabrous, unicostate reticulate venation. • Inflorescence: Solitary axillary.
- 4. • Flower: Ebracteate, pedicellate, complete, actinomorphic, hermaphrodite, pentamerous, hypogynous, large, red colour. • Epicalyx: Five to seven, green, linear. • Calyx: Sepals 5, gamosepalous, ovate, valvate aestivation. • Corolla: Petals 5, polypetalous, twisted aestivation, red, united at the base and adnate to the staminal tube.
- 5. • Androecium: Stamens numerous, forming a tube, monadelphous, epipetalous, anthers monothecous, yellow, reniform, transversely attached to the filament, pollen grains multiporate. • Gynoecium: Pentacarpellary, syncarpous, superior, pentalocular, axile placentation, many ovules in each loculus; style passing through the staminal tube; stigma 5 capitate, covered with velvety growth. • Fruit: Capsule. • Floral formula:
- 7. Economic Importance of Malvaceae: • Economically this family is of much importance because there are a number of fibre yielding plants. According to certain authorities nearly all genera can produce some or other kinds of fibres. • A. Fibre yielding plants: • 1. Cotton is perhaps the most important fibre inspite of many synthetic textile fibres. The seed coat of Gossypium produce epidermal hairs which is cellulosic in nature. This is cotton wool. These hairs are flattened, twisted and from the staple. Cotton plant grows best in the sandy damp soil of humid regions. • Egyptian cotton is derived from G. peruvianum whose staple length is 4 7/8 cms. G. barbadense produces sea inland cotton; its staple length in 5 cms. G. hirsutum is a native American species and is also considered superior cotton. The main Indian species is G. herbaceum; its staple length is 1 7/8 cms. G. arboreun is a small tree or a large shrub. It is also cultivated in India.
- 8. • Cotton seed is further important for it produces an edible oil which is semidrying and useful as oleomargarine and in soap. The oil cake is also a very nourishing cattle feed. The residue is also used in washing powder, in preparation of oil cloth, artificial leather, nitroglycerine etc. • 2. Hibiscus cannabinus produces a very valuable fibre from its stem which is used for making rope, cordage, coarse canvas, sacs, floor matting. It is thus used as a substitute for jute. • 3. Hibiscus sabdariffa, A strong silky brown fibre is produced from its stem. This is a good substitute for jute in textile and paper industry. • 4. Abutilon theophrasti produces China jute or Indian mallow. It is extensively cultivated in China. It takes up dyes quickly and used in making rugs. • 5. Urena lobata – It is a weed in all tropical countries and furnishes a yellowish fibre that lasts longer than jute and is used as a substitute at some places. In Barazil it is used for making coffee sacks.
- 9. • 7. Malachra capitata also produces a strong silky fibre like jute and used as a substitute. • B. Miscellaneous uses: • 8. Abelmoschus esculentus (Hindi-Bhindi, Eng.-Lady’s finger) fruits are used as a vegetable. • 9. Hibiscus rosa-sinesis or shoe flower is widely cultivated as an ornamental plant and also used in the worship of God and Godess Kali. Althea rosea is also a garden plant with its lovely pinkish flowers. Abutilon indicum (Hindi-Kanghi) is a wild plant which is sometimes used medicinally. • Malva sylvestris is also a garden plant. Urena repanda is supposed to be a cure for hydrophobia.
- 10. • Thank You