Molecular ecology lecture
- 1. Using genetics to answer questions about behavior, species, and populationsMolecular Ecology
- 2. Global warming and Joshua trees
- 3. Global warming and Joshua trees
- 4. Demographic survey9 study sites2-3 transects per siteSurveyed each treeNumber of branchesNumber of inflorescencesSeparated into size classes
- 5. Problem!Size class vs. ageMovement between classesWhat does a healthy population look like?How old is too old?
- 6. Important techniquesPCRCopies segments of DNADouble each cycle35 cycles more than 30 billion copies
- 7. Important techniquesPCRPCR-RFLPEnzymes cut DNA at specific sitesMutations result in different fragment lengthsDistinguish speciesDistinguish individualsVery cheap, very fast
- 8. Important techniquesPCRPCR-RFLPMicrosatellitesTandem repeatsMutate rapidlyCheap, fast
- 9. Important techniquesPCRPCR-RFLPMicrosatellitesSequenceGene sequenceExpensive, time consumingGetting cheaper
- 11. LekkingMales gather in one locationFemales can be choosyOnly “best” males breed“Lek paradox”Why do subordinate males attend leks?
- 12. LekkingBuff-breasted sandpiperMales lek, females are apparently choosy
- 13. LekkingBuff-breasted sandpiperMales lek, females are apparently choosyPaternity tests:
- 14. LekkingBuff-breasted sandpiperMales lek, females are apparently choosyPaternity tests:40% of broods had multiple siresMost males sired chicks
- 15. Monogamy or polygamy?Why be a promiscuous female?
- 16. Monogamy or polygamy?Why be a promiscuous female?Blue tits:Socially monogamous(Actually) polygynous and polyandrousMale survival correlates with extra-pair copulation
- 17. Monogamy or polygamy?Why be a promiscuous female?Great tits:Socially monogamous(Actually) polygynous and polyandrousMale survival does not correlate with extra-pair copulation
- 18. Monogamy or polygamy?Why be a promiscuous female?Studied during a bad yearStudied during a good year
- 19. Monogamy or polygamy?Why be a promiscuous female?Good genes!
- 20. Species identificationCryptic species complex:Group of organisms that are reproductively isolated (and thus separate species) but are morphologically indistinct
- 23. Identifying speciesParasitoid wasps177 morphologically distinct species313 genetically distinct species
- 24. Identifying speciesParasitoid wasps177 morphologically distinct species313 genetically distinct speciesNo generalists
- 31. Population size
- 32. Population sizeNorthern Divide Grizzly Bear ProjectCollect grizzly hairExtract DNA
- 33. Population sizeHardy-Weinberg Equilibrium:p + q = 1p2 + 2pq + q2
- 34. Population sizeHardy-Weinberg Equilibrium:p + q = 1p2 + 2pq + q2No mutation
- 35. Population sizeHardy-Weinberg Equilibrium:p + q = 1p2 + 2pq + q2No mutationNo migration
- 36. Population sizeHardy-Weinberg Equilibrium:p + q = 1p2 + 2pq + q2No mutationNo migrationNo selection
- 37. Population sizeHardy-Weinberg Equilibrium:p + q = 1p2 + 2pq + q2No mutationNo migrationNo selectionRandom mating
- 38. Population sizeHardy-Weinberg Equilibrium:p + q = 1p2 + 2pq + q2No mutationNo migrationNo selectionRandom matingInfinite population size
- 40. Population size2pq > H: bottleneck
- 41. Population sizeH0 > H: bottleneck
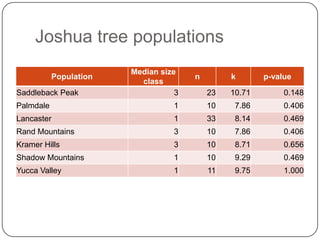
- 42. Joshua tree populationsBottleneck8 microsatellitesCalculates H0 based on kH < H0 bottleneck