microbiology.pptx
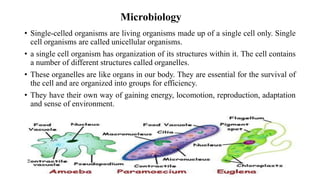
- 1. Microbiology • Single-celled organisms are living organisms made up of a single cell only. Single cell organisms are called unicellular organisms. • a single cell organism has organization of its structures within it. The cell contains a number of different structures called organelles. • These organelles are like organs in our body. They are essential for the survival of the cell and are organized into groups for efficiency. • They have their own way of gaining energy, locomotion, reproduction, adaptation and sense of environment.
- 3. Identification and Classification • Classified as Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya in the three domain system of classification of life forms. • Microorganisms can be classified on the basis of cell structure, cellular metabolism, or on differences in cell components such as DNA, fatty acids, pigments, antigens, and quinones. • Different staining techniques like gram staining are used to identify the structure of microorganisms. • In some cases, molecular and phylogenetic techniques are also used to classify them. • Some organisms are even identified by their growth in special media, or by other techniques, such as serology • Microscopy is an important tool in the study of microbiology.
- 4. Microscopy • A device called microscope is used to visualize such microorganisms which otherwise are invisible for a naked eye. • A microscope magnifies the image using many sets of optical lenses. • In light microscopy, light is focused on a specimen by a glass condenser lens; the image is then magnified by an objective lens and an ocular lens for projection on the eye, digital camera. • In electron microscopy, a beam of electrons (top of the microscope) is used instead of light, and electromagnets are used instead of glass lenses. The electron beam is focused on the specimen by a condenser lens; the image is magnified by an objective lens and a projector lens for projection on a digital detector.
- 6. Light Vs Electron microscope Light Microscope Electron Microscope Uses light as an illuminating source. Uses electron beam as illuminating source. Lower magnification Higher magnification Both live and dead specimen can be seen Only dead and dried specimen can be seen. Low resolution High resolution Image formation depends on absorption of light Image formation depends on the scattering of electrons. Image can be seen through eye piece Image is recorded on a photographic plate. Inexpensive and low maintenance. Very expensive and high maintenance.
- 7. Single Celled Organisms – Ecological Aspect • Biologists have found that microbial life has an amazing flexibility for surviving in extreme environments that would be completely inhospitable to complex organisms. • Different species of microorganisms use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon. These may be alternations between photo- and chemotrophy, between litho- and organotrophy, between auto- and heterotrophy or a combination of them. • Study of such organisms helps us to understand the relationship between living organisms and environment in a better way. • These organisms are also used in various studies as well as many industrial and restoration processes.
- 8. Growth kinetics • It is the relationship between specific growth rate and the concentration of substrate. • It is represented mathematically as first order kinetics. • A population growth curve for any bacterium may be determined by growing a pure culture of the organism in a liquid medium at constant temperature. • Samples of the culture are collected at fix intervals and the number of viable organisms is determined. • The data is then plotted on a logarithmic graph paper. • The logarithms of the number of bacteria per millilitre of medium is plotted against time.