Modern cellular communication
- 2. Overview Wireless communication networks was concept of 1960s and 1970s and become much more popular in 1990’s. Radio Spectrum licenses for personal communication service(PCS) in the 1800- 2000 MHz frequency bands. The rapid growth in cellular telephone subscribers has demonstrated conclusively that wireless communications are: Robust Viable voice and data transport mechanism. Next generations are being designed to facilitate high speed data communications traffic in addition to voice calls. New standards and technology are being implemented to replace fiber optic or copper lines.
- 4. Used as a replacement for wires within the homes, buildings, and office settings through the development of wireless local area networks (WLANs). Bluetooth modem standard promises to replace troublesome appliance communication cords with invisible wireless connections within a personal workspace. The WLAN’s and Bluetooth use low power levels and generally do not require a license for spectrum use. They are used as data networks within buildings without a license. Networks that don't require a licensed spectrum for there use
- 5. First Generation Wireless Systems (1G) First-generation wireless technology is based on analog signals. Mostly relied on FDMA/FDD and analog FM. Are very limited in capacity and did not extend across geographic areas Systems using 1G : AMPS, TACS, and NMT Working of 1G In this, mobile device sends the waves to a base station where they are processed to determine the signal’s next destination Once the destination is determined, the signal is reconstructed as accurately as possible
- 6. The analog signal received by the end user may closely resemble the original transmission but rarely duplicate it. Noticeable differences in quality and form occur due to: recreation errors. Signal destruction . translation and interference problems .
- 7. 2 Generation wireless systems Developed in Europe and the US to provide better voice quality, higher capacity as well as lower power consumption. 2G services are frequently referred as Personal Communications Service or PCS in the US. Offer support for simple non-voice services like SMS (simple messaging service). Difficult roaming between countries using different systems. Cannot meet subscriber demands for new, faster non-voice services on the move. Its standards use digital modulation formats and TDMA/FDD and CDMA/FDD multiple access techniques.
- 8. 2 G Continued……… The Standards include 3 TDMA standards and 1 CDMA: • A) Global System Mobile(GSM) It supports 8 time slotted users for each 200kHz radio channel • B) Interim Standard 136(IS-126) It supports 3 time slotted users for each 30KHz radio channel. • C) Pacific Digital Cellular It is similar to IS-136 with more than 50 million users • D) CDMA one It supports upto 64 users that are orthogonology coded and transmitted on each 1.25MHz channel. Modern cellular systems are also being installed to provide fixed telephone service to residences and businesses in developing nations- this is particularly cost effective for providing plain old telephone service(POTS) 2G technologies offer a three times increase in spectrum efficiency .
- 9. 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 Worldwide subscriber base as a function of cellular technology in late 2001 No.ofSubscribersusing(inmill) 1st GA GSM IS-136 &PDC IS-95 CDMA
- 10. Cdma2000-1xEV,DV,DO Cdma2000- 3xRTT IS-9 IS-136 & PDC GPRS HSCSD IS-95B EDGE Cdma200-1xRTT 3GPP2 HSCSD HSCSD HSCSD 3GPP 2G 3G 2.5G Various upgrade paths for 2G technologies GSM
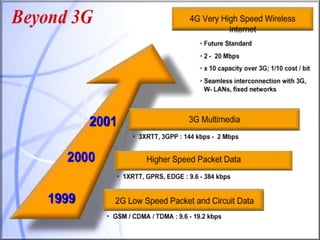
- 11. What is 2.5G Wireless? It was an effort to retrofit the 2G standards for compatibility with increased throughput data rates that are required to support modern internet applications. This standard allows existing 2G equipment to be modified and supplemented with new base station add-ons and subscriber unit software updates to support: High data rate transmission . E-mail traffic Mobile commerce Location based mobile services. This technology also support new web browsing format language , called wireless Applications Protocol (WAP). WAP allows standard web pages to be viewed in a compressed format specifically designed for small, portable hand held devices.
- 12. • HSCSD (High speed circuit switched data ) for 2.5G GSM • It simply requires the service provider to implement a software change at existing GSM base station. • is a circuit switched technique that allows a single mobile subscriber to use consecutive user time slots in the GSM standard . • HSCSD relaxes the error control coding algorithms • increases the available application data rate to 14,440bps as compared to 9,600bps in GSM specification. • by using up to 4 consecutive time slots it is able to provide a raw transmission rate of up to 57.6kbps to individual users. • GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) for 2.5G GSM and IS-136 • It is a packet based data network which is well suited for: » Non-real time internet usage • It supports multi-user network sharing individual radio channels and time slots. • In this all 8time slots of a GSM radio channel are dedicated to GPRS by which an individual user is able to achieve as much as 171.2kbps.
- 13. • EDGE(Enhanced data rates for GSM) • It is a more advanced upgrade to GSM standard. • It requires addition of new hardware and software at existing base stations. • It introduces a new digital modulation format, 8-PSK(octal phase shift keying) which is used in addition to GSM’s standard GMSK modulation. • IS-95B for 2.5G CDMA » CDMA has a single upgrade path for eventual 3G operation. » It supports medium data rate (MDR) service by allowing a dedicated user to command up to 8 different users walsh codes simultaneously and in parallel for an instantaneous throughput of 115.2 kbps per user.
