MICE MANAGEMENT
- 1. CONVENTIONCONVENTION MANAGEMENTMANAGEMENT Presented by:Presented by: MARIANNE T. EVANGELISTA, MSHRMMARIANNE T. EVANGELISTA, MSHRM
- 3. ROLE OF MICE TO TOURISMROLE OF MICE TO TOURISM INDUSTRYINDUSTRY The convention and exhibition industry is an exciting and profitable segment of the tourism industry. A major source of revenue for the tourism industry comes from the meetings, conventions and exhibitions segment of the industry.
- 4. COMPONENTS OF THECOMPONENTS OF THE CONVENTION INDUSTRYCONVENTION INDUSTRY There are 4 major components of the convention industry namely: 1. Planners and Groups they represent 2. Host Facilities 3. Services 4. Exhibitors
- 5. PLANNERSPLANNERS Are individuals or groups that plan meetings, conventions and exhibitions. Planners are classified into a number of categories such as corporate meeting planners, association meeting planners and independent meeting planners
- 6. CORPORATE MEETINGCORPORATE MEETING PLANNERSPLANNERS Are type of meeting planners who work exclusively for a corporation PLANNERS & GROUPS THEY REPRESENT
- 7. ASSOCIATION MEETINGASSOCIATION MEETING PLANNERSPLANNERS Are type of meeting planners who work exclusively for an association. PLANNERS & GROUPS THEY REPRESENT
- 8. INDEPENDENT MEETINGINDEPENDENT MEETING PLANNERSPLANNERS Are type of meeting planners who work contact their services to both associations and corporations PLANNERS & GROUPS THEY REPRESENT
- 9. HOST FACILITIESHOST FACILITIES Provide lodging, meeting rooms and food & beverage as well as a number of other services for groups attending meetings, conventions or exhibitions. Host facilities include: hotels, conference centers, resort hotels, universities, bed and breakfast inns, etc.
- 10. SERVICESSERVICES Refer to individuals and organizations that provide support for meetings, conventions and exhibitions segment of the tourism industry. Service suppliers include: 1. Transportation companies 2. Attractions 3. Tour guide companies 4. Entertainers.
- 11. EXHIBITORSEXHIBITORS Are financially linked with all segments of the meetings, conventions and exhibition industry. Exhibitors are persons who work for the company. Other names for exhibitor are advertising director, communication director or director of marketing who is involved with the corporate exhibit program. The main aim of exhibitors is to introduce their products, both new and old, to an interested audience.
- 12. HISTORY OF MEETINGS,HISTORY OF MEETINGS, CONVENTIONS AND EXHIBITIONSCONVENTIONS AND EXHIBITIONS Archeologist who investigated ancient cultures have found remains that served as places where primitive people gathered to discuss common interests such as hunting plans, war activities, peace negotiations and tribal celebrations. Each village had its common gathering place. As geographical areas grew, cities became the meeting paces for people who wanted to trade goods or discuss common problems. As cities became the center of activities for geographical regions and transportation improved, the desire of the people to gather and discuss things of common interest became more widespread.
- 13. THE GROWTH OF MEETINGS,THE GROWTH OF MEETINGS, CONVENTIONS AND EXHIBITIONCONVENTIONS AND EXHIBITION INDUSTRYINDUSTRY The growth of meetings, conventions and exhibitions industry has been remarkable. Most of this development has occurred within the past 2-5 years. This growth has been due to several factors: 1. Meeting Planners Association 2. The Airline Industry 3. The Lodging Industry 4. Convention Centers 5. Conference Centers 6. Meeting Technology 7. Ground Handlers
- 14. MEETING PLANNERSMEETING PLANNERS ASSOCIATIONASSOCIATION There was unmatched development of the associations connected with meeting planners. These associations not only grew in numbers but also expanded the list of services they offered to their numbers. Majority of these associations increased their emphasis on education. Other growth factors included the rise of the independent meeting planners, the increase in the number of women planners, certification and development of standards and the integration of travel agents into the profession.
- 15. AIRLINE INDUSTRYAIRLINE INDUSTRY The advancement of the airline industry enabled people to travel quickly and efficiently. This was made possible by the introduction of the jet airplane – an invention that revolutionized transportation worldwide.
- 16. LODGING INDUSTRYLODGING INDUSTRY The lodging industry recognized the financial importance of meetings, conventions and exhibitions. Hotels grew and became convention center. Hoteliers learned to adopt their services to different clients. Property marketing directors learned how to work with meeting planners.
