Milky Way_ AST 114, Derek & Rose
- 1. What is the Milky Way? “A GALAXY IS HUGE FORMATION OF STAR- SYSTEMS THAT TOGETHER FORM A CLUSTER THAT ROTATES ABOUT A COMMON CENTER OF MASS.” Home to our Solar System, and about 200 million other stars.
- 2. Like 2/3 of the other known galaxies, the Milky Way is a Barred Spiral Galaxy. Andromeda, followed by The Milky Way, are the largest of around 30 galaxies in the “Local Group” which is in turn part of the monstrous Virgo Supercluster that is 150 million ly across! More on this next week!!!
- 3. How Big is It? Galileo – 1610 - confirmed the ancient idea of Democritus - that the milky band in the night sky was great numbers of distant stars proving that the galaxy (known universe at that time) was more vast than commonly believed Harlow Shapley – 1917 - Made the first accurate measurement of the size of the galaxy by examining spatial distribution of globular clusters - He figured out the Milky Way was far more enormous than had been understood until then, and that our Sun was closer to the edge than to the bulge in the middle.
- 4. Galactic Mass total mass of all the matter within the orbit of the outermost stars and hydrogen clouds in the galaxy 200 billion times mass of the sun based on Newton’s version of Kepler’s third Law 1980s – uncertainties arose about these calculations due to: - massive amounts of unknown material surrounding the Milky Way - it’s dark matter: undetectable at all wavelengths; including radio, X- ray, ultraviolet, infrared, and optical telescopes
- 5. The main components of the Milky Way - • Disk: most of the gas and dust, majority of (young) stars • Bulge: center of galaxy • Hard to see clearly (dust & gas) • Halo: Spherical region around a spiral galaxy that contains dim stars and globular clusters. • Globular clusters: Oldest stars in clusters thousands of times more luminous than the sun
- 6. The Galactic Center The very center of the Milky Way is known as the Galactic Center. It has intrigued astronomers for many decades. Some examples of theories regarding its composition include: a supermassive black hole a collection of wispy magnetic filaments a few dense stellar superclusters which host mysterious and massive stars and a family of gas streamers spiraling toward a central dark mass.
- 7. How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Oscillate back and forth some ordered some random • Stars in the disk all orbit in the same direction, in the plane of the disk with some deviation away from the disk in either direction, but the stars are pulled back toward the disk by gravity. (Going around like a carousel) • Stars that form the bulge are in banana-like orbits, but a paper published suggests that the stars probably move in peanut-shell or figure-eight- shaped orbits instead. As stars go around in their orbits…
- 8. Where do all the Stars come from? The Halo and Bulge contain older stars which predate the disk shape of the galaxy, and so we know these are not an active area of star formation. New stars are actively being formed in the disk of the Milky Way, mostly in the dense spiral arms of
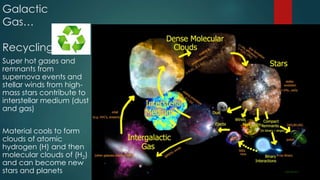
- 9. Galactic Gas… Recycling Super hot gases and remnants from supernova events and stellar winds from high- mass stars contribute to interstellar medium (dust and gas) Material cools to form clouds of atomic hydrogen (H) and then molecular clouds of (H2) and can become new stars and planets
- 10. Halo & Disk of the Milky Way
- 11. Spiral Arms Home to active star formation “Density Waves” Waves of star formation
- 12. Halo Stars and Disk Stars Halo Stars Formed before Disk stars On elliptical orbits A part of globular clusters Disk Stars Young stars Formed from the abundance of gas and dust in the Disk Wide range of mass and colors
- 13. How was our Galaxy formed? The future of the Milky Way? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lKDt7j8Rtfs