modern periodic table
- 1. Modern Periodic Table Mrs. Coyle
- 2. Part I Introduction. Periods and groups. Metals, nonmetals and metalloids.
- 3. The Modern Periodic Table The Periodic Table is a listing of all the known elements. The elements are organized by: Atomic number Chemical Properties
- 4. Groups and Periods Group( or Family): a vertical column. Elements in groups have similar chemical properties. Period: a horizontal row.
- 5. Groups and Periods are numbered. There are 7 periods. There are 18 numbered columns.
- 7. IUPAC International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry 1985 new system for labeling groups.
- 8. Metals, Nonmetals and Metalloids Elements can be classified into: Metals Nonmetals Metalloids (semimetals)
- 12. Physical Properties of Metals Good conductors of electricity and heat. Malleable (can be hammered into sheets). Ductile (can be drawn into wires). Lustrous.
- 13. Chemical Properties of Metals Easily lose electrons. Form positive (+) ions.
- 14. Nonmetal Physical Properties They do not have the properties of metals.
- 15. Nonmetal Chemical Properties Gain electrons. Form negative ions.
- 16. Part II Valence Electrons Group 1 Group 2
- 17. -Niels Bohr’s Model – Distinct Energy Levels
- 18. Periods The periods (rows) of the periodic table indicate the highest energy level occupied by one or more electrons.
- 19. Valence Electrons The electrons the occupy the highest energy level of an atom. Valence electrons play a key role in the chemical properties of an element.
- 20. “A” Groups (Old System) The “A” groups are numbered 18. The number of the “A” groups correspond to the number of valence electrons.
- 21. Group 1- Alkali Metals 1 valence electron (ns1) Form a 1+ ion. Note: Hydrogen, a nonmetal, is located in the first column because it has one valence electron.
- 22. Group 1- Alkali Metals Lithium Sodium Potassium Rubidium Cesium Francium
- 23. Sodium’s Reaction with H2O Produces Hydrogen
- 24. Reactivity of Alkali Metals Increases from top to bottom of the group. Which is more reactive Cesium or Sodium?
- 25. Note: Sodium and Potassium are stored in oil to keep them from reacting with oxygen and water in the air. Cesium is stored in glass tubes of argon gas( an inert gas).
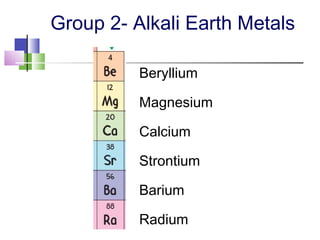
- 26. Group 2- Alkali Earth Metals Beryllium Magnesium Calcium Strontium Barium Radium
- 27. Group 2- Alkali Earth Metals Have 2 valence electrons. Form 2+ ions.
- 28. Group 2- Alkali Earth Metals Reactions with Water Be does not react with water. Mg reacts with hot water. Ca, Sr, Ba react easily with cold water. Which way along the group does reactivity increase?
- 29. Notes: There is Mg in chrolophyll C55H72O5N4Mg Calcium is in your bones, chalk, limestone, toothpaste, pearl (all as calcium carbonate).