- 17. CONVENTION CENTERSCONVENTION CENTERS Convention centers expanded in terms of exhibition spaces, accessibility and storage facilities. They were able to accommodate all the activities of a convention and trade show under one roof. Traffic was improved allowing large numbers of people to move quickly from one area to another.
- 18. CONVENTION BUREAUSCONVENTION BUREAUS Convention bureaus grew rapidly both in numbers and size of operations. The number of bureaus has doubled since 1980, from 100 to more than 250. their operators have become more professional. They actively participated in industry and association affairs.
- 19. CONFERENCE CENTERSCONFERENCE CENTERS Conference centers changed their appearances during the past two decades. For some time they maintained a “business only” appearance. This has been replaced by modern restaurants, recreational facilities and the latest high-tech audio-visual equipment.
- 20. MEETING TECHNOLOGYMEETING TECHNOLOGY Modern audiovisual equipment gave meeting planners a greater degree of flexibility and creativity that was never possible in the past. Video projectors, 360 degree projection techniques, multi-image presentations and unique sound systems have become very common.
- 21. GROUND HANDLERGROUND HANDLER Effective ground arrangements become necessary as meetings and conventions become more complex. Ground arrangement include planning tours, transportation, sightseeing, banquets and hotel reservation. Convention service companies were established in the 1970’s to develop creative meeting programs.
- 22. KEY PLAYERS IN THEKEY PLAYERS IN THE INDUSTRYINDUSTRY The size of the convention and meetings industry has greatly expanded. These players are the following: 1. Association 2. Convention Centers 3. Conference Centers 4. Corporate Meeting; Planners 5. Independent Meeting Planners 6. Tour Operators 7. Tradeshows and Expositions 8. Hotels 9. Convention and Visitor Bureaus 10. Incentive Travel
- 23. ASSOCIATIONSASSOCIATIONS An association is an organized body that promotes and enhances a common interest activity or purpose. Association are classified into 2 main categories – trade associations and professional associations. Both are organized for the betterment of their members. The main activity for both types of associations is to gather and exchange information through publications, educational seminars, newsletters and meetings.
- 24. CONVENTION CENTERSCONVENTION CENTERS A convention center is a public assembly facility which is designed to host meetings and exhibits under one roof. It has also provision banquet, food and beverage and concession service. Most convention centers are owned by city, country or state government and are operated by a designed board or authority.
- 25. MICE PACKAGE DEVELOPMENTMICE PACKAGE DEVELOPMENT PROCEDUREPROCEDURE
- 26. PROCESS OF MICE PACKAGEPROCESS OF MICE PACKAGE
- 27. TRAVEL AGENCIES ORTOURTRAVEL AGENCIES ORTOUR OPERATION SERVICES FOR MICEOPERATION SERVICES FOR MICE
- 28. AccessibilityAccessibility Cost: the monetary expense of transportation andthe monetary expense of transportation and access.access. TimeTime: the duration/distance of travel involved and: the duration/distance of travel involved and the opportunity cost of that time.the opportunity cost of that time. Frequency:Frequency: the frequency of connections to thethe frequency of connections to the site.site. Convenience:Convenience: the scheduling convenience of thethe scheduling convenience of the connections.connections. Barriers:Barriers: the extent of any travel formalities,the extent of any travel formalities, which inhibit travel such as visas, customs, etcwhich inhibit travel such as visas, customs, etc.
- 29. Local SupportLocal Support Local Chapter: the extent of assistance andthe extent of assistance and backing offered by the local chapter of thebacking offered by the local chapter of the Association.Association. CVB/Convention CentreCVB/Convention Centre: the extent of planning,: the extent of planning, logistical and promotional support offered.logistical and promotional support offered. SubsidiesSubsidies: the extent to which the destination: the extent to which the destination offers to defray costs through rebates andoffers to defray costs through rebates and Subsidies.Subsidies.
- 30. Other AttractionsOther Attractions Entertainment:Entertainment: Restaurants, Bars,Theatres,Restaurants, Bars,Theatres, Nightclubs etc.Nightclubs etc. Shopping:Shopping: Malls, Major Department Stores, LowMalls, Major Department Stores, Low Prices etc.Prices etc. Sightseeing:Sightseeing: Architecture, Museums, Monuments,Architecture, Museums, Monuments, Attractions, Parks, Historical Sites, Local Tours.Attractions, Parks, Historical Sites, Local Tours. Recreation:Recreation: Sports And Activities Either AsSports And Activities Either As Spectator Or Participant.Spectator Or Participant. Professional opportunities:Professional opportunities: Visiting LocalVisiting Local Clients, Negotiations, Business Deals, Selling, MakingClients, Negotiations, Business Deals, Selling, Making Contacts etc.Contacts etc.
