Mapping Techniques Chapter-2.pptx
- 1. GEOLOGICAL MAPPING Introduction to Topographic Maps CHAPTER- TWO PROF. DR. ABDI M. SIAD
- 3. Topographic Maps • A topographic map, also known as a contour map, is a map that shows the shape of the land using contour line. • Contour lines are lines that connect points that are of the same elevation. • They show the exact elevation, the shape of the land, and the steepness of the land’s slope. • Contour lines never touch or cross eachother.
- 4. Let’s take a walk up a hill!
- 5. We’re now at an elevation of 100 meters. 100m
- 7. Now we’re at 200m. 100m 200m
- 8. Shall we march on? 100m 200m
- 9. We’ve made it to 300m! 100m 200m 300m
- 10. On to the peak! 100m 200m 300m
- 11. We’re on the peak, but what’s our elevation? 100m 200m 300m
- 12. Any ideas? 100m 200m 300m Let’s add contour lines for every 50 meters and see if that helps.
- 13. 100m 200m 300m We know that we are above 350m, but less than 400m. 50m 150m 250m 350m
- 14. 100m 200m 300m Let’s head down the hill, it’s getting late! 50m 150m 250m 350m
- 15. 100m 200m 300m Now what’s our elevation? 50m 150m 250m 350m If you said somewhere between 200m and 250m you are right!
- 16. 100m 200m 300m Let’s try this again! 50m 150m 250m 350m
- 22. Topographic Maps • Contour Line – - line on a map that connects points of EQUAL elevation. - show elevation and shape of the land • Relief – Difference between high and low elevations
- 24. Topographic Maps • Contour Interval – difference in elevation between each line. MUST be equal spacing. Contour interval = 20 feet 520 540 560 580
- 25. Topographic Maps • Index Contour – Usually every 5th line is printed darker and has an elevation printed on it.
- 27. Rules for Contours 1. Contour lines never cross
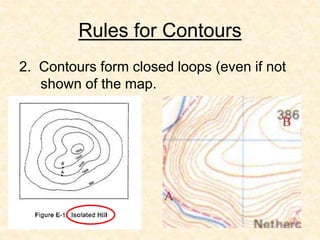
- 28. Rules for Contours 2. Contours form closed loops (even if not shown of the map.
- 29. Rules for Contours 3. Contours bend upstream (uphill) when crossing a stream. Contour lines form V’s that point upstream when they cross a stream It is important to remember that they point in the opposite direction as the flow of water
- 31. Rules for Contours 4. The maximum possible elevation for a hill is “1” less than what the next contour “should” be. The highest possible elevation of the hill is just below the value of the next line that is not shown 50 60 70 80 90
- 32. 239 399 179
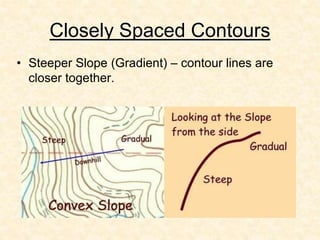
- 33. Closely Spaced Contours • Steeper Slope (Gradient) – contour lines are closer together.
- 34. Wide Spaced Contours • Gradual/Gentle Slope (Gradient) – contour lines are farther apart.
- 37. A B
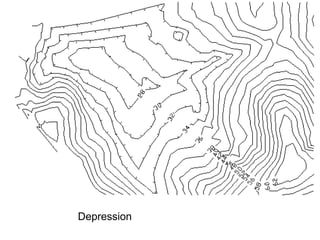
- 38. Depressions • Contour lines which show a depression, crater, or sinkhole on a map. • Shown by dashed lines (hachure marks) on the inside of a contour line
- 39. Depression
- 40. Rules for Contours The lowest possible elevation for a depression is “1” more than what the next contour “should” be. The lowest possible elevation of a depression is just above the value of the next line that is not shown 50 90 90 80 70 60 51
- 41. Benchmarks • a location whose exact elevation is known and is noted on a brass or aluminum plate. • bench marks are shown on maps by an X with the letters BM written next to them.
- 43. Map Scales • The relationship between distance as measured on a map and the actual distance on Earth’s surface
- 44. Types of Map Scales a. Verbal Scale – 1 inch = 20 miles b. Bar Scale One Mile
- 45. Types of Map Scales c. Ratio Scale - One of any unit on this map represents 24,000 of the same unit on Earth’ s surface. Ex, one inch would equal 24,000 inches on the Earth
- 46. • Maps often give you more than one way to measure distance Represents one mile on the map Represents parts of one mile, ex: one tenth of a mile One kilometer
- 48. Gradient • The slope between any two points on a hill • Gradient = Change in Field Value Distance
- 49. Gradient • A trail is four miles long as measured by the scale on a map. The beginning of the trail is at the 1,060 ft contour line and the end of the trail is at the 960 ft contour line. Calculate the gradient of the trail. Gradient = = 1060 ft – 960 ft 4 miles 25.0 ft/mi
- 50. 1- What A, B and C stands for ? 2- What is the gradient of XY while the distance between XY is 200M