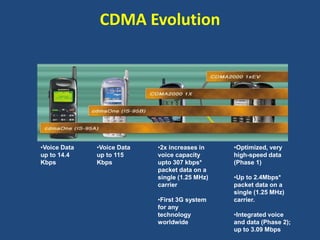
- 14. CDMA Evolution •Voice Data up to 14.4 Kbps •Voice Data up to 115 Kbps •2x increases in voice capacity upto 307 kbps* packet data on a single (1.25 MHz) carrier •First 3G system for any technology worldwide •Optimized, very high-speed data (Phase 1) •Up to 2.4Mbps* packet data on a single (1.25 MHz) carrier. •Integrated voice and data (Phase 2); up to 3.09 Mbps
- 15. 3G Wireless Systems They are new generation of systems that offer high bandwidth and support digital voice along with multimedia and global roaming. Globally, different systems are being used, so, to migrate to globally acceptable systems, numerous standardization activities were carried out and three systems emerged: W-CDMA, CDMA2000, and TD-SCDMA W-CDMA (Wideband Code-Division Multiple Access) Standard derived from Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA), is officially known as IMT-2000 direct spread. W-CDMA is a 3G mobile wireless technology that promises much higher data speeds to mobile and portable wireless devices than commonly offered in today's market. It can support mobile/portable voice, images, data, and video communications at up to 2 Mbps (local area access) or 384 Kbps (wide area access). The input signals are digitized and transmitted in coded, spread-spectrum mode over a broad range of frequencies. A 5 MHz-wide carrier is used, compared with 200 kHz-wide carrier for narrowband CDMA.
- 16. TD-SCDMA (time division synchronous code division multiple access) Supporting data transmission at speeds up to 2 Mbps, TD-SCDMA combines support for both circuit-switched data, such as speech or video, and also packet-switched data from the Internet. The standard combines time division multiple access (TDMA) with an adaptive, synchronous-mode code division multiple access (CDMA) component. cdma2000 The name cdma2000 actually denotes a family of standards that represent the successive, evolutionary stages of the underlying technology. These are, in order of evolution: CDMA2000 1xRTT CDMA2000 1xEV-DO: Release 0, Revision A, Revision B CDMA2000 1xEV-DO Revision C or Ultra Mobile Broadband (UMB) CDMA2000 1xEVDV In the above nomenclature, EVDO is short for Evolution - Data Optimized and EVDV, for Evolution - Data and Voice.
- 17. 3G System Capabilities Capabilities to support circuit and packet data at high bit rates: •144 kilobits/second or higher in mobility (vehicular) traffic •384 kilobits/second for pedestrian traffic •2 Megabits/second or higher for indoor traffic Common Billing/User Profiles Sharing of usage/rate information between service providers Standardized call detail recording Standardized user profiles Capability to determine geographic position of mobiles and report it to both the network and the mobile terminal Interoperability and roaming
- 18. 3G System Capabilities …. Capability to determine geographic position of mobiles and report it to both the network and the mobile terminal Support of Multimedia Services/Capabilities Fixed and variable rate bit traffic Bandwidth on demand Asymmetric data rates in the forward and reverse links Multimedia mail store and forward Broadband access up to 2 Megabits/second
- 19. Communication services •Video telephony •Video conference •Personal location (GPS) Education •Virtual schools •On-line science lab •On-line library •On-line language labs •Training Applications Using 3G Business services • Mobile office •Narrowcast business TV •Virtual workgroups •Expertise on tap Entertainment •Audio on demand •Games •Video clips •Virtual sightseeing
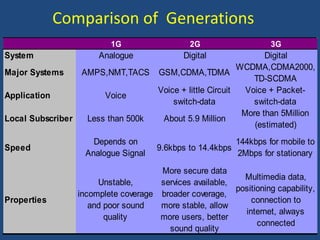
- 20. 1G 2G 3G System Analogue Digital Digital Major Systems AMPS,NMT,TACS GSM,CDMA,TDMA WCDMA,CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA Application Voice Voice + little Circuit switch-data Voice + Packet- switch-data Local Subscriber Less than 500k About 5.9 Million More than 5Million (estimated) Speed Depends on Analogue Signal 9.6kbps to 14.4kbps 144kbps for mobile to 2Mbps for stationary Properties Unstable, incomplete coverage and poor sound quality More secure data services available, broader coverage, more stable, allow more users, better sound quality Multimedia data, positioning capability, connection to internet, always connected Comparison of Generations
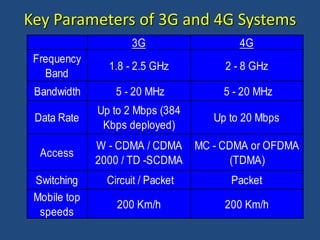
- 22. Key Parameters of 3G and 4G Systems 3G 4G Frequency Band 1.8 - 2.5 GHz 2 - 8 GHz Bandwidth 5 - 20 MHz 5 - 20 MHz Data Rate Up to 2 Mbps (384 Kbps deployed) Up to 20 Mbps Access W - CDMA / CDMA 2000 / TD -SCDMA MC - CDMA or OFDMA (TDMA) Switching Circuit / Packet Packet Mobile top speeds 200 Km/h 200 Km/h
- 23. Technologies that use Non licensed Spectrum • Bluetooth is a new short-range wireless technology designed to enable wireless communication between diverse devices. • A local area network (LAN) is a group of computers and associated devices that share a common communications line or wireless link. Typically, connected devices share the resources of a single processor or server within a small geographic area (for example, within an office building)
- 24. REFERENCES • Modern wireless communication by rappaport • Internet • 3G wireless ppt. by keith doughlas