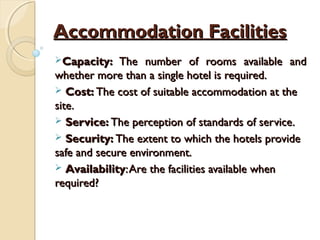
- 31. Accommodation FacilitiesAccommodation Facilities Capacity:Capacity: The number of rooms available andThe number of rooms available and whether more than a single hotel is required.whether more than a single hotel is required. Cost:Cost: The cost of suitable accommodation at theThe cost of suitable accommodation at the site.site. Service:Service: The perception of standards of service.The perception of standards of service. Security:Security: The extent to which the hotels provideThe extent to which the hotels provide safe and secure environment.safe and secure environment. AvailabilityAvailability:Are the facilities available when:Are the facilities available when required?required?
- 32. Meeting FacilitiesMeeting Facilities Capacity:Capacity: Ability of site to provide suitable sizedAbility of site to provide suitable sized facilities.facilities. Layout:Layout: suitability of facility layout and floor plan.suitability of facility layout and floor plan. Cost:Cost: the cost of the meeting space required.the cost of the meeting space required. Ambience:Ambience: the ability of the facility to create anthe ability of the facility to create an appropriate atmosphere and environment.appropriate atmosphere and environment. Service:Service: the perception of the standards ofthe perception of the standards of service.service. Security:Security: the extent to which the facility providesthe extent to which the facility provides a safe and secure meeting space.a safe and secure meeting space. Availability:Availability: are the facilities available whenare the facilities available when required.required.
- 33. InformationInformation Experience: has the site performed satisfactorily in the past. Reputation: what is the reputation of the destination among other meeting planners. Marketing: the effectiveness of the destination’s marketing activities. Site EnvironmentSite Environment Climate: the desirability of the destination’s climate. Setting: the attractiveness of the destinations surroundings. Infrastructure: the suitability and standard of local infrastructure. Hospitality: the extent to which the host
- 34. Other CriteriaOther Criteria RisksRisks: the possibility of strikes, natural disasters,the possibility of strikes, natural disasters, boycotts, and other possible adverse events.boycotts, and other possible adverse events. Profitability:Profitability: the extent to which the site wouldthe extent to which the site would produce a profit for the organizers.produce a profit for the organizers. Association Promotion:Association Promotion: would the site addwould the site add credibility to the association and build membership.credibility to the association and build membership. Novelty:Novelty: the extent to which the destinationthe extent to which the destination represents a novel location for the association’s nextrepresents a novel location for the association’s next Convention.Convention.
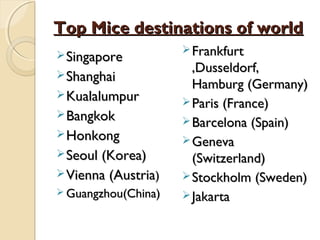
- 35. Top Mice destinations of worldTop Mice destinations of world SingaporeSingapore ShanghaiShanghai KualalumpurKualalumpur BangkokBangkok HonkongHonkong Seoul (Korea)Seoul (Korea) Vienna (AustriaVienna (Austria)) Guangzhou(China)Guangzhou(China) FrankfurtFrankfurt ,Dusseldorf,,Dusseldorf, Hamburg (Germany)Hamburg (Germany) Paris (France)Paris (France) Barcelona (Spain)Barcelona (Spain) GenevaGeneva (Switzerland)(Switzerland) Stockholm (Sweden)Stockholm (Sweden) JakartaJakarta
- 36. REFRENCESREFRENCES Mr. Surjeet sir (Department of Hotel & TourismMr. Surjeet sir (Department of Hotel & Tourism Management.Management. India as a Global Conventions DestinationIndia as a Global Conventions Destination prospects & strategy:- by Ministry of Tourism,prospects & strategy:- by Ministry of Tourism, Govt. of India.Govt. of India. Introduction to Hospitality Management :-Introduction to Hospitality Management :- By John R.WalkerBy John R.Walker http://www.haryanatourism.gov.in/destination/rahttp://www.haryanatourism.gov.in/destination/ra jhans.aspjhans.asp http://www.incredibleindia.org/newsite/cms_paghttp://www.incredibleindia.org/newsite/cms_pag e.asp?pageid=866e.asp?pageid=866 http://www.conventionicpb.org/conf_locations.ahttp://www.conventionicpb.org/conf_locations.a spsp
- 38. MEETINGMEETING Is a conference,Is a conference, workshop,workshop, seminar or eventseminar or event designed to bringdesigned to bring people togetherpeople together for the purpose offor the purpose of exchangingexchanging information.information. Meetings do notMeetings do not include exhibitsinclude exhibits
- 39. USE OF MEETINGSUSE OF MEETINGS Meetings are very important for the work of any organization. Good meetings are important for collective decision-making, planning and follow-up, accountability, democracy, and other practices that will help you to build a good organization. If meetings are used in the correct way, they can help an organization to be efficient. However, like all organizing tools, meetings can be used badly and end up not serving the purpose that they are supposed to. Sometimes we seem to attend too many long meetings, which discuss the same thing over and over again without seeming to move forward. Meetings can become places where conflict is played out.
