Medication Adherence
- 1. MEDICATION ADHERENCE: DEFINING THE PROBLEM November 7, 2012 Marquila Ferrell & Sarah Hudson The University of Toledo
- 2. Objectives 2 Define medication adherence Explore the differences between medication adherence and medication compliance Identify associated statistics Factors that contribute to medication adherence Why medication adherence matters?
- 3. Introduction 3 125,000 people die a year due to failure to take medication or taking medications improperly Almost 6 out of 10 people are taking at least one prescription drug More than 1 in 3 medicine-related hospital admissions occur due to people not properly adhering to their medications Script Your Future. (2012). National Consumers League.
- 4. What is Medication Adherence? 4 “The extent to which patients take medications as prescribed by health care providers.” Osterberg, L., & Blaschke, T. (2005). Adherence to medication. New England journal of medicine, 353(5), 487- 97.
- 5. Medication Adherence vs. Patient Compliance 5 “Compliance suggests that the patient is passively following the doctor’s orders and that the treatment plan is not based on a therapeutic alliance or contract established between the patient and the physician.” Osterberg, L., & Blaschke, T. (2005). Adherence to medication. New England journal of medicine, 353(5), 487.
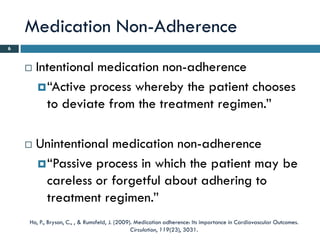
- 6. Medication Non-Adherence 6 Intentional medication non-adherence “Active process whereby the patient chooses to deviate from the treatment regimen.” Unintentional medication non-adherence “Passive process in which the patient may be careless or forgetful about adhering to treatment regimen.” Ho, P., Bryson, C., , & Rumsfeld, J. (2009). Medication adherence: Its importance in Cardiovascular Outcomes. Circulation, 119(23), 3031.
- 7. Effects of Medication Non-Adherence 7 Increased hospital readmission Increased disease progression and complications Increased health care costs Decreased quality of life Patient death
- 8. Patient Interviews 8 “Taking my medication helps balance my life. If I do not take it, I often get sick or have emotional episodes.”
- 9. Why Don’t Patients Take Their Medicine? 9 Most Common Reported Reasons Late Refill 10% Clinical Questions 15% Missed Dose 39% High Cost 16% Late Renewal 20% Express Scripts (2012). Retrieved from http://lab.express-scripts.com/wp- content/uploads/2012/07/Americas_317B_Condition.pdf
- 10. 5 Dimensions of Medication Adherence 10 Adult Meducation (2006). Overview of Medication Adherence. American Society on Aging and American Society of Consultant Pharmacists Foundation.
- 11. Clinical Case Study 11 Primary source 48 year old African American male with low socioeconomic status presenting myocardial infarction and end-stage renal disease Assessment of medication adherence behaviors Psychological screening Questionnaires Post-discharge phone interview Electronic pill bottle Ye, Siqin, Krupka, David, & Davidson, Karina. (2012). Diagnosing medication non-adherence in a patient with myocardial infarction. Frontiers In Psychology, 3:267, 1-3.
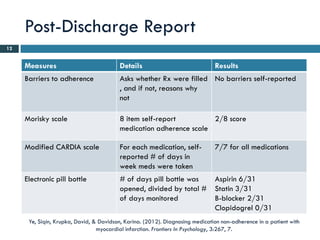
- 12. Post-Discharge Report 12 Measures Details Results Barriers to adherence Asks whether Rx were filled No barriers self-reported , and if not, reasons why not Morisky scale 8 item self-report 2/8 score medication adherence scale Modified CARDIA scale For each medication, self- 7/7 for all medications reported # of days in week meds were taken Electronic pill bottle # of days pill bottle was Aspirin 6/31 opened, divided by total # Statin 3/31 of days monitored B-blocker 2/31 Clopidogrel 0/31 Ye, Siqin, Krupka, David, & Davidson, Karina. (2012). Diagnosing medication non-adherence in a patient with myocardial infarction. Frontiers In Psychology, 3:267, 7.
- 13. Study Results 13 Limitations to medication adherence for Mr. P Low socioeconomic status Lived alone Distrust in medications efficacy Belief medications being overused Outcomes Hypertension poorly controlled Intermittent chest pain Progression of coronary artery disease concern Ye, Siqin, Krupka, David, & Davidson, Karina. (2012). Diagnosing medication non-adherence in a patient with myocardial infarction. Frontiers In Psychology, 3:267, 4.
- 14. Summary 14 What medication adherence is Significance of adhering to medications Barriers to proper medication adherence Pharmacists and MTM services Health outcomes and pharmacy administrators
- 15. Questions 15
- 16. Resources 16 Adult Meducation. (2006). Overview of Medication Adherence. American Society on Aging and American Society of Consultant Pharmacists Foundation. Retrieved from http://www.adultmeducation.com/OverviewofMedicationAdherence_4.html. Express Scripts (2012). Retrieved from http://lab.express-scripts.com/wp-content/uploads/ 2012/07/Americas_317B_Condition.pdf Ho, P., Bryson, C., , & Rumsfeld, J. (2009). Medication adherence: its importance in cardiovascular outcomes. Circulation, 119(23), 3028-35. Retrieved from http:// www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19528344. Osterberg, L., & Blaschke, T. (2005). Adherence to medication. New England journal of medicine, 353(5), 487-97. Retrieved from http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/ 10.1056/NEJMra050100. Script Your Future. (2012). National Consumers League. Retrieved from http:// scriptyourfuture.org/medication-adherence/. Ye, Siqin, Krupka, David, & Davidson, Karina. (2012). Diagnosing medication non- adherence in a patient with myocardial infarction. Frontiers In Psychology, 3:267, 1-7. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3411184/.
Editor's Notes
- Patient stated he could afford his medications and foresaw no difficulties in obtaining and filling medications.Morisky scale-POOR ADHERENCEElectronic pill bottle-POOR ADHERENCE