- 40. COMMON TYPES OF MEETINGCOMMON TYPES OF MEETING Investigative Meeting, generally when conducting a pre-interview, exit interview or a meeting among the investigator and representative Work Meeting, which produces a product or intangible result such as a decision Staff meeting, typically a meeting between a manager and those that report to the manager Team meeting, a meeting among colleagues working on various aspects of a team project Ad-hoc meeting, a meeting called for a special purpose
- 41. COMMON TYPES OF MEETINGCOMMON TYPES OF MEETING Management meeting, a meeting among managers Board meeting, a meeting of the Board of directors of an organization One-on-one meeting, between two individuals Off-site meeting, also called "offsite retreat" and known as an ”Away day” meeting in the UK Kickoff meeting, the first meeting with the project team and the client of the project to discuss the role of each team member
- 42. COMMON TYPES OF MEETINGCOMMON TYPES OF MEETING Pre-Bid Meeting, a meeting of various competitors and or contractors to visually inspect a jobsite for a future project. The meeting is normally hosted by the future customer or engineer who wrote the project specification to ensure all bidders are aware of the details and services expected of them. Attendance at the Pre-Bid Meeting may be mandatory. Failure to attend usually results in a rejected bid
- 43. MEETING FREQUENCYMEETING FREQUENCY OPTIONSOPTIONS Since a meeting can be held once or often, the meeting organizer has to determine the repetition and frequency of occurrence of the meeting. Options generally include the following: One-time Meeting Recurring Meeting Series Meeting
- 44. ONE-TIME MEETINGONE-TIME MEETING A one-time meeting is the most common meeting type and covers events that are self- contained. While they may repeat often, the individual meeting is the entirety of the event. This can include a 2006 conference. The 2007 version of the conference is a stand-alone meeting event.
- 45. RECURRING MEETINGRECURRING MEETING A recurring meeting is a meeting that recurs periodically, such as an every Monday staff meeting from 9:00AM to 9:30 AM. The meeting organizer wants the participants to be at the meeting on a constant and repetitive basis. A recurring meeting can be ongoing, such as a weekly team meeting, or have an end date, such as a 5 week training meeting, held every Friday afternoon.
- 46. SERIES MEETINGSERIES MEETING A series meeting is like a recurring meeting, but the details differ from meeting to meeting. One example of a series meeting is a monthly "lunch and learn" event at a company, church, club or organization. The placeholder is the same, but the agenda and topics to be covered vary. This is more of a recurring meeting with the details to be determined.
- 47. MEETING ETIQUETTEMEETING ETIQUETTE Make sure you have an agenda for the meeting. During meeting let people know what is the agenda. First explain the what the meeting is about and what is the purpose of the meeting? Make sure that the meeting time is worth the attending persons time. Have action items as a product of the meeting. Listen carefully and then speak. Make sure you are on time to the meeting. Always be well dressed. Always put your mobile devices on silent mode during meetings.
- 48. MEETING ETIQUETTEMEETING ETIQUETTE Presentations and print outs save a lot of time during meeting. All your power point presentations should be available on shared server and you should always carry one copy in the USB flash drive. Do not jump to conclusions during the meeting. It should come out as the minutes of the meeting. If the meeting is a teleconference call over phone or web, then make sure that you dial in well ahead of time. Keep your phone on mute mode if you are not talking.
- 49. MEETING SET-UP &MEETING SET-UP & ARRANGEMENTARRANGEMENT THEATRE OCTAGONHOLLOW SQUARE CLASSROOM U - SHAPED V-SHAPED
- 50. PLANNING A MEETINGPLANNING A MEETING Planning should improve participation by ensuring that discussion is on a single topic and that the members are well prepared for the meeting. This is the responsibility of the Chairperson, Secretary and Executive, depending on the type of organization. Planning does not mean controlling and directing the meeting in such a way that it restricts participation
- 51. PLANNING A MEETINGPLANNING A MEETING INCLUDE THE FF:INCLUDE THE FF: Notification Preparing the Agenda Taking a Minutes Voting Chairing a Meeting
- 52. NOTIFICATIONNOTIFICATION Notification: It is the executive’s responsibility to ensure that everyone has been notified of the date, time and venue of the meeting, as well as the main issues to be discussed. For many organizations it is a useful practice to always have their meetings on the same day at the same time in the same place – for example on the first Saturday of every month at the local church hall. If you do not money to always inform your members of meetings then over time this will help you to cut costs, and to make sure that everyone knows where they can find the meeting.
- 53. PREPARING THE AGENDAPREPARING THE AGENDA Preparing the agenda: The agenda is a list of the most important issues for the members to discuss. It is drawn from the Matters Arising from the previous meeting and from the discussions of the Executive or Secretariat. The agenda is the responsibility of the Chairperson and the Secretary. The chairperson should read the minutes of the previous meeting to familiarize him/herself with the issues. This will for the basis of a list of matter arising from these minutes.
- 54. MATTERS ARISING INMATTERS ARISING IN AGENDA INCLUDE:AGENDA INCLUDE: Tasks – a report back must be given Matters for which further information was required for discussion Matters that were deferred to this meeting There are standard items for any agenda. These items should be arranged in order of priority and time should be allocated for each discussion. Where possible, try to familiarize yourself with each area of discussion. An agenda should include a last item known as General or Any Other Business to allow individuals to raise short items not included on the agenda.
- 55. HOW TO RUN A MEETINGHOW TO RUN A MEETING The agenda Open the meeting and welcome everyone. Then go through the agenda step by step. Those present and apologies: The apologies of those members not able to attend the meeting are recorded as part of the minutes. Send round an attendance register if there are too many people to just record it in the minutes. Ask if there are any apologies from people who are not there.
- 56. MINUTESMINUTES Minutes: Minutes are accurate notes of what is discussed and decided on at meetings. Make sure that the minutes of the previous meeting are circulated to everyone or at least read at the beginning of the meeting. (See section on writing minutes) Minutes must be adopted at the beginning of a meeting. Give people a chance to read the minutes or read them out aloud. Everyone must agree that they are an accurate record of the last meeting. Members must be given the chance to add where item/points might have been left out.
- 57. MATTERS ARISING FROMMATTERS ARISING FROM MINUTESMINUTES Correspondence: This means all the letters that have been received by the organization since the last meeting. They can be dealt with in different ways. If your group does not receive many letters, they could be read out and then discussed. Another way is for the secretary to list them with a brief explanation. The chairperson then goes through the list and suggests action. If the issue raised in the letter needs decisive action it can be more fully discussed.
- 58. MATTERS ARISING FROMMATTERS ARISING FROM MINUTESMINUTES Writing the minutes The following information should be included: Nature of meeting, date, time, venue Names of those present Names of visitors Apologies Summaries of decisions and discussions
- 59. HOW TO WRITE MINUTES IN AHOW TO WRITE MINUTES IN A MEETINGMEETING It is essential that minutes are recorded accurately. This not only serves as a reminder of issues that need to be followed up but also prevents arguments about previous decisions. Minutes are also a guide for the secretary and chairperson when drawing up the agenda for the next meeting. Minutes help the organization to learn from its past failures and successes. This is done when the secretary reflects on the minutes of the past year when drawing up an annual report.
- 60. ASPECTS IN TAKING GOODASPECTS IN TAKING GOOD MINUTESMINUTES Listening This is a very important skill to develop. You must not only listen to what is being said but you have to ensure that you understand as well. Taking notes Write down only the main points and the decisions taken. It is impossible to write down everything that is being said.
- 61. ASPECTS IN TAKING GOODASPECTS IN TAKING GOOD MINUTESMINUTES Always try to identify the main points What is the main aim of the discussion? What information is important? Use your own words. If you do this you will find that your minutes are more accurate and complete than if you try to jot down everything a speaker says. Pay special attention to decisions. If necessary, ask for the decisions to be repeated. Ask for clarification. Do not hesitate to stop the meeting if you are not clear about any decisions or issues being discussed.
- 62. MEETING PROCEDURESMEETING PROCEDURES Meeting Procedures – All members should know meeting procedures. There are a number of points that people use in meetings to ensure that the meetings run smoothly. Often members use these points to assist the chairperson.
- 63. PROCEDURAL POINTS USEDPROCEDURAL POINTS USED IN MEETINGSIN MEETINGS Point of Order: It should be used when a member feels that the meeting procedure is not being stuck to and s/he wants the meeting to return to the correct procedure or order. For example, when an individual is speaking totally off the point, another member might ask on a point of order for the speaker to stick to the agenda.
- 64. PROCEDURAL POINTS USEDPROCEDURAL POINTS USED IN MEETINGSIN MEETINGS Point of Information: A member may raise their hand and ask to make point of information (or request information) when it is not his or her turn to speak. This can enable a member to speak (by putting up his/her hand and asking to speak) when it is not his/her turn to request more information on the matter being discussed, or to give more information on a point being discussed.
- 65. PROCEDURAL POINTS USEDPROCEDURAL POINTS USED IN MEETINGSIN MEETINGS Quorums: This is the minimum number of people who must be present for the meeting to conduct business and take decisions. This minimum number is stated in the organizations constitution. The meeting cannot start until there is a quorum. Always ensure that you have this minimum number of people at a meeting, especially when decisions must be taken. If you do not, and decisions are taken, members who were not present can request that it is re- discussed, meaning that time was wasted.
- 66. PROCEDURAL POINTS USEDPROCEDURAL POINTS USED IN MEETINGSIN MEETINGS Out of Order: When an individual is not sticking to meeting procedure, being rude, interjecting or misbehaving in some way, the chairperson might rule him/her out of order.
- 67. PROCEDURAL POINTS USEDPROCEDURAL POINTS USED IN MEETINGSIN MEETINGS Protection: A speaker who is being harassed when he/she is speaking can ask for the protection of the Chairperson.
- 68. HOW TO TAKE DECISIONS INHOW TO TAKE DECISIONS IN MEETINGMEETING Decisions are usually reached through two main ways: Consensus This means reaching decisions by discussion and general agreement. Voting People vote for a particular proposal. Usually one person will put forward a proposal, someone else will second it and then people will vote. If the majority of people accept the proposal, it then becomes binding on the organization.
- 69. VOTING CAN BE DONEVOTING CAN BE DONE THROUGHTHROUGH Show of hand The Chairperson would call for a show of hand when there is a difference of opinion amongst members when a decision needs to be reached. S/he will call on members to raise their hands to show their support for or against a proposal. These votes are then counted – majority would then ensure that the proposal stands or falls away.
- 70. VOTING CAN BE DONEVOTING CAN BE DONE THROUGHTHROUGH Secret ballot Each person would be given a piece of paper where s/he would write whether s/he supports a particular proposal or not. The votes would be counted and the majority would ensure that the proposal stands or falls away. It is usually better to reach consensus than to vote. Reaching consensus often means that there are compromises from everyone but it ensures that most people feel part of the decision. Sometimes a vote does need to be taken, for example in elections or when the meeting cannot reach a decision through consensus.
- 71. VOTING CAN BE DONEVOTING CAN BE DONE THROUGHTHROUGH Resolutions These are formal proposals put forward to the meeting, for people to agree or disagree with. If some disagree, they are voted on. If passed, they become resolutions and therefore policy of the organization. There should be a proposer and seconder of each resolution. Resolutions are a clear way to set out the policies and decisions of an organization. Usually a resolution has three parts to it:
- 72. HOW TO CHAIR A MEETINGHOW TO CHAIR A MEETING The chairperson is the most important person in the meeting. He or she will set the pace for the meeting, make sure that people stick to the topics, ensure that democratic decisions are taken, and that everyone is on board with these decisions. Chairing is a great skill and it is important to teach members to chair meetings and rotate the job where possible so that more people can practice this skill. However, it is always good to have an experienced chairperson for important meetings.
- 73. HOW TO CHAIR A MEETINGHOW TO CHAIR A MEETING A good chairperson is an active chairperson; it is not the chairperson’s job to simply keep a list of speakers and to let them speak one after the other. The chairperson should introduce the topic clearly and guide the discussion especially when people start repeating points. When a discussion throws up opposing views, the chairperson should also try to summarize the different positions and where possible, propose a way forward. The way forward can involve taking a vote on an issue, having a further discussion at another date, or making a compromise that most people may agree with. The chairperson should ask for agreement from the meeting on the way forward, and apologize to those who still wanted to speak.
- 74. STEPS IN CHAIRING A MEETINGSTEPS IN CHAIRING A MEETING The Chairperson opens the meeting and presents the agenda. S/he should start a meeting by setting a cut-off time when everyone agrees that the meeting should end. This helps to encourage people to be brief. S/he calls on individuals to introduce or lead the discussion of points on the agenda and gives everyone a chance to speak. S/he also ensures that no one dominates discussion. S/he should try to summarize the discussion clearly restating ideas and proposals put forward. However, there is no need to repeat everything that has been said.
- 75. STEPS IN CHAIRING A MEETINGSTEPS IN CHAIRING A MEETING S/he must be able to get agreement on what the decision is – s/he must ensure that everyone understands the decision, delegates to someone the duty of carrying out the decision, ensures that the person given the responsibility knows what s/he has to do and when it should be done and reported on. S/he ensures that everyone takes part in the discussions and decision-making. S/he ensures that the date for the next meeting is always set at the meeting.
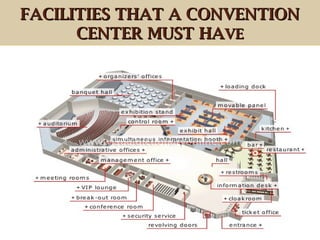
- 76. FACILITIES THAT A CONVENTIONFACILITIES THAT A CONVENTION CENTER MUST HACENTER MUST HAVEVE
- 77. Conference room –Room that is big enough to hold a relatively large number of people. Break-out room – Room designed for working sessions involving small groups. VIP lounge – Room reserved for distinguished guests. Meeting rooms – Rooms used by small groups to hold meetings and discussions. Management office – Office occupied by the person who manages the convention center’s various services. Administrative offices – Rooms where tasks related to the management of the convention center are carried out. Simultaneous interpretation booth –Room set aside for interpreters, who provide an oral translation of a conference. Control room –Room equipped to control sound, lighting and projection. FACILITIES THAT A CONVENTIONFACILITIES THAT A CONVENTION CENTER MUST HACENTER MUST HAVEVE
- 78. Auditorium – Hall designed for the public to attend lectures and audiovisual presentations. Banquet hall – Large site used for assemblies, banquets, social events, etc. Organizers’ offices – Meeting rooms used by a convention’s organizers. Movable panel – Lightweight divider usually with feet that is used to enclose an exhibition stand. Exhibition stand – Area where exhibitors showcase their products or services. Exhibit hall – Hall where exhibition stands are set up. Kitchen – Room where meals are prepared. Bar –Area with a counter and tables where alcoholic drinks are sold. Restaurant – Business establishment where meals are served for a fee. FACILITIES THAT A CONVENTIONFACILITIES THAT A CONVENTION CENTER MUST HACENTER MUST HAVEVE
- 79. Hall – Large open space used to access other rooms. Information desk – Kiosk that provides information on events and services at the convention center. Restrooms – Rooms equipped with toilets and sinks. Cloakroom – Space designated for storing clothes, hats, umbrellas and so forth. Security service – Room equipped with monitors where staff watch over the convention center’s various rooms. Ticket office – Counter where admission tickets are purchased. Loading dock – Installation used to unload crates and pallets containing convention articles, equipment, etc. Revolving doors – Revolving doors composed of three or four glass wings that pivot around a vertical axis; they are pushed open like a turnstile. FACILITIES THAT A CONVENTIONFACILITIES THAT A CONVENTION CENTER MUST HACENTER MUST HAVEVE
- 81. ConventionsConventions:-:- conventions areconventions are generally largely meetings with some formgenerally largely meetings with some form of exposition or trade show included. Aof exposition or trade show included. A number of Associations have one or morenumber of Associations have one or more conventions per year . These conventionsconventions per year . These conventions raise a large part of the association budget.raise a large part of the association budget. ExhibitionsExhibitions:-:- Events at whichEvents at which products & services are displayed. Anproducts & services are displayed. An exhibitions may simply be a few table- topexhibitions may simply be a few table- top booths designed to display goods & services.booths designed to display goods & services.
- 83. conventionsonventions are generally largely meetingsare generally largely meetings with some form of exposition or trade showwith some form of exposition or trade show included. A number of Associations have one orincluded. A number of Associations have one or more conventions per year .These conventionsmore conventions per year .These conventions raise a large part of the association budgetraise a large part of the association budget ATYPICAL CONVENTION FOLLOWS AATYPICAL CONVENTION FOLLOWS A FORMAT LIKETHIS:-FORMAT LIKETHIS:- Welcome/Registration.Welcome/Registration. Introduction of president.Introduction of president. President’s welcome speech, opening thePresident’s welcome speech, opening the convention.convention. First keynote address by a featured speakerFirst keynote address by a featured speaker Exposition booths open.Exposition booths open. Several workshops or presentations on specificSeveral workshops or presentations on specific topics.topics.
- 84. Continues…Continues… Demonstrations of special topicsDemonstrations of special topics Vendor’s private receptionsVendor’s private receptions DinnerDinner Convention centre closesConvention centre closes Convention services for incoming touristConvention services for incoming tourist TransportationTransportation Hotels & MotelsHotels & Motels RestaurantsRestaurants AttractionsAttractions Suppliers & etc….Suppliers & etc….
- 88. Incentive TravelIncentive Travel Incentive travel refers to the segment of business travelIncentive travel refers to the segment of business travel that uses the allure of a trip as an incentive or reward forthat uses the allure of a trip as an incentive or reward for achievement.achievement. A Typical example of incentive travel would be aA Typical example of incentive travel would be a company-paid vacation to a resort for top-performingcompany-paid vacation to a resort for top-performing salespersons.salespersons. Sometimes this type of vacation will includeSometimes this type of vacation will include motivational seminars, morale-building activities, and othermotivational seminars, morale-building activities, and other activities that build upon a gathering of employees.activities that build upon a gathering of employees. Incentive trips also can include business-related groupIncentive trips also can include business-related group activities, such as the introduction of new products oractivities, such as the introduction of new products or promotional campaigns, or training programs forpromotional campaigns, or training programs for employeesemployees..
- 89. FORMS OF INCENTIVESTRAVELFORMS OF INCENTIVESTRAVEL Pure Incentives.Pure Incentives. •Luxury pure incentives.Luxury pure incentives. •Mid range pure incentives.Mid range pure incentives. Motivational MeetingsMotivational Meetings Fam tourFam tour
- 90. INCENTIVETOURISMINCENTIVETOURISM DESTINATION NEEDTODESTINATION NEEDTO PERFORMWELL INTRAVELPERFORMWELL INTRAVEL FOLLOWING CRITERIAFOLLOWING CRITERIA •Service levelService level •Safety & securitySafety & security •Accommodation costAccommodation cost •Scenic beautyScenic beauty •Varieties of activities for all tastesVarieties of activities for all tastes •Sightseeing & cultural attractionsSightseeing & cultural attractions •Modern technical systemModern technical system •Sport & recreational facilitiesSport & recreational facilities •Unusual destinationUnusual destination •ClimateClimate •Public transportPublic transport •Duration of flightDuration of flight
- 93. TYPES OF EXHIBITIONSTYPES OF EXHIBITIONS Trade & Industrial Fairs.Trade & Industrial Fairs. Combined conferences & exhibitions Company product launches. Consumer & Public Exhibitions.Consumer & Public Exhibitions. Public exhibitions. Garden festivals. Company “In – House” Events.Company “In – House” Events. Prospective staff interview. Product launching. Other Exhibitions / Display Attractions.Other Exhibitions / Display Attractions. Manufactures' Promotions.
- 94. ORGANISE AN EXHIBITIONORGANISE AN EXHIBITION EXHIBITION PROCESSEXHIBITION PROCESS Space requirementSpace requirement ProposalProposal BookingsBookings Feasibility phaseFeasibility phase Preliminary design phasePreliminary design phase Detail design phaseDetail design phase Production planning phaseProduction planning phase Production phaseProduction phase Operational phaseOperational phase Termination phaseTermination phase Assessment phaseAssessment phase
Editor's Notes
- CORPORATION – IS A BUSINESS ASSOCIATION – IS A GUILD / GROUP